Featured
-
-
Article |
 A coupled model of episodic warming, oxidation and geochemical transitions on early Mars
A coupled model of episodic warming, oxidation and geochemical transitions on early Mars
Mars’s early climate and surface chemistry varied between a generally cold, oxidizing environment and warmer, more reducing conditions, according to a model of atmospheric evolution driven by stochastic, random injection of greenhouse gases.
- Robin Wordsworth
- , Andrew H. Knoll
- & Kathryn Steakley
-
Article |
 The future lifespan of Earth’s oxygenated atmosphere
The future lifespan of Earth’s oxygenated atmosphere
Earth’s oxygen-rich atmosphere will probably persist for only one billion more years before it sharply deoxygenates to low-level oxygen similar to those of the Archaean, according to a combined biogeochemistry and climate model.
- Kazumi Ozaki
- & Christopher T. Reinhard
-
Article |
 Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
Drivers of river reactivation in North Africa during the last glacial cycle
The presence of large rivers in North Africa critical for Quaternary human migrations were controlled by a combination of orbital forcing and Mediterranean storminess, according to terrestrial proxy records from a marine core off Libya integrated with paleoclimate modelling.
- Cécile L. Blanchet
- , Anne H. Osborne
- & Martin Frank
-
Article |
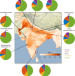 Enhanced aerosol particle growth sustained by high continental chlorine emission in India
Enhanced aerosol particle growth sustained by high continental chlorine emission in India
Half of the reduced visibility due to haze formation in cities in India is attributed to local emission of gas-phase hydrochloric acid from waste-burning and industry, according to measurements of particulate matter and thermodynamic modelling.
- Sachin S. Gunthe
- , Pengfei Liu
- & Hugh Coe
-
Article |
 Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Nonlinear forcing of climate on mountain denudation during glaciations
Constraints on the denudation of the Southern Alps over the last glacial cycle indicate a nonlinear influence of climate on landscape evolution in glaciated areas, according to a beryllium isotope record measured from quartz in a sequence of Mediterranean turbidites.
- Apolline Mariotti
- , Pierre-Henri Blard
- & Karim Keddadouche
-
Article |
 Archaean seafloors shallowed with age due to radiogenic heating in the mantle
Archaean seafloors shallowed with age due to radiogenic heating in the mantle
In contrast to present-day seafloor subsidence with age, there may have been Archaean seafloor shallowing and landmass exposure due to high internal heating in the mantle that halted subsidence, according to numerical models of mantle convection.
- Juan Carlos Rosas
- & Jun Korenaga
-
Article |
 Eleven-year solar cycles over the last millennium revealed by radiocarbon in tree rings
Eleven-year solar cycles over the last millennium revealed by radiocarbon in tree rings
11-year solar cycles consistently occurred throughout the last thousand years, according to a synthesis of annually resolved tree ring radiocarbon records from central Europe.
- Nicolas Brehm
- , Alex Bayliss
- & Lukas Wacker
-
Article |
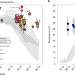 Spatial pattern of super-greenhouse warmth controlled by elevated specific humidity
Spatial pattern of super-greenhouse warmth controlled by elevated specific humidity
The reduced Equator-to-pole temperature gradient during the Eocene greenhouse climate was maintained by elevated atmospheric humidity, according to temperature and precipitation isotope estimates from terrestrial siderite clumped isotopes.
- Joep van Dijk
- , Alvaro Fernandez
- & Tim White
-
Article |
 Active crustal differentiation beneath the Rio Grande Rift
Active crustal differentiation beneath the Rio Grande Rift
A link between post-thickening lithospheric extension and the differentiation of continental crust is implied by granulite conditions beneath the Rio Grande Rift, inferred from analysis of lower-crustal xenoliths and thermobarometric modelling.
- Jacob H. Cipar
- , Joshua M. Garber
- & Andrew J. Smye
-
News & Views |
 The magmatic forge
The magmatic forge
Time capsules of fluid, trapped within the oxide minerals from two iron ore deposits reveal an important role for sediment-derived carbonate–sulfate-rich melts in the concentration of iron, a crucial element for humanity’s development.
