Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Prioritizing multiple therapeutic targets in parallel using automated DNA-encoded library screening
Prioritizing multiple therapeutic targets in parallel using automated DNA-encoded library screening
Encoded Library Technology (ELT) has streamlined the identification of chemical ligands for protein targets in drug discovery. Here, the authors optimize the ELT approach to screen multiple proteins in parallel and identify promising targets and antibacterial compounds forS. aureus, A. baumannii and M. tuberculosis.
- Carl A. Machutta
- , Christopher S. Kollmann
- & Ghotas Evindar
-
Article
| Open Access A covalent PIN1 inhibitor selectively targets cancer cells by a dual mechanism of action
A covalent PIN1 inhibitor selectively targets cancer cells by a dual mechanism of action
PIN1 is a promising therapeutic target for cancer treatment. In this study, the authors identify a covalent inhibitor of PIN1 with anti-tumour and anti-metastatic properties thanks to PIN1 inactivation and to the release, after binding to PIN1, of a quinone-mimicking compound that elicits reactive oxygen generation and causes DNA damage.
- Elena Campaner
- , Alessandra Rustighi
- & Giannino Del Sal
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Synthesis and preliminary PET imaging of 11C and 18F isotopologues of the ROS1/ALK inhibitor lorlatinib
Lorlatinib—a ROS1/ALK inhibitor—is currently undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancers. Here the authors develop synthetic routes to11C- and 18F-labelled lorlatinib, with subsequent PET imaging showing good blood brain barrier permeability in non-human primates.
- Thomas Lee Collier
- , Marc D. Normandin
- & Neil Vasdev
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of first-in-class reversible dual small molecule inhibitors against G9a and DNMTs in hematological malignancies
Discovery of first-in-class reversible dual small molecule inhibitors against G9a and DNMTs in hematological malignancies
Epigenetic drugs are emerging as a powerful therapeutic option for cancer treatment. Here, the authors synthesized selective chemical probes that simultaneously inhibit the G9a and DNMTs methyltransferase activity and demonstrate their anti-tumour activity usingin vitro and in vivomodels of haematological neoplasia.
- Edurne San José-Enériz
- , Xabier Agirre
- & Felipe Prosper
-
Article
| Open Access A tetraoxane-based antimalarial drug candidate that overcomes PfK13-C580Y dependent artemisinin resistance
A tetraoxane-based antimalarial drug candidate that overcomes PfK13-C580Y dependent artemisinin resistance
Artemisinin-resistantPlasmodium is an increasing problem. Here, using a medicinal chemistry programme, the authors identify a tetraoxane-based drug candidate that shows no cross-resistance with an artemisinin-resistant strain (PfK13-C580Y) and is efficient in Plasmodiummouse models.
- Paul M. O’Neill
- , Richard K. Amewu
- & Stephen A. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access An in vivo strategy to counteract post-administration anticoagulant activity of azido-Warfarin
An in vivo strategy to counteract post-administration anticoagulant activity of azido-Warfarin
The interaction of long circulating drugs with biological molecules might trigger harmful side effects. Here, the authors design an anticoagulant compound that can be deactivatedin vivo using click chemistry, paving the way to the design of drugs with tunable in vivoproperties.
- Sylvain Ursuegui
- , Marion Recher
- & Alain Wagner
-
Article
| Open Access Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Facile access to potent antiviral quinazoline heterocycles with fluorescence properties via merging metal-free domino reactions
Heterocycles are ubiquitous in bioactive compounds and routes to different substitution patterns are important to access the full substrate space. Here the authors report a route to 4,5,7,8-substituted antiviral fluorescent quinazolines, to allow cellular uptake visualization without external marker.
- Felix E. Held
- , Anton A. Guryev
- & Svetlana B. Tsogoeva
-
Article
| Open Access Steviol glycosides enhance pancreatic beta-cell function and taste sensation by potentiation of TRPM5 channel activity
Steviol glycosides enhance pancreatic beta-cell function and taste sensation by potentiation of TRPM5 channel activity
Steviol glycosides are sweet-tasting compounds isolated from a South American shrub and are increasingly used as sweeteners in foods and beverages. Philippaertet al. demonstrate that steviol glycosides potentiate Ca2+-dependent TRPM5 activity and promote glucose-induced insulin secretion and glucose tolerance.
