Review Article |
Featured
-
-
Comment |
Strategies for the delivery of sex-based equity in cardiovascular clinical trials
The under-representation of women in cardiovascular clinical trials persists across participant, clinician and research roles. This gap perpetuates health inequity and hampers the generation, translation and implementation of optimal evidence-based care. Urgent action is needed to address barriers, promote diversity, and ensure inclusive trial design and health-care delivery and dissemination, for more equitable cardiovascular health.
- Julie Sanders
- , Tim Clayton
- & Rochelle Wynne
-
Review Article |
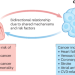 Cardiovascular disease and cancer: shared risk factors and mechanisms
Cardiovascular disease and cancer: shared risk factors and mechanisms
Patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) have an increased risk of cancer, and patients with cancer have an increased risk of CVD. In this Review, the authors discuss the shared modifiable risk factors and the shared pathophysiological mechanisms underlying the bidirectional relationship between these two prevalent diseases.
- Nicholas S. Wilcox
- , Uri Amit
- & Bonnie Ky
-
Comment |
Not a spectator sport: improving participation of Black patients in cardiovascular clinical trials
Representation of Black patients in cardiovascular clinical trials remains dismally low, reflective of systemic and structural barriers, which can lead to missed opportunities to meet community-identified needs, understand responses to medical therapies and improve cardiovascular care. Innovative, multilevel strategies focused on Black communities are warranted to increase enrolment of this population into clinical research.
- LaPrincess C. Brewer
- & Joshua J. Joseph
-
Review Article |
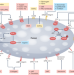 Lipoprotein(a), platelet function and cardiovascular disease
Lipoprotein(a), platelet function and cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Tsimikas and co-workers re-examine the role of lipoprotein(a) in the regulation of platelet function and propose areas for future research to define its clinical relevance for cardiovascular disease.
- Harpreet S. Bhatia
- , Richard C. Becker
- & Sotirios Tsimikas
-
Clinical Outlook |
Migraines and cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and methodological challenges
The link between migraine and cardiovascular disease is complex and involves overlapping mechanisms, such as endovascular disturbances. Challenges in measuring migraine, in distinguishing between causation and prediction, and in the understanding of clinical implications highlight the need for further research to guide treatment and cardiovascular risk assessment for the millions of individuals living with migraine.
- Tobias Kurth
- & Pamela M. Rist
-
Review Article |
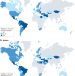 Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes
Global epidemiology of acute coronary syndromes
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) are a major contributor to death from cardiovascular disease. In this Review, Timmis and colleagues present data on mortality from ACS for 122 countries and examine the regional and temporal changes in the epidemiology of ACS over the past 20 years.
- Adam Timmis
- , Denis Kazakiewicz
- & Panos Vardas
-
Review Article |
 The contribution of the exposome to the burden of cardiovascular disease
The contribution of the exposome to the burden of cardiovascular disease
In this Review, Münzel and colleagues describe the exposome concept with a focus on environmental physical and chemical exposures and their effects on the burden of cardiovascular disease. Additionally, they discuss selected exposome studies and the relevance of the exposome concept for future health research and preventive medicine.
- Thomas Münzel
- , Mette Sørensen
- & Andreas Daiber
-
Comment |
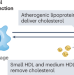 Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Size matters: HDL particle populations and the risk of infection
Low plasma levels of HDL cholesterol are a risk factor for infection and hospitalization for infectious disease. Recent work suggests that inadequate levels of HDL particles of specific sizes — small and medium — account for this risk. In this Comment, we discuss the mechanistic implications of these observations and the methodologies used to quantify HDL size.
- Jay W. Heinecke
- & W. Sean Davidson
-
Comment |
The need for new clinical trials of old cardiovascular drugs
While there is understandable excitement about the development of new cardiovascular drugs, an unmet and equally important need is to perform new clinical trials of old drugs, including to determine their longer-term effects and if and when they should be discontinued after years of use. New trials of old drugs can inform clinical practice and are much needed.
- Christopher B. Granger
- , Stuart J. Pocock
- & Bernard J. Gersh
-
Review Article |
 Epidemiology and prevention of venous thromboembolism
Epidemiology and prevention of venous thromboembolism
In this Review, Lutsey and Zakai describe the epidemiology of venous thromboembolism, including incidence, risk factors and outcomes; summarize opportunities for primordial, primary and secondary prevention; and highlight the importance of reducing disparities in venous thromboembolism incidence and management, and opportunities to reduce them.
