Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenome environment interactions accelerate epigenomic aging and unlock metabolically restricted epigenetic reprogramming in adulthood
Epigenome environment interactions accelerate epigenomic aging and unlock metabolically restricted epigenetic reprogramming in adulthood
Early life exposure to environmental stressors, including endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs), can impact health later in life. Here, the authors show that neonatal EDC exposure in rats causes epigenetic reprogramming in the liver, which is transcriptionally silent until animals are placed on a Western-style diet.
- Lindsey S. Treviño
- , Jianrong Dong
- & Cheryl Lyn Walker
-
Article
| Open Access Timing the initiation of multiple myeloma
Timing the initiation of multiple myeloma
The initial mutational processes and how these lead to progression in multiple myeloma (MM) are unclear. Here, the authors identify mutational signatures that occur over time in a large cohort of MM patients and suggest features that may help in early diagnosis.
- Even H. Rustad
- , Venkata Yellapantula
- & Francesco Maura
-
Article
| Open Access GenomeScope 2.0 and Smudgeplot for reference-free profiling of polyploid genomes
GenomeScope 2.0 and Smudgeplot for reference-free profiling of polyploid genomes
Prior to genome assembly, the raw sequencing reads must be analyzed for assessment of major genome characteristics such as genome size, heterozygosity, and repetitiveness. For this purpose, the authors introduce GenomeScope 2.0, an extension of GenomeScope for polyploid genomes, and Smudgeplot, which can estimate a genome’s ploidy.
- T. Rhyker Ranallo-Benavidez
- , Kamil S. Jaron
- & Michael C. Schatz
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic specifications of host chromosome docking sites for latent Epstein-Barr virus
Epigenetic specifications of host chromosome docking sites for latent Epstein-Barr virus
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) episomes tether to the host chromosome via EBNA1. Here, using circular chromosome conformation capture (4C), Kim et al. identify attachment sites and show that EBV episomes preferentially associate with transcriptionally silenced genes in Burkitt lymphoma cells.
- Kyoung-Dong Kim
- , Hideki Tanizawa
- & Paul M. Lieberman
-
Article
| Open Access Novel approach reveals genomic landscapes of single-strand DNA breaks with nucleotide resolution in human cells
Novel approach reveals genomic landscapes of single-strand DNA breaks with nucleotide resolution in human cells
Single strand breaks represent the most common form of DNA damage yet no methods to map them in a genome-wide fashion at single nucleotide resolution exist. Here the authors develop such a method and apply to uncover patterns of single-strand DNA “breakome” in different biological conditions.
- Huifen Cao
- , Lorena Salazar-García
- & Philipp Kapranov
-
Article
| Open Access LinkedSV for detection of mosaic structural variants from linked-read exome and genome sequencing data
LinkedSV for detection of mosaic structural variants from linked-read exome and genome sequencing data
Compared to single nucleotide variants and short indels, structural variants (SVs) are often more challenging to detect using high-throughput sequencing based methods. Here, the authors develop LinkedSV, a computational tool for SV detection using linked-read exome and genome sequencing data.
- Li Fang
- , Charlly Kao
- & Kai Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Thermodynamics and kinetics guided probe design for uniformly sensitive and specific DNA hybridization without optimization
Optimisation of nucleic acid probes and blocker strands can be laborious. Here the authors construct a theoretical model of competitive DNA hybridisation to design DNA probes for optimisation-free mutation detection.
- Xin Chen
- , Na Liu
- & Xianjin Xiao
-
Article
| Open Access Linked-read sequencing of gametes allows efficient genome-wide analysis of meiotic recombination
Linked-read sequencing of gametes allows efficient genome-wide analysis of meiotic recombination
Meiotic crossovers (COs) generate genetic variation and ensure proper chromosome segregation. Here, the authors develop a method for identifying COs at kilobase resolution in pooled recombinants using linked-read sequencing data, and apply it to investigate genome-wide CO landscapes of Arabidopsis thaliana.