- Koenraad Philippaert
- , Andy Pironet
- & Rudi Vennekens
-
Article
| Open Access Allosteric cross-talk in chromatin can mediate drug-drug synergy
Allosteric cross-talk in chromatin can mediate drug-drug synergy
Allostery and drug-drug synergism can yield potential novel therapies with existing molecules. Here, the authors provide evidence that two unrelated drugs have increased cytotoxicity in cancer cells, which coincides with increased formation of chromatin adducts.
- Zenita Adhireksan
- , Giulia Palermo
- & Curt A. Davey
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of delta-secretase improves cognitive functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Inhibition of delta-secretase improves cognitive functions in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease
Delta-secretases are associated with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) as they cleave both amyloid precursor protein and tau. Here the authors develop a series of orally bioactive small molecule delta-secretase inhibitors and report its therapeutic effects in mouse models of AD.
- Zhentao Zhang
- , Obiamaka Obianyo
- & Keqiang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical chaperone improves muscle function in mice with a RyR1 mutation
A chemical chaperone improves muscle function in mice with a RyR1 mutation
Mutations in the RyR1 channel cause core myopathies. Here the authors show that ER stress and the unfolded protein response underlie the pathology caused by a common RyR1 channel mutation, and show that treatment with a chemical chaperone restores muscle function in mice.
- Chang Seok Lee
- , Amy D. Hanna
- & Susan L. Hamilton
-
Article
| Open Access Sansanmycin natural product analogues as potent and selective anti-mycobacterials that inhibit lipid I biosynthesis
Sansanmycin natural product analogues as potent and selective anti-mycobacterials that inhibit lipid I biosynthesis
Drug resistant tuberculosis (TB) infections are emerging at a high rate, with only few therapeutic options currently available. Here, the authors report synthetic analogues of the natural product sansanmycin that target mycobacterial cell wall biosynthesis and represent potent leads for improved anti-TB treatments.
- Anh T. Tran
- , Emma E. Watson
- & Richard J. Payne
-
Article
| Open Access In situ click chemistry generation of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors
In situ click chemistry generation of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors
Traditional inflammation and pain relief drugs target both cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX-1 and COX-2), causing severe side effects. Here, the authors use in situ click chemistry to develop COX-2 specific inhibitors with high in vivo anti-inflammatory activity.
- Atul Bhardwaj
- , Jatinder Kaur
- & Frank Wuest
-
Article
| Open Access Arylmethylamino steroids as antiparasitic agents
Arylmethylamino steroids as antiparasitic agents
Steroid units can facilitate membrane permeation and bioavailability in drugs. Here, using a medicinal chemistry program, Krieget al. identify an arylmethylamino steroid that kills Plasmodium parasites, likely through a chelate-based quinone methide mechanism, and has activity against Schistosoma mansoni.
- Reimar Krieg
- , Esther Jortzik
- & Katja Becker
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular dissection of colorectal cancer in pre-clinical models identifies biomarkers predicting sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors
Molecular dissection of colorectal cancer in pre-clinical models identifies biomarkers predicting sensitivity to EGFR inhibitors
The heterogeneity of colorectal cancer has important clinical and therapeutic implications. Here the authors analysed the responses of a large biobank of organoids and xenografts derived from colorectal patients to a panel of clinically relevant therapeutic agents to identify genes signatures associated with drug response.
- Moritz Schütte
- , Thomas Risch
- & Marie-Laure Yaspo
-
Article
| Open Access SC83288 is a clinical development candidate for the treatment of severe malaria
SC83288 is a clinical development candidate for the treatment of severe malaria
Severe malaria is a life-threatening infection with limited treatment options. Here, using a medicinal chemistry approach starting from amicarbalide, Pegoraroet al. identify a compound that, when delivered intravenously, can cure Plasmodium falciparuminfection in a humanized mouse model.
- Stefano Pegoraro
- , Maëlle Duffey
- & Michael Lanzer
-
Article
| Open Access Cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand profiling reveals biased signalling and off-target activity
Cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand profiling reveals biased signalling and off-target activity
CB2 receptor agonists are developed as potential analgesics or immune-modulatory compounds. Here, the authors characterize the pharmacological properties of widely used CB2 receptor agonists and antagonists, recommending three that appear most suitable for in vitro and in vivostudies.
