Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A strong fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy with nano-bridged honeycomb microstructure intrinsically toughened by 3D-printing
A strong fracture-resistant high-entropy alloy with nano-bridged honeycomb microstructure intrinsically toughened by 3D-printing
Developing superior structural materials has been challenging because of the inherent conflict between their strength and toughness. Here, the authors use 3D-printing to produce a high-entropy alloy with a microstructure resembling nano-bridged honeycomb structure with good strength and toughness.
- Punit Kumar
- , Sheng Huang
- & Robert O. Ritchie
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable biomimetic solar distillation with edge crystallization for passive salt collection and zero brine discharge
Sustainable biomimetic solar distillation with edge crystallization for passive salt collection and zero brine discharge
Conventional desalination processes generate clean water and reject brine to sea, which is harmful to the aquatic life. Here, the authors propose a low- cost scalable and foldable mangrove-mimetic device for solar thermal distillation and passive salt collection without brine discharge.
- Mohamed A. Abdelsalam
- , Muhammad Sajjad
- & TieJun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration
Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration
Four-dimensional (4D) printing ceramics is a challenge due to their weak deformability. Here, the authors report a hydrogel-dehydration-driven direct 4D printing approach, enabling simple and efficient manufacturing of various complex ceramic objects
- Rong Wang
- , Chao Yuan
- & Qi Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired handheld time-share driven robot with expandable DoFs
Bioinspired handheld time-share driven robot with expandable DoFs
Handheld robots are limited in controllable degrees of freedom, which can result in lower dexterity for clinical applications. Here, Wang et al. report a handheld time-share driven robot with one motor that powers multiple motion modules for high-dextrous operation.
- Yunjiang Wang
- , Xinben Hu
- & Haoran Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Low-k nano-dielectrics facilitate electric-field induced phase transition in high-k ferroelectric polymers for sustainable electrocaloric refrigeration
Low-k nano-dielectrics facilitate electric-field induced phase transition in high-k ferroelectric polymers for sustainable electrocaloric refrigeration
Low-k nanodiamonds are discovered to possess the ability to concurrently enhance the electrocaloric effect, thermal conductivity, and electrical stability of polymeric nanocomposites, providing support for electrocaloric refrigeration.
- Qiang Li
- , Luqi Wei
- & Xiaoshi Qian
-
Article
| Open Access A retrofit sensing strategy for soft fluidic robots
A retrofit sensing strategy for soft fluidic robots
In existing soft robotic sensing strategies, additional components and design changes are often required to sense the environment. Zou et al. introduce a retrofit self-sensing strategy for soft pneumatic actuators, utilizing internal pressure variations arising from interactions.
- Shibo Zou
- , Sergio Picella
- & Johannes T. B. Overvelde
-
Article
| Open Access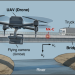 Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drone-based displacement measurement of infrastructures utilizing phase information
Drones are an effective and flexible tool for safety assessment of aging infrastructure, especially in locations with challenging accessibility. Here, authors demonstrate a phase-based sampling moiré technique with a drone for measurement of millimeter-scale infrastructural displacement in bridges.
- Shien Ri
- , Jiaxing Ye
- & Norihiko Ogura
-
Article
| Open Access Online legal driving behavior monitoring for self-driving vehicles
Online legal driving behavior monitoring for self-driving vehicles
Ambiguity in human-oriented traffic laws poses a significant challenge to the regulation of self-driving vehicles. Here, the authors present a trigger-based hierarchical online compliance monitor for self-assessment of self-driving vehicles using ambiguous compliance threshold selection principles.
- Wenhao Yu
- , Chengxiang Zhao
- & Ding Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
Stretchable and negative-Poisson-ratio porous metamaterials
In this work, authors demonstrate highly stretchable conductive porous elastomers that can achieve up to 1200% strain with low or negative Poisson’s ratios by uniaxial, biaxial, and triaxial hot-pressing strategies.
- Xiaoyu Zhang
- , Qi Sun
- & Guoqing Zu
-
Article
| Open Access A micro-architectured material as a pressure vessel for green mobility
A micro-architectured material as a pressure vessel for green mobility
A shellular is a micro-architectured material, composed of a continuous smooth-curved thin shell in the form of a triply periodic minimal surface. Here, authors propose schellular designs applied to pressure vessels and demonstrate its competitive practical features against spherical and cylindrical vessels.