- Pamela L. Lutsey
- & Neil A. Zakai
-
World View |
 Addressing gender imbalances in health: unique challenges for African female cardiologists
Addressing gender imbalances in health: unique challenges for African female cardiologists
Women who are health providers face unique challenges when building their careers. Despite this, African female cardiologists should have a role in building equitable health systems and minimizing gender disparities in health care by mentoring girls and young women who aspire to a career in medicine and science.
- Ana O. Mocumbi
-
-
Review Article |
 The need for increased pragmatism in cardiovascular clinical trials
The need for increased pragmatism in cardiovascular clinical trials
In this Review, Khan and colleagues discuss the benefits and challenges of including pragmatism in the design, conduct and interpretation of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for cardiovascular disease and highlight selected ongoing and completed cardiovascular RCTs that incorporate a pragmatic design.
- Muhammad Shariq Usman
- , Harriette G. C. Van Spall
- & Muhammad Shahzeb Khan
-
Roadmap |
 A roadmap of strategies to support cardiovascular researchers: from policy to practice
A roadmap of strategies to support cardiovascular researchers: from policy to practice
Cardiovascular researchers face a range of challenges, including reduced grant funding, job insecurity and a lack of diversity in leadership roles. In this Roadmap article, Marques and colleagues propose strategies to overcome these challenges, focusing on three key areas: capacity building, research funding and fostering diversity and equity.
- Niamh Chapman
- , Emma E. Thomas
- & Francine Z. Marques
-
Research Highlight |
 A proteomic model shows potential as a surrogate end point for CVD risk
A proteomic model shows potential as a surrogate end point for CVD risk
A model generated using proteomics and machine learning that included 27 proteins was able to predict the 4-year risk of myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke or all-cause death better than a clinical model and was sensitive to the adverse and beneficial changes in outcome.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
News & Views |
 Long COVID and cardiovascular disease: a learning health system approach
Long COVID and cardiovascular disease: a learning health system approach
Cardiovascular disease is both a risk factor and potential outcome of the direct, indirect and long-term effects of COVID-19. A recent analysis in >150,000 survivors of COVID-19 demonstrates an increased 1-year risk of numerous cardiovascular diseases. Preventing and managing this new disease burden presents challenges to health systems and requires a learning health system approach.
- Mohamed O. Mohamed
- & Amitava Banerjee
-
Research Highlight |
 An all-virtual clinical trial to assess a heart failure drug
An all-virtual clinical trial to assess a heart failure drug
The CHIEF-HF trial investigators employed a novel all-virtual study design to show that canagliflozin significantly reduces symptom burden in patients with heart failure.
- Karina Huynh
-
Comment |
 The health digital twin: advancing precision cardiovascular medicine
The health digital twin: advancing precision cardiovascular medicine
Precision medicine envisages a changed paradigm for health care through better understanding of individual disease susceptibility and prognosis, enabling more personalized treatment. Enabling technologies such as the health digital twin are rapidly evolving, presenting important challenges and opportunities to be tackled within local contexts.
- Genevieve Coorey
- , Gemma A. Figtree
- & Julie Redfern
-
Review Article |
 Global epidemiology of valvular heart disease
Global epidemiology of valvular heart disease
Valvular heart disease (VHD) is a major contributor to loss of physical function, quality of life and longevity. In this Review, Prendergast and colleagues discuss the global burden of VHD, geographical variation in the presentation and clinical management, and temporal trends in disease burden.
- Sean Coffey
- , Ross Roberts-Thomson
- & Bernard D. Prendergast
-
Research Highlight |
 Cavity-forming, chamber-like cardioids derived from hPSCs
Cavity-forming, chamber-like cardioids derived from hPSCs
A new study published in Cell shows that cardiac mesoderm has the capacity to self-organize and form into chamber-like structures known as cardioids.
- Andrew Robson
-
Comment |
 Increasing representation and diversity in cardiovascular clinical trial populations
Increasing representation and diversity in cardiovascular clinical trial populations
The homogeneity of cardiovascular clinical trial populations limits the generalizability of results and compounds health inequities faced by women, older adults and people of colour. This Comment highlights the importance of diversity in clinical trial populations and describes multifaceted interventions that might help to close the diversity gap in trial enrolment.
- Erin D. Michos
- & Harriette G. C. Van Spall
-
Review Article |
 Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias
Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias
Dyslipidaemias, particularly hypercholesterolaemia, are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. In this Review, Catapano and colleagues summarize the latest data on plasma lipid levels and associated deaths and trends in these parameters over the past four decades in different regions of the world.