- Marjolein Soethoudt
- , Uwe Grether
- & Mario van der Stelt
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis of feglymycin based on a linear/convergent hybrid approach using micro-flow amide bond formation
Total synthesis of feglymycin based on a linear/convergent hybrid approach using micro-flow amide bond formation
Feglymycin is a biologically active peptide but a challenging synthetic target due to the highly racemizable nature of the 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine groups. Here the authors report the synthesis of feglymycin using a microflow system, allowing amide bond formation without severe racemization.
- Shinichiro Fuse
- , Yuto Mifune
- & Hiroshi Tanaka
-
Article
| Open Access Potent and selective chemical probe of hypoxic signalling downstream of HIF-α hydroxylation via VHL inhibition
Potent and selective chemical probe of hypoxic signalling downstream of HIF-α hydroxylation via VHL inhibition
Small molecule probes used to trigger hypoxic response by activating hypoxia inducible factors (HIFs) often lack specificity. Here the authors report a potent small molecule inhibitor that induces hypoxic response by blocking VHL:HIF interactions, providing a selective route to probe hypoxic signalling.
- Julianty Frost
- , Carles Galdeano
- & Alessio Ciulli
-
Article
| Open Access Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Accelerated oral nanomedicine discovery from miniaturized screening to clinical production exemplified by paediatric HIV nanotherapies
Nanomedicine efficacy in a clinical setting depends on the pharmacological properties of the therapeutic nanoparticles. Here, the authors exemplify an accelerated translational strategy from small-scale screening to clinical scale-up for an orally-dosed aqueous paediatric HIV nanomedicine.
- Marco Giardiello
- , Neill J. Liptrott
- & Andrew Owen
-
Article
| Open Access Spatiotemporal control of cell–cell reversible interactions using molecular engineering
Spatiotemporal control of cell–cell reversible interactions using molecular engineering
Reversible manipulation of cell-cell interactions has potential applications in basic research and cell-based therapy. Here the authors control cell-cell adhesion in vitrowith light, by modifying the surface sugars of cells to display β-cyclodextrin, which recognises one isoform of light-isomerizable azobenzene linkers.
- Peng Shi
- , Enguo Ju
- & Xiaogang Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanistic evaluation and transcriptional signature of a glutathione S-transferase omega 1 inhibitor
Mechanistic evaluation and transcriptional signature of a glutathione S-transferase omega 1 inhibitor
Glutathione S-transferase omega 1 (GSTO1) is an atypical GST isoform overexpressed in several cancers that has been implicated in drug resistance. Here the authors identify a small molecule inhibitor of GSTO1 that effectively inhibits tumor growth in colon cancer models, and establish its mechanism of action.
- Kavya Ramkumar
- , Soma Samanta
- & Nouri Neamati
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-tubulin drugs conjugated to anti-ErbB antibodies selectively radiosensitize
Anti-tubulin drugs conjugated to anti-ErbB antibodies selectively radiosensitize
Drugs that sensitize tumour cells to ionizing radiation are prized because they can overcome resistance to radiotherapy. Here, the authors show that anti-tubulin drugs conjugated to cetuximab or trastuzumab can radiosensitize EGFR- or HER2-expressing tumors by increasing DNA damage and cell death due to ionizing radiation.
- Stephen R. Adams
- , Howard C. Yang
- & Sunil J. Advani
-
Article
| Open Access Irreversible inhibitors of the 3C protease of Coxsackie virus through templated assembly of protein-binding fragments
Irreversible inhibitors of the 3C protease of Coxsackie virus through templated assembly of protein-binding fragments
Molecular fragments are useful tools in drug-discovery but they might be hard to identify due to their weak affinity to the targets. Here, the authors use a protein-templated assembly to design high affinity inhibitors of Coxsackie virus 3C protease, a pharmacological target against enteroviral infections.
- Daniel Becker
- , Zuzanna Kaczmarska
- & Jörg Rademann
-
Article
| Open Access Fragment-based discovery of a new family of non-peptidic small-molecule cyclophilin inhibitors with potent antiviral activities
Fragment-based discovery of a new family of non-peptidic small-molecule cyclophilin inhibitors with potent antiviral activities
Cyclophilins play a key role in the life cycle of many viruses and represent important drug targets for broad-spectrum antiviral therapies. Here, the authors use fragment-based drug discovery to develop non-peptidic inhibitors of human cyclophilins with high activity against replication of a number of viral families.