- Yoon Chang Jeong
- , Seung Chul Han
- & Kiju Kang
-
Article
| Open Access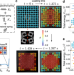 Phase transitions in 2D multistable mechanical metamaterials via collisions of soliton-like pulses
Phase transitions in 2D multistable mechanical metamaterials via collisions of soliton-like pulses
In high-dimensional multistable mechanical metamaterials, phase transitions can be remotely nucleated and controlled via collisions of nonlinear pulses, potentially bringing new insights for the design of reconfigurable structures.
- Weijian Jiao
- , Hang Shu
- & Jordan R. Raney
-
Article
| Open Access Moving event detection from LiDAR point streams
Moving event detection from LiDAR point streams
Timely detection of moving events in a scene plays a vital role in autonomous robots. In this work, authors develop a method to detect moving events from lidar points, achieving a temporal resolution in the order of microseconds.
- Huajie Wu
- , Yihang Li
- & Fu Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot
The unequal distribution of medical resources means that bronchoscopic services are often unavailable in underdeveloped areas. Here, the authors present an AI co-pilot bronchoscope robot that features a user-friendly plug-and-play catheter and an AI-human shared control algorithm, to enable novice doctors to conduct lung examinations safely.
- Jingyu Zhang
- , Lilu Liu
- & Haojian Lu
-
Article
| Open Access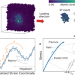 Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
Anomalous temperature dependence of elastic limit in metallic glasses
It is still challenging to study the atomistic mechanism of inelastic deformation in metallic glasses owing to their amorphous structure. Here, the authors report an anomalous temperature dependence of the onset of plasticity in metallic glasses at low temperature.
- Yifan Wang
- , Jing Liu
- & Wei Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Design automation of microfluidic single and double emulsion droplets with machine learning
Design automation of microfluidic single and double emulsion droplets with machine learning
Generating microfluidic droplets with application-specific desired characteristics is hard. Here the authors report fluid-agnostic machine learning models capable of accurately predicting device geometries and flow conditions required to generate stable single and double emulsions.
- Ali Lashkaripour
- , David P. McIntyre
- & Polly M. Fordyce
-
Article
| Open Access Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
Physics-aware differentiable design of magnetically actuated kirigami for shape morphing
A differentiable design framework that integrates both geometrical and magnetomechanical analyses to inversely program the shape morphing in magnetically actuated kirigami is proposed, achieving intricate shapes and multistate transitions.
- Liwei Wang
- , Yilong Chang
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
Roll-to-plate 0.1-second shear-rolling process at elevated temperature for highly aligned nanopatterns
In this work, authors demonstrate a 0.1-second shear rolling process capable of shearing without peeling up to 280 °C. This enables roll-to-plate fabrication of highly and unidirectionally aligned sub−10 nm block copolymer patterns over large wafer areas.
- Junghyun Cho
- , Jinwoo Oh
- & Jeong Gon Son
-
Article
| Open Access How frictional slip evolves
How frictional slip evolves
Conventionally, a continuous motion or “dynamic friction” is expected to take place after the initial rupture under friction. Here, the authors perform direct measurement of real contact and slip at the frictional interface and show that the secondary rupture takes place after each initial rupture.
- Songlin Shi
- , Meng Wang
- & Jay Fineberg
-
Article
| Open Access Cell geometry regulates tissue fracture
Cell geometry regulates tissue fracture
The epidermal surface of leaves and flower petals often display cells with wavy geometries. Here the authors provide evidence that this pattern represents an energy-efficient mechanism to protect plants from deleterious surface fissures and toughen the plants’ protective surface.
- Amir J. Bidhendi
- , Olivier Lampron
- & Anja Geitmann
-
Article
| Open Access Nonintrusive thermal-wave sensor for operando quantification of degradation in commercial batteries
Nonintrusive thermal-wave sensor for operando quantification of degradation in commercial batteries
Monitoring real-world battery degradation is crucial for the widespread application of batteries in different scenarios. Here, the authors report a simple non-embedded thermal-wave sensing technique that can quantitatively distinguish different battery degradation sources during operation.