- Angela Pirillo
- , Manuela Casula
- & Alberico L. Catapano
-
Research Highlight |
 Role of sex hormones in cardiovascular diseases
Role of sex hormones in cardiovascular diseases
Biological sex is increasingly being recognized as an important variable in cardiovascular health and disease and, consequently, in cardiovascular research. Three new studies highlight the influence of sex hormones in pulmonary arterial hypertension, arterial senescence and abdominal aortic aneurysms.
- Gregory B. Lim
-
Review Article |
 Diffuse myocardial fibrosis: mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic approaches
Diffuse myocardial fibrosis: mechanisms, diagnosis and therapeutic approaches
In this Review, Díez and colleagues summarize the mechanisms of diffuse myocardial fibrosis in heart failure, discuss imaging techniques and circulating biomarkers to characterize the variability of this lesion in patients, and highlight the available and potential future therapeutic strategies for personalizing the prevention and reversal of diffuse myocardial fibrosis.
- Begoña López
- , Susana Ravassa
- & Javier Díez
-
Research Highlight |
 Exosomes improve myocardial recovery after infarction
Exosomes improve myocardial recovery after infarction
A new study shows that exosomes secreted by cardiac cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells improve myocardial recovery without arrhythmogenic complications and might provide an acellular therapeutic option for myocardial infarction.
- Andrew Robson
-
Research Highlight |
Upregulating RBM20 as a therapy for DCM
A study in an in vitro model of RBM20-deficient dilated cardiomyopathy suggests that pharmacological upregulation of RBM20 with all-trans retinoic acid is a potential therapeutic strategy in patients with a heterozygous RBM20 mutation.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Review Article |
 Epidemiology of the inherited cardiomyopathies
Epidemiology of the inherited cardiomyopathies
Current estimates of the prevalence of hypertrophic, dilated and arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathies are probably conservative because of the overlapping phenotypes, incomplete and age-related expression, and variable penetrance of these conditions. In this Review, McKenna and Judge discuss the clinical and genetic diagnosis of the inherited cardiomyopathies, with the aim of better defining the epidemiology of these diseases.
- William J. McKenna
- & Daniel P. Judge
-
Comment |
The COVID-19 pandemic: a catalyst to improve clinical trials
The COVID-19 pandemic has provided the vital stepping stones to improve how clinical trials are conducted. We provide an overview of the major changes to the clinical trial process instigated by the pandemic and suggest ways to make these changes sustainable.
- Prakriti Gaba
- & Deepak L. Bhatt
-
Research Highlight |
Lovastatin improves endothelial cell function in LMNA-related DCM
A new clinical trial in a dish study sheds light on a new mechanism that restores endothelial dysfunction with lovastatin in induced pluripotent stem cells that are derived from patients with dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Andrew Robson
-
Review Article |
 Myocardial ischaemia–reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective
Myocardial ischaemia–reperfusion injury and cardioprotection in perspective
In this Review, Gerd Heusch revisits the pathophysiology of myocardial ischaemia–reperfusion injury, discusses the latest developments in cardioprotective interventions and the signalling pathways involved, identifies the challenges for their clinical translation and advocates the use of additive cardioprotective interventions and a focus on patients with severe haemodynamic alterations.
- Gerd Heusch
-
Review Article |
 Device-based therapies for arterial hypertension
Device-based therapies for arterial hypertension
Novel strategies to improve blood pressure control and treat drug-resistant hypertension are needed despite the efficacy and widespread availability of current antihypertensive drugs. In this Review, Mahfoud and colleagues summarize the pathophysiological rationale and available clinical evidence for device-based therapies for hypertension, including renal sympathetic denervation.
- Lucas Lauder
- , Michel Azizi
- & Felix Mahfoud
-
Review Article |
 Single-cell RNA sequencing in cardiovascular development, disease and medicine
Single-cell RNA sequencing in cardiovascular development, disease and medicine
Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) technologies have helped to identify rare cell populations and allowed the comparison of healthy and diseased tissues at single-cell resolution. This Review discusses the available scRNA-seq tools and summarizes the scRNA-seq findings that have contributed to our understanding of cardiovascular development and disease.
- David T. Paik
- , Sangkyun Cho
- & Joseph C. Wu
-
Research Highlight |
 New developments in gene editing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
New developments in gene editing for Duchenne muscular dystrophy
A somatic gene editing therapy for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) improves skeletal and cardiac muscle function and reduces cardiac arrhythmogenic vulnerability in a pig model of DMD and an in vitro model of human DMD.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
-
Research Highlight |
Dissecting the benefits of sacubitril–valsartan for heart failure
New analyses of the PARAGON-HF and PARADIGM-HF trials indicate that sacubitril–valsartan treatment might be beneficial in patients with heart failure with mildly reduced left ventricular ejection fraction and that the benefit might be greater in women than in men.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
News & Views |
 Remote ischaemic conditioning: in search of a suitable match
Remote ischaemic conditioning: in search of a suitable match
Preclinical data and small clinical trials suggest that remote ischaemic conditioning (RIC) therapy protects patients with acute myocardial infarction undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. In the CONDI-2/ERIC-PPCI trial, RIC proved to be safe but did not have any short-term benefits in reducing cardiac-related death and hospitalization for heart failure.