- James M. Brenan
-
Article |
 A fundamental role of carbonate–sulfate melts in the formation of iron oxide–apatite deposits
A fundamental role of carbonate–sulfate melts in the formation of iron oxide–apatite deposits
Iron-rich carbonate–sulfate melts are fundamental to the formation of iron oxide–apatite ore deposits, according to a detailed fluid-inclusion study that characterized the mineralizing fluids for two mineralizing systems in the United States.
- Wyatt M. Bain
- , Matthew Steele-MacInnis
- & Erin E. Marsh
-
Perspective |
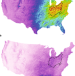 A shift in sulfur-cycle manipulation from atmospheric emissions to agricultural additions
A shift in sulfur-cycle manipulation from atmospheric emissions to agricultural additions
Deliberate application of sulfur onto croplands as fertilizer and pesticide probably causes environmental damage similar to historical acid rain events, according to a literature review and four case studies from the United States.
- Eve-Lyn S. Hinckley
- , John T. Crawford
- & Charles T. Driscoll
-
Article |
 Heavy iron isotope composition of iron meteorites explained by core crystallization
Heavy iron isotope composition of iron meteorites explained by core crystallization
Experiments show that the iron isotopic composition of iron meteorites can be explained by core crystallization, and suggest the presence of sulfur-rich core material that remains unsampled by meteorite collections.
- Peng Ni
- , Nancy L. Chabot
- & Anat Shahar
-
News & Views |
 Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
Redrawing the early sulfur cycle
The Archaean atmosphere may have been well oxygenated, according to a reconsideration of sulfur cycling at that time. This challenges the view that sedimentary sulfur records oxygen-poor conditions during Earth’s first two billion years.
- Desiree Roerdink
-
Article |
 Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Late Cenozoic climate change paces landscape adjustments to Yukon River capture
Increased river incision and landscape erosion can be attributed to late Cenozoic cooling/changes in hydroclimate, according to cosmogenic isotope and luminescence ages of a sequence of bedrock terraces in the Yukon River basin.
- Adrian M. Bender
- , Richard O. Lease
- & Tammy M. Rittenour
-
News & Views |
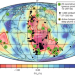 Plate tectonics from crust to core
Plate tectonics from crust to core
Compositional signatures of subducted crust in the deep-mantle sources of ocean island volcanoes in the Atlantic Ocean but not the Pacific reveal that plate motions on Earth’s surface influence the characteristics of Earth’s deepest interior.
- Richard W. Carlson
-
Article |
 Distinct formation history for deep-mantle domains reflected in geochemical differences
Distinct formation history for deep-mantle domains reflected in geochemical differences
Earth’s deep-mantle domains are geochemically distinct. The African domain is enriched in subducted material, which suggests a different history from the Pacific domain and a dynamic relationship between plate tectonics and deep-mantle structures.
- Luc S. Doucet
- , Zheng-Xiang Li
- & Ross N. Mitchell
-
Article |
 Steady erosion rates in the Himalayas through late Cenozoic climatic changes
Steady erosion rates in the Himalayas through late Cenozoic climatic changes
Long-term Himalayan erosion rates remained stable through the global climatic changes of the past six million years, according to the cosmogenic nuclide composition of terrestrial sediments recovered from the Bay of Bengal.
- Sebastien J. P. Lenard
- , Jérôme Lavé
- & Karim Keddadouche
-
Article |
 The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core as a reservoir of water
The Earth’s core may host most of the planet’s water inventory, according to calculations of the partitioning behaviour of water at conditions of core formation.
- Yunguo Li
- , Lidunka Vočadlo
- & John P. Brodholt
-
Perspective |
 Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust
Critical role of water in the formation of continental crust
Migration of water from the slab to the surface during subduction is highlighted as a key process in the formation of continental crust.
- William J. Collins
- , J. Brendan Murphy
- & Hui-Qing Huang
-
Article |
 Rapid crystallization of precious-metal-mineralized layers in mafic magmatic systems
Rapid crystallization of precious-metal-mineralized layers in mafic magmatic systems
Mineralization of platinum-group elements in mafic intrusions occurs due to repeated self-intrusion of magma, according to strontium isotope heterogeneities preserved in the Rum layered intrusion, Scotland.