- Abdelhakim Ahmed-Belkacem
- , Lionel Colliandre
- & Jean- François Guichou
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent synthesis and identification of the cellular targets of deoxyelephantopins
Divergent synthesis and identification of the cellular targets of deoxyelephantopins
Deoxyelephantopin is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene lactone with known anticancer properties. Here, the authors synthesize deoxyelephantopins and a range of analogues including alkyne-tagged probes, using them to identify its cellular targets.
- Roman Lagoutte
- , Christelle Serba
- & Nicolas Winssinger
-
Article
| Open Access Total synthesis of teixobactin
Total synthesis of teixobactin
Teixobactin is a recently identified antibiotic that shows activity against drug resistant strains of bacteria. Here, the authors report a highly convergent total synthesis of this natural product, with sufficient flexibility to also allow the synthesis of a number of analogues.
- Kang Jin
- , Iek Hou Sam
- & Xuechen Li
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided development of heterodimer-selective GPCR ligands
Structure-guided development of heterodimer-selective GPCR ligands
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are involved in key signalling pathways and represent important targets for the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders. Here, the authors describe powerful bivalent ligands that efficiently bind to therapeutically relevant GPCR heterodimers
- Harald Hübner
- , Tamara Schellhorn
- & Peter Gmeiner
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple capsid-stabilizing interactions revealed in a high-resolution structure of an emerging picornavirus causing neonatal sepsis
Multiple capsid-stabilizing interactions revealed in a high-resolution structure of an emerging picornavirus causing neonatal sepsis
Human parechovirus 3 (HPeV3) can cause severe central nervous system infections and is a major cause of neonatal sepsis. Here the authors determine the structure of HPeV3 that provides a high-resolution view of the capsid’s organization and shows multiple interactions of the RNA genome with coat proteins.
- Shabih Shakeel
- , Brenda M. Westerhuis
- & Sarah J. Butcher
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering biosynthesis of the anticancer alkaloid noscapine in yeast
Engineering biosynthesis of the anticancer alkaloid noscapine in yeast
Noscapine is a potential anticancer drug that is traditionally isolated from the opium poppy Papaver somniferum. Here, Li and Smolke reconstitute the noscapine gene cluster in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, to achieve the microbial production of noscapine and related pathway intermediates, and provide new insights into the biosynthesis of noscapine.
- Yanran Li
- & Christina D. Smolke
-
Article
| Open Access Design of a bioactive small molecule that targets r(AUUCU) repeats in spinocerebellar ataxia 10
Design of a bioactive small molecule that targets r(AUUCU) repeats in spinocerebellar ataxia 10
Expanded RNA repeats in non-coding region of a gene represent a hallmark of several diseases. Here, the authors identify two small molecules that selectively bind AU repeats and use them to design a compound that targets the pathogenic RNA associated with spinocerebellar ataxia type 10.
- Wang-Yong Yang
- , Rui Gao
- & Matthew D. Disney
-
Article
| Open Access A human genome-wide loss-of-function screen identifies effective chikungunya antiviral drugs
A human genome-wide loss-of-function screen identifies effective chikungunya antiviral drugs
Chikungunya virus is a mosquito transmitted untreatable emergent pathogen that causes joint pain and fever. Here the authors perform a host genome-wide loss-of-function screen to identify targets for chikungunya antiviral drugs and validate hits using a mouse model of chikungunya infection.
- Alexander Karlas
- , Stefano Berre
- & Marc Lecuit
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraflexible organic amplifier with biocompatible gel electrodes
Ultraflexible organic amplifier with biocompatible gel electrodes
Flexible electronics promise the opportunity to monitor biological activity via implanted devices. Here, the authors develop a biocompatible conductive carbon nanotube/gel composite and couple it with an ultrathin flexible amplifier, enabling in vivomeasurement of epicardial electrocardiogram signals.
