Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Industrial brewing yeast engineered for the production of primary flavor determinants in hopped beer
Industrial brewing yeast engineered for the production of primary flavor determinants in hopped beer
Production of aromatic monoterpene molecules in hop flowers is affected by genetic, environmental, and processing factors. Here, the authors engineer brewer’s yeast for the production of linalool and geraniol, and show pilot-scale beer produced by engineered strains reconstitutes some qualities of hop flavor.
- Charles M. Denby
- , Rachel A. Li
- & Jay D. Keasling
-
Article
| Open Access One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
One-step fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains
Fermentative production of aromatic polyesters from glucose has been unsuccessful. Here, the authors achieve the objective by one-step fermentation of metabolically engineered E. coli expressing a isocaprenoyl-CoA:2-hydroxyisocaproate CoA-transferase and an evolved polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase.
- Jung Eun Yang
- , Si Jae Park
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access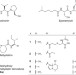 Warhead biosynthesis and the origin of structural diversity in hydroxamate metalloproteinase inhibitors
Warhead biosynthesis and the origin of structural diversity in hydroxamate metalloproteinase inhibitors
Metalloproteinase inhibitors are leads for drug development, but their biosynthetic pathways are often unknown. Here the authors show that the acyl branched warhead of actinonin and matlystatins derives from an ethylmalonyl-CoA-like pathway and the structural diversity of matlystatins is due to the activity of a decarboxylase-dehydrogenase enzyme.
- Franziska Leipoldt
- , Javier Santos-Aberturas
- & Leonard Kaysser
-
Article
| Open Access The industrial anaerobe Clostridium acetobutylicum uses polyketides to regulate cellular differentiation
The industrial anaerobe Clostridium acetobutylicum uses polyketides to regulate cellular differentiation
Polyketides are secondary metabolites mainly found in aerobic organisms with wide applications in medicine and agriculture. Here, the authors uncover new polyketides native to the anaerobic bacterium Clostridium acetobutylicum and show their role in triggering sporulation and granulose accumulation.
- Nicolaus A. Herman
- , Seong Jong Kim
- & Wenjun Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Biotransformation of p-xylene into terephthalic acid by engineered Escherichia coli
Biotransformation of p-xylene into terephthalic acid by engineered Escherichia coli
Terephthalic acid (TPA) is an important commodity chemical typically produced from the oxidation of fossil fuel-derivedp-xylene (pX) at high temperature and pressure. Here the authors report an engineered Escherichia coli strain that can transform pX into TPA with a high conversion yield.
- Zi Wei Luo
- & Sang Yup Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic network analysis reveals microbial community interactions in anammox granules
Metabolic network analysis reveals microbial community interactions in anammox granules
The use of anammox microbiomes to treat wastewater is an escalating biotechnology, yet the functional role heterotrophic bacteria play in these systems remains poorly understood. Here, Lawsonet al. use metagenomics and metatranscriptomics to reveal that heterotrophs degrade free peptides, while recycling nitrate to nitrite.
- Christopher E. Lawson
- , Sha Wu
- & Daniel R. Noguera
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cpf1 assisted genome editing of Corynebacterium glutamicum
CRISPR-Cpf1 assisted genome editing of Corynebacterium glutamicum
Corynebacterium glutamicum is an important industrial microbe, however it has proven difficult to genetically engineer using Cas9 from Streptococcus pyogenes. Here the authors report effective genome engineering of the bacterium using Cpf1 from Francisella novicida.
- Yu Jiang
- , Fenghui Qian
- & Sheng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Global metabolic rewiring for improved CO2 fixation and chemical production in cyanobacteria
Global metabolic rewiring for improved CO2 fixation and chemical production in cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria are promising biofactories to reduce atmospheric CO2 and convert it into chemicals. Here the authors engineer Synechococcus elongatus carbon metabolism to increase 2,3-butanediol production from glucose and CO2under light and dark conditions.
- Masahiro Kanno
- , Austin L. Carroll
- & Shota Atsumi
-
Article
| Open Access Dissection of goadsporin biosynthesis by in vitro reconstitution leading to designer analogues expressed in vivo
Dissection of goadsporin biosynthesis by in vitro reconstitution leading to designer analogues expressed in vivo
Goadsporin is an antibacterial peptide highly customized by multiple post-translational modifying enzymes. Here, the authors dissect its biosynthetic pathway byin vitro reconstitution and use their insights to produce goadsporin analogues in vitro and in vivo.
- Taro Ozaki
- , Kona Yamashita
- & Hiroyasu Onaka
-
Article
| Open Access CO2 fixation by anaerobic non-photosynthetic mixotrophy for improved carbon conversion
CO2 fixation by anaerobic non-photosynthetic mixotrophy for improved carbon conversion
Microbial fermentation yield is limited by CO2 loss in glycolysis. Here, the authors engineered Clostridium ljungdahlii for the anaerobic, non-photosynthetic mixotrophy production of acetone, increasing carbon product yield while reducing CO2emissions from a biogenic feedstock fermentation.