- Luke N. Hepworth
- , J. Stephen Daly
- & Brian O’Driscoll
-
Article |
 Iron isotope fractionation at the core–mantle boundary by thermodiffusion
Iron isotope fractionation at the core–mantle boundary by thermodiffusion
Iron isotopic fractionation at the core–mantle boundary due to thermal diffusion may partly explain the iron isotope composition of the upper mantle, according to high-temperature experiments and numerical simulations.
- Charles E. Lesher
- , Juliane Dannberg
- & James M. Brenan
-
Article |
 Multiple early-formed water reservoirs in the interior of Mars
Multiple early-formed water reservoirs in the interior of Mars
Mars’s mantle is chemically heterogeneous and contains multiple primordial water reservoirs, according to an analysis of the hydrogen isotopic composition of minerals in Martian meteorites.
- Jessica J. Barnes
- , Francis M. McCubbin
- & Carl B. Agee
-
Article |
 Early crust building enhanced on the Moon’s nearside by mantle melting-point depression
Early crust building enhanced on the Moon’s nearside by mantle melting-point depression
Early magmatism on the Moon’s nearside may have been enhanced by a geochemical anomaly lowering the melting point of the mantle source region, according to high-temperature experiments and thermal numerical modelling.
- Stephen M. Elardo
- , Matthieu Laneuville
- & Charles K. Shearer
-
Article |
 Supply of phosphate to early Earth by photogeochemistry after meteoritic weathering
Supply of phosphate to early Earth by photogeochemistry after meteoritic weathering
Reduced phosphorus species delivered by meteorites can be oxidized in reactions with hydrogen sulfide under ultraviolet light to provide a ready supply of phosphate to support prebiotic chemistry, as demonstrated by experiments.
- Dougal J. Ritson
- , Stephen J. Mojzsis
- & John. D. Sutherland
-
Article |
 Palaeoproterozoic oxygenated oceans following the Lomagundi–Jatuli Event
Palaeoproterozoic oxygenated oceans following the Lomagundi–Jatuli Event
The oceans probably remained well-oxygenated for millions of years after the Palaeoproterozoic Lomagundi–Jatuli Event, according to high concentrations and isotope signatures of redox-sensitive metals in the 2-billion-year-old Zaonega Formation, Russia.
- Kaarel Mänd
- , Stefan V. Lalonde
- & Kurt O. Konhauser
-
Article |
 Instantaneous rock transformations in the deep crust driven by reactive fluid flow
Instantaneous rock transformations in the deep crust driven by reactive fluid flow
Fluid-mediated reaction fronts in rocks can propagate up to 10 centimetres per year, according to a transport model informed by observations of an ophiolite in Norway.
- A. Beinlich
- , T. John
- & Y. Y. Podladchikov
-
Article |
 Distinct oxygen isotope compositions of the Earth and Moon
Distinct oxygen isotope compositions of the Earth and Moon
High-precision measurements suggest that the Earth and Moon have distinct oxygen isotope compositions. This implies distinct oxygen isotopic compositions of the proto-Earth and its impactor that were not fully homogenized by the Moon-forming impact.
- Erick J. Cano
- , Zachary D. Sharp
- & Charles K. Shearer
-
Article |
 Earth’s earliest granitoids are crystal-rich magma reservoirs tapped by silicic eruptions
Earth’s earliest granitoids are crystal-rich magma reservoirs tapped by silicic eruptions
The chemical diversity of Earth’s early continental building blocks can be explained by differentiation of a single melt, without complex geodynamic settings, according to petrological and geochemical analysis of samples from South Africa.
- Oscar Laurent
- , Jana Björnsen
- & Olivier Bachmann
-
Article |
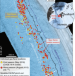 Reduced methane seepage from Arctic sediments during cold bottom-water conditions
Reduced methane seepage from Arctic sediments during cold bottom-water conditions
Methane release rate from Arctic Ocean sediments in winter is significantly lower than in summer, according to surveys of cold-seep activity along the shelf break offshore Svalbard.