- Hequan Sun
- , Beth A. Rowan
- & Korbinian Schneeberger
-
Article
| Open Access Cell-type-specific genomics reveals histone modification dynamics in mammalian meiosis
Cell-type-specific genomics reveals histone modification dynamics in mammalian meiosis
Meiotic DSB formation, repair and recombination occur in a continuum of substages termed leptonema, zygonema, pachynema, and diplonema. Here, authors develop a method for isolating pure sub-populations of nuclei that allows for detailed study of meiotic substages.
- Kwan-Wood Gabriel Lam
- , Kevin Brick
- & R. Daniel Camerini-Otero
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping histone modifications in low cell number and single cells using antibody-guided chromatin tagmentation (ACT-seq)
Mapping histone modifications in low cell number and single cells using antibody-guided chromatin tagmentation (ACT-seq)
The authors introduce ACT-seq: a Tn5-based method for rapidly profiling epigenetic marks in bulk-cell and single-cell samples. ACT-seq avoids many laborious or time-consuming steps required for similar techniques including chromatin fragmentation and end repair.
- Benjamin Carter
- , Wai Lim Ku
- & Keji Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Proteogenomic landscape of squamous cell lung cancer
Proteogenomic landscape of squamous cell lung cancer
Squamous cell lung cancer has dismal prognosis due to the dearth of effective treatments. Here, the authors perform an integrated proteogenomic analysis of the disease, revealing three proteomics-based subtypes and suggesting potential therapeutic opportunities.
- Paul A. Stewart
- , Eric A. Welsh
- & Eric B. Haura
-
Article
| Open Access A consensus S. cerevisiae metabolic model Yeast8 and its ecosystem for comprehensively probing cellular metabolism
A consensus S. cerevisiae metabolic model Yeast8 and its ecosystem for comprehensively probing cellular metabolism
Genome-scale metabolic models provide a platform to study metabolism through simulations and analysis of omics data. Here the authors introduce Yeast8 with its model ecosystem, a comprehensive computational resource for simulating the metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
- Hongzhong Lu
- , Feiran Li
- & Jens Nielsen
-
Article
| Open Access NASC-seq monitors RNA synthesis in single cells
NASC-seq monitors RNA synthesis in single cells
Sequencing of newly synthesised RNA can reveal the transcriptional dynamics in a population of cells. Here the authors develop NASC-seq to bring this sensitivity and temporal resolution to single-cell analysis.
- Gert-Jan Hendriks
- , Lisa A. Jung
- & Rickard Sandberg
-
Article
| Open Access The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
The use of technical replication for detection of low-level somatic mutations in next-generation sequencing
Somatic mutations of low allele frequencies are often difficult to detect. Here, the authors develop RePlow, a computational method that leverages technical replication for detecting low-level somatic mutations using next-generation sequencing.
- Junho Kim
- , Dachan Kim
- & Sangwoo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Single gametophyte sequencing reveals that crossover events differ between sexes in maize
Single gametophyte sequencing reveals that crossover events differ between sexes in maize
Meiotic crossover (CO) landscape differs inter- and intra-species, as well as between sexes. Here, the authors show that male meiosis produces more COs than female in maize and detect CO maturation inefficiency in some genetic backgrounds, which may help to improve breeding efficiency.
- Cheng Luo
- , Xiang Li
- & Jianbing Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Selective single molecule sequencing and assembly of a human Y chromosome of African origin
Selective single molecule sequencing and assembly of a human Y chromosome of African origin
Due to various structural and sequence complexities, the human Y chromosome is challenging to sequence and characterize. Here, the authors develop a strategy to sequence native, unamplified flow sorted Y chromosomes with a nanopore sequencing platform, and report the first assembly of a human Y chromosome of African origin.