- Shawn W. Jones
- , Alan G. Fast
- & Bryan P. Tracy
-
Article
| Open Access Automated optogenetic feedback control for precise and robust regulation of gene expression and cell growth
Automated optogenetic feedback control for precise and robust regulation of gene expression and cell growth
Optogenetics has emerged as a promising means to achieve gene expression control in bioprocess engineering, but current systems cannot respond to fluctuations in growth conditions. Here the authors overcome this limitation and develop an automated optogenetic feedback control system for precise and robust control of protein production in E. coli.
- Andreas Milias-Argeitis
- , Marc Rullan
- & Mustafa Khammash
-
Article
| Open Access A dynamic pathway analysis approach reveals a limiting futile cycle in N-acetylglucosamine overproducing Bacillus subtilis
A dynamic pathway analysis approach reveals a limiting futile cycle in N-acetylglucosamine overproducing Bacillus subtilis
Rate-limiting steps in synthetic metabolic pathways are difficult to identify. Here, the authors monitor metabolite dynamics and apply kinetic modelling during the start-up phase of the Bacillus subtilisGlcNAc pathway to discover a futile cycle, allowing them to identify a more productive strain.
- Yanfeng Liu
- , Hannes Link
- & Uwe Sauer
-
Article
| Open Access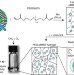 Printable enzyme-embedded materials for methane to methanol conversion
Printable enzyme-embedded materials for methane to methanol conversion
There is a need for small-scale reactors that convert methane emissions to more valuable products to reduce climate impacts. Here, the authors show that printing 3D structures of the pMMO enzyme enables continuous methane conversion under ambient conditions and reduces mass transfer limitations.
- Craig D. Blanchette
- , Jennifer M. Knipe
- & Sarah E. Baker
-
Article
| Open Access The dynamic transcriptional and translational landscape of the model antibiotic producer Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)
The dynamic transcriptional and translational landscape of the model antibiotic producer Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2)
Bacteria of the genus Streptomyces produce a great variety of natural products, the biosynthesis of which is subject to complex regulatory networks. Here the authors present a high-resolution, genome-wide analysis of the transcriptome and translatome of Streptomyces coelicolorunder various growth conditions.
- Yujin Jeong
- , Ji-Nu Kim
- & Byung-Kwan Cho
-
Article
| Open Access Production of fatty acid-derived oleochemicals and biofuels by synthetic yeast cell factories
Production of fatty acid-derived oleochemicals and biofuels by synthetic yeast cell factories
While yeast is an attractive alternative to bacteria for the production of biofuels it currently has low production yields. Here, the authors systematically engineer Saccharomyces cerevisiae for high-level production of fatty acids, alkanes and fatty alcohols, which are important fuel precursors.
- Yongjin J. Zhou
- , Nicolaas A. Buijs
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-based microbial ecology of anammox granules in a full-scale wastewater treatment system
Genome-based microbial ecology of anammox granules in a full-scale wastewater treatment system
ANaerobic AMMonium OXidation (ANAMMOX) combined with partial nitritation has been adopted for removal of ammonium from wastewater. Here, Speth et al. describe the bacterial metagenome of a partial-nitritation/anammox (PNA) reactor, and provide 23 draft genomes, 19 of which were previously uncharacterized/sequenced/cultivated.
- Daan R. Speth
- , Michiel H. in ’t Zandt
- & Mike S. M. Jetten
-
Article
| Open Access A portable expression resource for engineering cross-species genetic circuits and pathways
A portable expression resource for engineering cross-species genetic circuits and pathways
Organism-specific genetic parts are often used to express circuits and pathways, limiting their portability. Here the authors engineer a cross-species expression resource, without using host-specific parts, to control protein and pathway expression in non-model bacteria.
- Manish Kushwaha
- & Howard M. Salis
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional isobutyl acetate production pathways to improve carbon yield
Two-dimensional isobutyl acetate production pathways to improve carbon yield
Achieving high carbon yields is crucial for biotechnological production of metabolites in engineered microorganisms. Here, Tashiroet al. generate E. colistrains that produce acetyl-CoA and a derived metabolite (isobutyl acetate) in the absence of pyruvate decarboxylation, leading to increased carbon yields.
- Yohei Tashiro
- , Shuchi H. Desai
- & Shota Atsumi
-
Article
| Open Access An auto-inducible mechanism for ionic liquid resistance in microbial biofuel production
An auto-inducible mechanism for ionic liquid resistance in microbial biofuel production
Ionic liquids (ILs) are important solvents in the microbial production of biofuels, but can inhibit microbial growth. Here, the authors transfer newly discovered IL-resistance genes from rain forest soil bacteria to E. coliand report growth and biofuel production at IL levels that are otherwise toxic to native strains.