- Bénédicte Ferré
- , Pär G. Jansson
- & Helge Niemann
-
News & Views |
 What goes down must come up
What goes down must come up
Differential cycling of carbonate and organic carbon in the mantle may link the Great Oxidation Event and the subsequent increase in carbon isotope values, according to a model that links the Earth’s surface and interior.
- Jeremy K. Caves Rugenstein
-
Article |
 Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events linked by deep cycling and enhanced degassing of carbon
Great Oxidation and Lomagundi events linked by deep cycling and enhanced degassing of carbon
Carbon cycling in the mantle may be a common mechanism that links the Great Oxidation Event and the subsequent Lomagundi increase in carbon isotope values, according to a box model that accounts for carbon and oxygen fluxes and reservoirs.
- James Eguchi
- , Johnny Seales
- & Rajdeep Dasgupta
-
Article |
 Release of oxidizing fluids in subduction zones recorded by iron isotope zonation in garnet
Release of oxidizing fluids in subduction zones recorded by iron isotope zonation in garnet
Lawsonite dehydration and release of oxidizing fluids could play an important role in sub-arc mantle oxidation in subduction zones, suggest measurements of changing oxygen fugacity in zoned garnets from Sifnos, Greece.
- Anna R. Gerrits
- , Edward C. Inglis
- & Kevin W. Burton
-
Article |
 An interval of high salinity in ancient Gale crater lake on Mars
An interval of high salinity in ancient Gale crater lake on Mars
Brines from evaporation of a lake in Gale crater on Mars are inferred from bulk enrichments of Ca- and Mg-sulfates in Hesperian sedimentary rocks, identified by geochemical analyses and observations by NASA’s rover Curiosity.
- W. Rapin
- , B. L. Ehlmann
- & A. R. Vasavada
-
Article |
 Extensive crustal extraction in Earth’s early history inferred from molybdenum isotopes
Extensive crustal extraction in Earth’s early history inferred from molybdenum isotopes
Steady-state chemical differentiation between Earth’s mantle and crust was reached 3.5 billion years ago, following vigorous crustal recycling, according to mass balance modelling of molybdenum isotopes measured in mantle-derived volcanic rocks.
- Alex J. McCoy-West
- , Priyadarshi Chowdhury
- & Helen M. Williams
-
Article |
 Ubiquitous ultra-depleted domains in Earth’s mantle
Ubiquitous ultra-depleted domains in Earth’s mantle
Depleted mantle is a volumetrically dominant component of the Azores plume and possibly of oceanic basalt sources more generally, according to neodymium isotope compositions of olivine-hosted melt inclusions from lavas of the Azores mantle plume.
- Andreas Stracke
- , Felix Genske
- & Janne M. Koornneef
-
News & Views |
 A silicon memory of subduction
A silicon memory of subduction
Subduction processes may have operated very early in Earth’s history according to the heavy silicon isotope compositions of Archaean igneous rocks. The silicon that precipitated out of the Archaean oceans as chert was subducted and melted to yield seawater-like heavy isotope signatures in early granitic rocks.
- Franck Poitrasson
-
Article |
 Tin isotopes indicative of liquid–vapour equilibration and separation in the Moon-forming disk
Tin isotopes indicative of liquid–vapour equilibration and separation in the Moon-forming disk
Vigorous mixing between the protolunar disk and Earth followed by processes in the cooling disk may explain the enrichment in light isotopes of tin on the Moon relative to Earth, as found by analysis of lunar rocks and geochemical calculations.
- Xueying Wang
- , Caroline Fitoussi
- & Sébastien Charnoz
-
Article |
 An oceanic subduction origin for Archaean granitoids revealed by silicon isotopes
An oceanic subduction origin for Archaean granitoids revealed by silicon isotopes
Archaean granitic rocks formed by melting of silica-enriched subducted basaltic crust through interaction with seawater, according to heavy silicon isotopes measured in Archaean samples.