- Yuqiang Zeng
- , Fengyu Shen
- & Ravi S. Prasher
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Measuring gas discharge in contact electrification
Contact electrification triggers gas breakdown. Using Coulomb force to estimate voltage, this work provides experimental evidence for the Paschen curves that govern such discharge.
- Hongcheng Tao
- & James Gibert
-
Article
| Open Access Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
Harmonizing sound and light: X-ray imaging unveils acoustic signatures of stochastic inter-regime instabilities during laser melting
In the pursuit of advancing laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) technology, researchers have successfully converged the realms of sound and light. Here, the authors unveil the synergistic potential of synchronized x-ray imaging and acoustics to illuminate hidden instabilities in LPBF process.
- Milad Hamidi Nasab
- , Giulio Masinelli
- & Roland E. Logé
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous and efficient elastocaloric air cooling by coil-bending
Continuous and efficient elastocaloric air cooling by coil-bending
In this work, authors demonstrate a low-force and energy-efficient elastocaloric air cooling approach based on coil-bending of NiTi ribbons/wires. The device achieves continuous cold outlet airflow with a temperature drop of 10.6 K and a specific cooling power of 2.5 W g−1 at a low specific driving force of 26 N g−1.
- Xueshi Li
- , Peng Hua
- & Qingping Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Solute trapping and non-equilibrium microstructure during rapid solidification of additive manufacturing
Solute trapping and non-equilibrium microstructure during rapid solidification of additive manufacturing
Solute transport during rapid and repeated thermal cycles is important in additive manufacturing process. Here, the authors develop a fully-coupled model to rationalise solute transport process, elemental segregation, and non-equilibrium solid/liquid interfacial evolution at sub-grain scale.
- Neng Ren
- , Jun Li
- & Jianguo Li
-
Article
| Open Access Higher-order singularities in phase-tracked electromechanical oscillators
Higher-order singularities in phase-tracked electromechanical oscillators
The authors report a controllable third-order cusp singularity in the phase-tracked closed-loop oscillation of two coupled mechanical modes. This finding addresses the challenge of constructing and controlling higher-order singularities.
- Xin Zhou
- , Xingjing Ren
- & Hui Jing
-
Article
| Open Access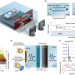 Ultrasonic barrier-through imaging by Fabry-Perot resonance-tailoring panel
Ultrasonic barrier-through imaging by Fabry-Perot resonance-tailoring panel
Breakthrough ultrasonic imaging captures objects behind barriers. Leveraging Fabry-Perot resonance with a unique resonance-tailoring panel, our method allows imaging through high-impedance barriers helping to revolutionise underwater and brain imaging.
- Chung Il Park
- , Seungah Choe
- & Yoon Young Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal free-surface pumping by an undulating carpet
Optimal free-surface pumping by an undulating carpet
Pumping fluids at small scales near fluid-fluid interfaces remains challenging. Pandey et al. present a pump that drives interfacial flow by traveling waves on a deformable boundary.
- Anupam Pandey
- , Zih-Yin Chen
- & Sunghwan Jung
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustofluidic Interfaces for the Mechanobiological Secretome of MSCs
Acoustofluidic Interfaces for the Mechanobiological Secretome of MSCs
Efficient production of MSC secretome for therapeutic applications remains a challenging task. Here, the authors present an approach whereby an acoustofluidic mechanobiological environment can form reproducible 3D MSC aggregates, allowing for secretome production with high efficiency.
- Ye He
- , Shujie Yang
- & Tony Jun Huang
-
Comment
| Open Access Exploration of truss metamaterials with graph based generative modeling
Exploration of truss metamaterials with graph based generative modeling
Optimisation tasks in the inverse design of metamaterials with machine learning were limited due to the representations of generative models. Here the author comments a recent publication in Nature Communications which generates a latent space representation that unlocks non-linear optimisations.
- Angkur Jyoti Dipanka Shaikeea
-
Article
| Open Access Unifying the design space and optimizing linear and nonlinear truss metamaterials by generative modeling
Unifying the design space and optimizing linear and nonlinear truss metamaterials by generative modeling
Truss metamaterials are ubiquitous but their vast design space is far from fully explored. Here, authors use machine learning to present a unified, continuous latent space description, enabling the rapid generation of trusses with tunable or exceptional linear and nonlinear mechanical properties.