- Tsuyoshi Sekitani
- , Tomoyuki Yokota
- & Takao Someya
-
Article
| Open Access Foldamer-mediated manipulation of a pre-amyloid toxin
Foldamer-mediated manipulation of a pre-amyloid toxin
Intrinsically disordered proteins that form amyloid fibrils are hard to target with traditional therapeutic approaches. Here, the authors report on an oligoquinoline derivative that binds the human islet amyloid polypeptide, stabilising an alpha-helical structure that reduces its cellular toxicity.
- Sunil Kumar
- , Melissa Birol
- & Andrew D. Miranker
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of pyrazolopyridazinones as PDEδ inhibitors
Identification of pyrazolopyridazinones as PDEδ inhibitors
PDEδ is a widely expressed factor that sustains the spatial organization and signalling of Ras family proteins. Here the authors describe the activity of Deltazinone 1, a new highly selective PDEδ inhibitor of KRAS-dependent cancer cell growth with low cytotoxic side effects.
- Björn Papke
- , Sandip Murarka
- & Philippe I.H. Bastiaens
-
Article
| Open Access Orthogonal ring-closing alkyne and olefin metathesis for the synthesis of small GTPase-targeting bicyclic peptides
Orthogonal ring-closing alkyne and olefin metathesis for the synthesis of small GTPase-targeting bicyclic peptides
Bicyclic peptides can inhibit biological targets hard to address with small molecules. Here, the authors combine two orthogonal ring-closing reactions to produce bicyclic peptides with improved bioactivity thereby providing a strategy that can greatly improve the structural diversity of such peptides.
- Philipp M. Cromm
- , Sebastian Schaubach
- & Herbert Waldmann
-
Article
| Open Access Applying medicinal chemistry strategies to understand odorant discrimination
Applying medicinal chemistry strategies to understand odorant discrimination
Understanding the basis of odour perception and discrimination is a challenging task, due to the inherent complexity of the olfactory system. Here, the authors use a medicinal chemistry approach to derive biologically relevant rules for odorant classification.
- Erwan Poivet
- , Zita Peterlin
- & Stuart Firestein
-
Article
| Open Access CETSA screening identifies known and novel thymidylate synthase inhibitors and slow intracellular activation of 5-fluorouracil
CETSA screening identifies known and novel thymidylate synthase inhibitors and slow intracellular activation of 5-fluorouracil
Drugs therapeutic efficacy relies on their capability of binding the relevant targets in a physiological environment, which has so far been hard to measure. Here, the authors present a compound library screen based on a target engagement assay that reports on protein stability upon ligands binding in cell.
- Helena Almqvist
- , Hanna Axelsson
- & Pär Nordlund
-
Article
| Open Access Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Lysosome triggered near-infrared fluorescence imaging of cellular trafficking processes in real time
Real time cellular fluorescence imaging requires a probe that displays high degrees of localisation, low toxicity and good photostability. Here, the authors report a near infrared fluorophore that displays pH-sensitive fluorescence based on phenol/phenolate interconversion, showing real time imaging of cellular processes.
- Marco Grossi
- , Marina Morgunova
- & Donal F. O’Shea
-
Article
| Open Access Drug design from the cryptic inhibitor envelope
Drug design from the cryptic inhibitor envelope
The conformational dynamics of a compound has a large effect on ligand/receptor binding. Here, the authors employ NMR spectroscopy to study ligand binding to the enzyme LpxC, discovering an inhibitor envelope that was not identifiable by crystallography and subsequently developing a highly potent inhibitor.
- Chul-Jin Lee
- , Xiaofei Liang
- & Pei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity
Repositioning tolcapone as a potent inhibitor of transthyretin amyloidogenesis and associated cellular toxicity
Misfolding of transthyretin can cause amyloid aggregation disorders that can be treated by stabilizing the tetrameric form with tafamidis. Here the authors show that tolcapone, a drug already FDA-approved for Parkinson disease, has strong transthyretin stabilizing function and might be a superior therapeutic option for CNS amyloidosis as it can cross the blood brain barrier.
- Ricardo Sant'Anna
- , Pablo Gallego
- & Salvador Ventura
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo covalent cross-linking of photon-converted rare-earth nanostructures for tumour localization and theranostics
In vivo covalent cross-linking of photon-converted rare-earth nanostructures for tumour localization and theranostics
Directing nanomedicines to desired locations - such as tumour sites - is difficult to achieve selectively. Here, the authors develop a method to covalently crosslink peptide-modified upconversion nanocrystals into tumour sites for photodynamic therapy and show in vivotumour inhibition in mice.