- Zhengbin Deng
- , Marc Chaussidon
- & Frédéric Moynier
-
Article |
 Early continental crust generated by reworking of basalts variably silicified by seawater
Early continental crust generated by reworking of basalts variably silicified by seawater
Granitic continental crust in the Archaean formed from a basaltic source that was enriched in silica due to interaction with the early oceans before melting, according to silicon isotope analyses on rocks from the Kaapvaal craton.
- Luc André
- , Kathrin Abraham
- & Stephen Foley
-
News & Views |
 The Earth–Moon late-accretion conundrum
The Earth–Moon late-accretion conundrum
The distribution of iron-loving elements between the mantles of the Moon and Earth may differ from established belief, suggest two studies that determine the hafnium–tungsten ratio and sulfide–silicate melt partitioning of elements in the lunar mantle.
- Philipp Gleißner
-
Article |
 Abundance of highly siderophile elements in lunar basalts controlled by iron sulfide melt
Abundance of highly siderophile elements in lunar basalts controlled by iron sulfide melt
The abundance of iron-loving elements in Moon rocks cannot indicate the amount of late accretion onto the Moon, according to experiments and thermodynamic calculations constraining the behaviour of these elements under lunar mantle conditions.
- James M. Brenan
- , James E. Mungall
- & Neil R. Bennett
-
Article |
 Selenium isotopes as tracers of a late volatile contribution to Earth from the outer Solar System
Selenium isotopes as tracers of a late volatile contribution to Earth from the outer Solar System
Material that accreted to Earth after its core formed largely comprised carbonaceous, volatile-rich meteorites, according to analysis of the selenium isotopic composition of terrestrial mantle rocks.
- María Isabel Varas-Reus
- , Stephan König
- & Ronny Schoenberg
-
Article |
 Global fire emissions buffered by the production of pyrogenic carbon
Global fire emissions buffered by the production of pyrogenic carbon
Pyrogenic carbon produced from vegetation fires could be a globally important carbon sink, which amounts to 12% of the carbon emitted from wildfires annually, according to a global fire emission database that incorporates the estimate of pyrogenic carbon.
- Matthew W. Jones
- , Cristina Santín
- & Stefan H. Doerr
-
Article |
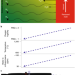 Arc magmas oxidized by water dissociation and hydrogen incorporation in orthopyroxene
Arc magmas oxidized by water dissociation and hydrogen incorporation in orthopyroxene
Oxidation of arc magmas may be a secondary feature, acquired as hydrogen from magmatic water is incorporated into anhydrous minerals in the mantle wedge, according to analyses of orthopyroxenes in mantle xenoliths from an arc setting.
- Peter Tollan
- & Jörg Hermann
-
Article |
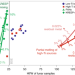 Early Moon formation inferred from hafnium–tungsten systematics
Early Moon formation inferred from hafnium–tungsten systematics
The Moon formed around 50 Myr after the Solar System, suggests a lunar silicate Hf/W ratio higher than that of Earth, from high-precision compositional analysis of lunar rock samples.
- Maxwell M. Thiemens
- , Peter Sprung
- & Carsten Münker
-
Article |
 Palaeoarchaean deep mantle heterogeneity recorded by enriched plume remnants
Palaeoarchaean deep mantle heterogeneity recorded by enriched plume remnants
Deep mantle heterogeneity and large-scale deep mantle convection has been operating since the Palaeoarchaean, according to enriched plume signatures found in a 3.45-billion-year-old ultramafic–mafic suite from the North China Craton.
- Chao Wang
- , Shuguang Song
- & Jinlong Dong
-
News & Views |
 Earth’s volatile-element jigsaw
Earth’s volatile-element jigsaw
Earth’s formation by the accretion of volatile-rich carbonaceous chondrite-like materials, without a need for exotic building blocks or secondary volatile loss, is supported by recognition of a plateau pattern for highly volatile elements.
- Zaicong Wang
-
News & Views |
 Ancient rust
Ancient rust
Confidence that banded iron formations record oxic conditions during deposition is established, as a model demonstrates that they are formed of primary iron oxides rather than secondarily altered silicate minerals.
- Eva E. Stüeken

 Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle
Superionic iron oxide–hydroxide in Earth’s deep mantle