- Li Zheng
- , Konstantinos Karapiperis
- & Dennis M. Kochmann
-
Article
| Open Access Wind-driven device for cooling permafrost
Wind-driven device for cooling permafrost
This work demonstrates a wind-powered device for cooling permafrost in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region. Composed of a windmill, mechanical clutch, and a heat exchanger with a phase change material, pilot experiments show soil temperature reduction with superior efficiency compared to traditional thermosyphons.
- Yinghong Qin
- , Tianyu Wang
- & Weixin Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Direct methane protonic ceramic fuel cells with self-assembled Ni-Rh bimetallic catalyst
Direct methane protonic ceramic fuel cells with self-assembled Ni-Rh bimetallic catalyst
Direct methane protonic ceramic fuel cells are promising electrochemical energy conversion devices. However, their performance and stability remain challenging. Here, the authors develop a self-assembled Ni-Rh bimetallic catalyst which shows great enhancements in power output and long-term operational sustainability.
- Kyungpyo Hong
- , Mingi Choi
- & Jongsup Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-modal deformation and temperature sensing for context-sensitive machines
Multi-modal deformation and temperature sensing for context-sensitive machines
Future robots require compact sensing architectures capable of discerning multiple stimuli. Here, Baines et al., present a multi-modal deformation and temperature sensor which, exploiting the light-to-state mapping, discerns combined stimuli of bending, stretching, compression, and temperature.
- Robert Baines
- , Fabio Zuliani
- & Jamie Paik
-
Article
| Open Access Three-degrees-of-freedom orientation manipulation of small untethered robots with a single anisotropic soft magnet
Three-degrees-of-freedom orientation manipulation of small untethered robots with a single anisotropic soft magnet
Existing magnetic actuation systems using a single permanent magnet can only achieve 2-DoF orientation manipulation. Wang et al. propose a magnetic actuation method that uses a single anisotropic soft magnet instead of a permanent magnet to enable full 3-DoF orientation manipulation of small, untethered robots.
- Heng Wang
- , Junhao Cui
- & Yuxiang Han
-
Article
| Open Access Electroconvective viscous fingering in a single polyelectrolyte fluid on a charge selective surface
Electroconvective viscous fingering in a single polyelectrolyte fluid on a charge selective surface
When a low-viscosity fluid displaces into a higher viscosity fluid, the liquid-liquid interface becomes unstable causing finger-like patterns. These patterns are usually observed in two fluids, but here Kim et al. describes the development of fingers in a single polyelectrolyte fluid adjacent to a charge-selective interface under the influence of a potential gradient.
- Jeonghwan Kim
- , Joonhyeon Kim
- & Rhokyun Kwak
-
Perspective
| Open Access Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration
Bioinspired soft robots for deep-sea exploration
High pressure and low temperature are the greatest challenges faced by scientists to explore deep oceans, which remain largely unknow to us today. Li et al. review these challenges and give insight into designing soft robots, inspired by deep-sea creatures, that enable resilient operations in harsh conditions.
- Guorui Li
- , Tuck-Whye Wong
- & Tiefeng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
The authors demonstrate that laser Doppler vibrometer measurements are a powerful tool for predicting the maximum pressure enhancement of high-Q modes. The results presented enable future applications of acoustic BICs by filling the missing data gap on field enhancement.
- Felix Kronowetter
- , Marcus Maeder
- & Steffen Marburg
-
Article
| Open Access A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
Programmability is a key property for multifunctional metamaterials, but it is limited by homo-element. Here, the authors show a mechanical metamaterials with heterogeneous elements, achieving various mechanical behaviours by functional group transformation and ring configuration.
- Xinyu Hu
- , Ting Tan
- & Zhimiao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinearity synergy: An elegant strategy for realizing high-sensitivity and wide-linear-range pressure sensing
Nonlinearity synergy: An elegant strategy for realizing high-sensitivity and wide-linear-range pressure sensing
The development of flexible pressure sensors with a wide linear range and high sensitivity is challenging. Chen et al. demonstrate a sensor for robotics and wearable devices, using nonlinear elasticity of an elastic spacer as a stiffness regulator and a microstructured sensing layer with non-linear piezoresistivity.