- Martin Cour
- & Sandrine Lecour
-
Viewpoint |
 Looking back and thinking forwards — 15 years of cardiology and cardiovascular research
Looking back and thinking forwards — 15 years of cardiology and cardiovascular research
November 2019 marks 15 years since the launch of Nature Reviews Cardiology. To celebrate, we invited six of our Advisory Board members to discuss some of the highlights of cardiovascular research in the past 15 years and to make some projections about scientific research in the next 15 years.
- Jonathan M. Kalman
- , Sergio Lavandero
- & Dong Zhao
-
Comment |
Current state of cardiovascular research in China
Scientific research drives discoveries and innovations that improve the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular research in China is thriving, as evidenced by the increasing number of publications and funding support for projects. However, data collection and the quality of publications require much improvement to propel the research field forward.
- Jing Liu
- & Changsheng Ma
-
Research Highlight |
 Systolic and diastolic hypertension independently predict CVD risk
Systolic and diastolic hypertension independently predict CVD risk
Both systolic and diastolic hypertension independently contribute to the risk of adverse cardiovascular events, even though systolic hypertension has a greater effect on cardiovascular outcomes, and this relationship is not altered by the threshold used for the definition of hypertension.
- Irene Fernández-Ruiz
-
Perspective |
 70-year legacy of the Framingham Heart Study
70-year legacy of the Framingham Heart Study
The Framingham Heart Study (FHS) has been collecting epidemiological data on cardiovascular risk factors and disease for >70 years. In this Timeline Perspectives article, the authors summarize the major achievements of the FHS, highlight some of the seminal publications and discuss how epidemiological research has changed and continues to evolve.
- Charlotte Andersson
- , Andrew D. Johnson
- & Ramachandran S. Vasan
-
Review Article |
 Animal models of arrhythmia: classic electrophysiology to genetically modified large animals
Animal models of arrhythmia: classic electrophysiology to genetically modified large animals
Various models of cardiac arrhythmia have been developed in several different animal species to study the mechanisms of disease. In this Review, Clauss and colleagues summarize the advantages and disadvantages of the models and species used in arrhythmia research and provide guidance to investigators planning experiments in this field.
- Sebastian Clauss
- , Christina Bleyer
- & Stefan Kääb
-
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Aspirin-free strategies in cardiovascular disease and cardioembolic stroke prevention
Aspirin-free strategies in cardiovascular disease and cardioembolic stroke prevention
In this Review, a panel of leading experts in antithrombotic pharmacotherapy discuss the principles guiding the role of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)-free strategies in the prevention and management of cardiovascular disease, along with their implications for clinical trial design and development.
- Davide Capodanno
- , Roxana Mehran
- & Dominick J. Angiolillo
-
News & Views |
 Exercising engineered heart muscle to maturity
Exercising engineered heart muscle to maturity
The immaturity of stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes has impeded their use for in vitro disease modelling, cardiotoxicity assays, and cell-replacement therapy. Ronaldson-Bouchard and colleagues report unparalleled in vitro maturation of stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes. This advance promises to unlock the translational potential of these cells.
- Donghui Zhang
- & William T. Pu
-
Review Article |
 Cell therapy trials for heart regeneration — lessons learned and future directions
Cell therapy trials for heart regeneration — lessons learned and future directions
The conflicting results of cell therapy clinical trials for heart regeneration have led to some confusion over the efficacy of this approach. This Review summarizes the main outcomes of these studies and gives perspectives for future cell-based regenerative trials largely based on the primary therapeutic target: regeneration of lost myocardium by exogenous cells or promotion of intrinsic repair though paracrine signalling.
- Philippe Menasché
-
-

 Stress and cardiovascular disease: an update
Stress and cardiovascular disease: an update A new organoid model to study diabetic vasculopathy
A new organoid model to study diabetic vasculopathy Breakthrough in heart xenotransplantation
Breakthrough in heart xenotransplantation Tafamidis: a new treatment for ATTR cardiomyopathy
Tafamidis: a new treatment for ATTR cardiomyopathy