- Lukas F. K. Kuderna
- , Esther Lizano
- & Tomas Marques-Bonet
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide study of hair colour in UK Biobank explains most of the SNP heritability
Genome-wide study of hair colour in UK Biobank explains most of the SNP heritability
Natural hair colour in Europeans is a complex genetic trait. Here, the authors carry out a genome-wide association study using UK BioBank data, suggesting that in combination with pigmentation genes, variants with roles in hair texture and growth can affect hair colouration or our perception of it.
- Michael D. Morgan
- , Erola Pairo-Castineira
- & Ian J. Jackson
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptome-wide identification of transient RNA G-quadruplexes in human cells
Transcriptome-wide identification of transient RNA G-quadruplexes in human cells
In vivo existence of guanine-rich four-stranded RNA structures (G4-RNAs) has been a matter of debate. Here the authors developed a protocol, G4RP-seq, to capture and identify transcriptome-wide G4-RNA, providing insights into the formation of transient G4-RNA in live human cells.
- Sunny Y. Yang
- , Pauline Lejault
- & David Monchaud
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery of rare cells from voluminous single cell expression data
Discovery of rare cells from voluminous single cell expression data
Algorithms designed to find rare cells in single cell RNA-seq data sets cannot cope with data sets containing tens of thousands of cells. Here the authors present Finder of Rare Entities (FiRE), an algorithm that uses the Sketching technique to assign a rareness score to every expression profile in large RNA-seq data sets.
- Aashi Jindal
- , Prashant Gupta
- & Debarka Sengupta
-
Article
| Open Access Common mechanism of transcription termination at coding and noncoding RNA genes in fission yeast
Common mechanism of transcription termination at coding and noncoding RNA genes in fission yeast
Termination of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) transcription is an essential step of gene expression. Here the authors provide evidence that in fission yeast termination of ncRNA genes occurs by a cleavage-dependent mechanism involving recruitment of mRNA 3′ end processing factors and requires the conserved Ysh1/CPSF-73 and Dhp1/XRN2 nucleases.
- Marc Larochelle
- , Marc-Antoine Robert
- & François Bachand
-
Article
| Open Access Facultative dosage compensation of developmental genes on autosomes in Drosophila and mouse embryonic stem cells
Facultative dosage compensation of developmental genes on autosomes in Drosophila and mouse embryonic stem cells
In Drosophila the Male-Specific Lethal complex (MSLc) mediates upregulation of the single male X chromosome. Here the authors provide evidence that MSL2 also targets autosomal genes required for proper development and that MSL2 binds and similarly regulates mouse orthologues.
- Claudia Isabelle Keller Valsecchi
- , M. Felicia Basilicata
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article
| Open Access Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates
Early selection of bZIP73 facilitated adaptation of japonica rice to cold climates
Japonica rice can grow further north than wild or indica rice and is more tolerant of cold climates. Here, the authors show that bZIP73 likely underwent selection in the early phase of rice domestication to facilitate cold tolerance in japonica by modulating ABA and ROS homeostasis.
- Citao Liu
- , Shujun Ou
- & Chengcai Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Sensitive and powerful single-cell RNA sequencing using mcSCRB-seq
Sensitive and powerful single-cell RNA sequencing using mcSCRB-seq
Single-cell RNA-barcoding and sequencing is an efficient, genome-wide method to characterize cellular identities. Here the authors systematically evaluate the protocol and develop molecular crowding SCRB-seq with improved sensitivity and cost-efficiency.
- Johannes W. Bagnoli
- , Christoph Ziegenhain
- & Wolfgang Enard
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput screening of prostate cancer risk loci by single nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing
High-throughput screening of prostate cancer risk loci by single nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing
Functional characterization of disease-causing variants at risk loci in cancer is challenging. Here, in prostate cancer the authors report a pipeline for high-throughput single-nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing (SNPs-seq) for large scale screening of functional SNPs at disease risk loci.
- Peng Zhang
- , Ji-Han Xia
- & Liang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access The Gastrodia elata genome provides insights into plant adaptation to heterotrophy
The Gastrodia elata genome provides insights into plant adaptation to heterotrophy
Gastrodia elata is an obligate mycoheterotrophic plant with highly reduced leaves and bracts in scape. Here, Yuan et al sequence and analyze its 1.06 Gb genome which provides insights in adaptation to a lifestyle of heterotrophy.