- Rui Chen
- , Tao Luo
- & Wei Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Golden section criterion to achieve droplet trampoline effect on metal-based superhydrophobic surface
Golden section criterion to achieve droplet trampoline effect on metal-based superhydrophobic surface
The relation between the rebound behavior of droplets and surface structure is crucial to regulating the surface dynamic wettability based on structure design. Zhao et al. explore droplet rebound numbers when the droplet impacts laser-ablated microstructures with different structure spaces and report that droplets can consecutively rebound 17 times.
- Shengteng Zhao
- , Zhichao Ma
- & Luquan Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
Fast and versatile electrostatic disc microprinting for piezoelectric elements
In this work, authors demonstrate a fast and versatile microprinting technique to produce high-performance and customizable piezoelectric elements by employing a conductive spiny disc to electrostatically trigger instability to the liquid-air interface of the ink.
- Xuemu Li
- , Zhuomin Zhang
- & Zhengbao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Fully automatic transfer and measurement system for structural superlubric materials
Fully automatic transfer and measurement system for structural superlubric materials
A critical step to enable practical structural superlubricity (SSL) applications is to enable high throughput to both fabrication and performance evaluation. Here, the authors demonstrate an automated system for efficient and multiple SSL materials transfer and tribological measurement.
- Li Chen
- , Cong Lin
- & Ming Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Statistical laws of stick-slip friction at mesoscale
Statistical laws of stick-slip friction at mesoscale
Whether stick-slip instabilities can give rise to avalanches of slip lengths is an outstanding issue in solid friction. Here, the authors demonstrated that there indeed exists a critical regime in which stick-slip friction can be described by a common set of statistical laws of avalanche dynamics.
- Caishan Yan
- , Hsuan-Yi Chen
- & Penger Tong
-
Comment
| Open Access Extending research impact by sharing maker information
Extending research impact by sharing maker information
The availability of maker resources such as 3D printers, makerspaces, and public repositories enable researchers to share information with research peers, educators, industry, and the general public. This broadens the impact of research and inspires its extension and application.
- Larry L. Howell
- & Terri Bateman
-
Article
| Open Access Electro-capillary peeling of thin films
Electro-capillary peeling of thin films
Current methods for thin film peeling suffer from limitations because of complicated preparations and the limitations of applied films. Li et al. present a peeling method for the thin film’s detachment that is achieved by driving liquid to percolate and spread into the bonding layer under electric fields.
- Peiliu Li
- , Xianfu Huang
- & Ya-Pu Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Embedded shape morphing for morphologically adaptive robots
Embedded shape morphing for morphologically adaptive robots
Sun et al. introduce a novel embedded shape-morphing method, enabling robots to adapt to environments or tasks by changing their morphologies through embedded actuation, sensing, and shape locking, all within a robot’s body.
- Jiefeng Sun
- , Elisha Lerner
- & Jianguo Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Tensorial stress-plastic strain fields in α - ω Zr mixture, transformation kinetics, and friction in diamond-anvil cell
Tensorial stress-plastic strain fields in α - ω Zr mixture, transformation kinetics, and friction in diamond-anvil cell
Fields of stress and plastic strain tensors in a sample under high pressures in diamond-anvil cells are important, but measuring them is difficult. Here, the authors suggest a coupled experimental-analytical-computational approach to measure them before, during, and after α−ω transformation in Zr.
- Valery I. Levitas
- , Achyut Dhar
- & K. K. Pandey
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasound trapping and navigation of microrobots in the mouse brain vasculature
Ultrasound trapping and navigation of microrobots in the mouse brain vasculature
The intricate and delicate anatomy of the brain poses challenges to achieving efficient and precise medical treatments. Here, the authors introduce ultrasound-activated microrobots that can autonomously aggregate and propel upstream inside the complex vasculature of a living mouse brain.
- Alexia Del Campo Fonseca
- , Chaim Glück
- & Daniel Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Creating speech zones with self-distributing acoustic swarms
Want to mute or focus on speech from a specific region in a crowded room? Here, the authors built an acoustic swarm that, along with neural networks, separates and localizes concurrent speakers in the 2D space with high precision.
- Malek Itani
- , Tuochao Chen
- & Shyamnath Gollakota

 Data-centric artificial olfactory system based on the eigengraph
Data-centric artificial olfactory system based on the eigengraph