- Xiangzhao Ai
- , Chris Jun Hui Ho
- & Bengang Xing
-
Article
| Open Access Toxic tau oligomer formation blocked by capping of cysteine residues with 1,2-dihydroxybenzene groups
Toxic tau oligomer formation blocked by capping of cysteine residues with 1,2-dihydroxybenzene groups
Aggregation of microtubule associated protein tau is one of cause of neuronal loss in tauopathies including Alzheimer’s disease. Here, the authors show that compounds with a 1,2-dihydroxybenzene skeleton can modify cysteine residues in tau and block toxic tau aggregation.
- Yoshiyuki Soeda
- , Misato Yoshikawa
- & Akihiko Takashima
-
Article
| Open Access Target engagement and drug residence time can be observed in living cells with BRET
Target engagement and drug residence time can be observed in living cells with BRET
Drug molecules operate through physical interaction with specific cellular targets, and understanding this interaction is important for mechanisms and the potential therapeutic effect of drug candidates. Here, the authors show that bioluminescence resonance energy transfer can be used to monitor the intracellular engagement of a drug with its target.
- Matthew B. Robers
- , Melanie L. Dart
- & Keith V. Wood
-
Article
| Open Access Perfluorocarbon nanoparticles enhance reactive oxygen levels and tumour growth inhibition in photodynamic therapy
Perfluorocarbon nanoparticles enhance reactive oxygen levels and tumour growth inhibition in photodynamic therapy
Photodynamic therapy is used in cancer treatment and generates reactive oxygen species to kill tumour cells but is limited by the availability of oxygen. Here, the authors modify a photodynamic sensitiser so that it produces excess oxygen species and show enhanced tumour cell killing in vitro and in vivo.
- Yuhao Cheng
- , Hao Cheng
- & Yiqiao Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Lipophilic prodrugs of nucleoside triphosphates as biochemical probes and potential antivirals
Lipophilic prodrugs of nucleoside triphosphates as biochemical probes and potential antivirals
Charged phosphorylated metabolite such as nucleoside tri-phosphates exhibit poor membrane permeability due to their high polarity, limiting their utility as drugs or cellular probes. Here the authors develop a method to render nucleoside triphosphates cell permeable and allows their release by an enzyme-triggered mechanism.
- Tristan Gollnest
- , Thiago Dinis de Oliveira
- & Chris Meier
-
Article
| Open Access Pharmaceutical screen identifies novel target processes for activation of autophagy with a broad translational potential
Pharmaceutical screen identifies novel target processes for activation of autophagy with a broad translational potential
Autophagy is a homeostatic process that could be a potential drug target in the treatment of disease. Here the authors identify in a pharmaceutical screen flubendazole as an inducer of autophagy initiation and flux by affecting microtubules, mTOR, TFEB and Beclin 1 activity.
- Santosh Chauhan
- , Zahra Ahmed
- & Vojo Deretic
-
Article
| Open Access Development of high-yield influenza A virus vaccine viruses
Development of high-yield influenza A virus vaccine viruses
The availability of high-yield virus strains remains an important bottleneck in the rapid production of influenza vaccines. Here, the authors report the development of influenza A vaccine backbone that improves the virus yield of various seasonal and pandemic influenza vaccine strains in cell culture.
- Jihui Ping
- , Tiago J.S. Lopes
- & Yoshihiro Kawaoka
-
Article
| Open Access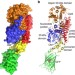 Structural basis for drug-induced allosteric changes to human β-cardiac myosin motor activity
Structural basis for drug-induced allosteric changes to human β-cardiac myosin motor activity
Omecamtiv Mecarbil (OM) is a small molecule allosteric effector of cardiac myosin in clinical trials for treatment of systolic heart failure. Here the authors determine the crystal structure of an OM-bound human β-cardiac myosin motor domain to provide molecular level insight into the mechanism of drug action.
- Donald A. Winkelmann
- , Eva Forgacs
- & Ann M. Stock

 A potent series targeting the malarial cGMP-dependent protein kinase clears infection and blocks transmission
A potent series targeting the malarial cGMP-dependent protein kinase clears infection and blocks transmission