- Thomas L. Ruegg
- , Eun-Mi Kim
- & Michael P. Thelen
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple recent horizontal transfers of a large genomic region in cheese making fungi
Multiple recent horizontal transfers of a large genomic region in cheese making fungi
Horizontal gene transfers are known to play an important role in prokaryote evolution but their impact and prevalence in eukaryotes is less clear. Here, the authors sequence the genomes of cheese making fungi P. roqueforti and P. camemberti, and provide evidence for recent horizontal transfers of a large genomic region.
- Kevin Cheeseman
- , Jeanne Ropars
- & Yves Brygoo
-
Article |
 Microbial biosynthesis of the anticoagulant precursor 4-hydroxycoumarin
Microbial biosynthesis of the anticoagulant precursor 4-hydroxycoumarin
4-hydroxycoumarin (4HC), a precursor for anticoagulant drugs such as warfarin, has a major role in the treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Here, the authors present an artificial biosynthetic pathway for 4HC production in E. coliand demonstrate its potential for large-scale microbial production.
- Yuheng Lin
- , Xiaolin Shen
- & Yajun Yan
-
Article |
 Enhanced biofuel production through coupled acetic acid and xylose consumption by engineered yeast
Enhanced biofuel production through coupled acetic acid and xylose consumption by engineered yeast
Biofuel produced from renewable biomass is attractive, but inefficient conversion of cellulosic sugars and the toxicity of plant biomass hydrolysates hamper commercial production. Wei et al.use engineered yeast to address these problems simultaneously, converting both xylose and acetic acid into ethanol.
- Na Wei
- , Josh Quarterman
- & Yong-Su Jin
-
Article |
 Synthetic RNA devices to expedite the evolution of metabolite-producing microbes
Synthetic RNA devices to expedite the evolution of metabolite-producing microbes
Genome-wide variation in the directed evolution of metabolite-overproducing microbes requires high-throughput screening platforms. Yang et al.show that synthetic RNA devices can sense target metabolites, enrich pathway optimisation, and expedite the evolution of metabolite-producing microbes.
- Jina Yang
- , Sang Woo Seo
- & Gyoo Yeol Jung
-
Article |
 A platform pathway for production of 3-hydroxyacids provides a biosynthetic route to 3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone
A platform pathway for production of 3-hydroxyacids provides a biosynthetic route to 3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone
3-hydroxy-γ-butyrolactone (3HBL) is a building block for many valuable drugs and is synthesized via a costly industrial process. Martin et al. engineer a novel biosynthetic pathway for the inexpensive production of 3HBL and other 3-hydroxyacids in E. coli.
- Collin H. Martin
- , Himanshu Dhamankar
- & Kristala L.J. Prather
-
Article |
 Modular optimization of multi-gene pathways for fatty acids production in E. coli
Modular optimization of multi-gene pathways for fatty acids production in E. coli
Microbial fatty acid-derived fuels represent promising alternatives to the traditionally used fossil fuels. Koffas and colleagues report that E. colicentral metabolism can be modified to produce large quantities of fatty acids through a modular pathway engineering strategy.
- Peng Xu
- , Qin Gu
- & Mattheos A.G. Koffas
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-omic map of the lipid-producing yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides
A multi-omic map of the lipid-producing yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides
The ability of oleaginous fungi to produce lipids for biofuels remains untapped, in part due to a lack of genetic information required to engineer industrial strains. Zhuet al. present the genome of R. toruloides, and identify transcriptomic and proteomic changes associated with lipid production.
- Zhiwei Zhu
- , Sufang Zhang
- & Zongbao K. Zhao
-
Article |
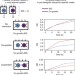 Competitive and cooperative metabolic interactions in bacterial communities
Competitive and cooperative metabolic interactions in bacterial communities
Genome-scale metabolic models for bacterial species allow a systematic study of inter-species interactions. Here, competitive and cooperative potential is predicted between 6,903 pairs of species, to explore the role of these interactions in shaping coexistence patterns in natural communities.
- Shiri Freilich
- , Raphy Zarecki
- & Eytan Ruppin
-
Article
| Open Access A bacterial platform for fermentative production of plant alkaloids
A bacterial platform for fermentative production of plant alkaloids
Secondary metabolites are widely used in human health and nutrition, but extraction yields from plants are often low. Nakagawaet al. have engineered the metabolism of Escherichia colito develop a fermentation system that produces plant alkaloids from simple carbon sources.
- Akira Nakagawa
- , Hiromichi Minami
- & Hidehiko Kumagai

 Methanol-essential growth of Escherichia coli
Methanol-essential growth of Escherichia coli