- Yuan Yuan
- , Xiaohua Jin
- & Luqi Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways
Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways
The UK Biobank provides data for three depression-related phenotypes. Here, Howard et al. perform a genome-association study for broad depression, probable major depressive disorder (MDD) and hospital record-coded MDD in up to 322,580 UK Biobank participants which highlights excitatory synaptic pathways.
- David M. Howard
- , Mark J. Adams
- & Andrew M. McIntosh
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell RNA-seq of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue using low-cost microfluidic instrumentation
Single-cell RNA-seq of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue using low-cost microfluidic instrumentation
Droplet-based single-cell RNA-seq is a powerful tool for cellular heterogeneity profiling in disease but is limited by instrumentation required. Here the authors develop a 3D printed microfluidic platform for massive parallel sequencing of rheumatoid arthritis tissues.
- William Stephenson
- , Laura T. Donlin
- & Rahul Satija
-
Article
| Open Access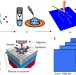 DNA nanomapping using CRISPR-Cas9 as a programmable nanoparticle
DNA nanomapping using CRISPR-Cas9 as a programmable nanoparticle
Physical mapping of DNA can be used to detect structural variants and for whole-genome haplotype assembly. Here, the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 and high-speed atomic force microscopy to ‘nanomap’ single molecules of DNA.
- Andrey Mikheikin
- , Anita Olsen
- & Jason Reed
-
Article
| Open Access Using ALoFT to determine the impact of putative loss-of-function variants in protein-coding genes
Using ALoFT to determine the impact of putative loss-of-function variants in protein-coding genes
Variants causing loss of function (LoF) of human genes have clinical implications. Here, the authors present a method to predict disease-causing potential of LoF variants, ALoFT (annotation of Loss-of-Function Transcripts) and show its application to interpreting LoF variants in different contexts.
- Suganthi Balasubramanian
- , Yao Fu
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access Improved genome recovery and integrated cell-size analyses of individual uncultured microbial cells and viral particles
Improved genome recovery and integrated cell-size analyses of individual uncultured microbial cells and viral particles
Single-cell genomics can be used to study uncultured microorganisms. Here, Stepanauskas et al. present a method combining improved multiple displacement amplification and FACS, to obtain genomic sequences and cell size information from uncultivated microbial cells and viral particles in environmental samples.
- Ramunas Stepanauskas
- , Elizabeth A. Fergusson
- & Arvydas Lubys
-
Article
| Open Access Single-virus genomics reveals hidden cosmopolitan and abundant viruses
Single-virus genomics reveals hidden cosmopolitan and abundant viruses
Viruses play an important role in microbial communities but, due to limitations of available techniques, our understanding of viral diversity is limited. Here, the authors use SVGs and identify highly abundant viruses in marine communities that have been previously overlooked.
- Francisco Martinez-Hernandez
- , Oscar Fornas
- & Manuel Martinez-Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access TruePrime is a novel method for whole-genome amplification from single cells based on TthPrimPol
TruePrime is a novel method for whole-genome amplification from single cells based on TthPrimPol
Single cell genomic analysis needs DNA amplification with high fidelity and accuracy. Here, the authors devise a novel multiple displacement amplification method called TruePrime that is based in Thermus thermophilusPrimPol and Phi29 DNA polymerase, and demonstrate its utility and accuracy.
- Ángel J. Picher
- , Bettina Budeus
- & Armin Schneider
-
Article
| Open Access Capture of associated targets on chromatin links long-distance chromatin looping to transcriptional coordination
Capture of associated targets on chromatin links long-distance chromatin looping to transcriptional coordination
Chromatin architecture is a key regulator of transcriptional processes, however current methods to investigate it have technical limitations. Here, the authors describe a novel chromatin capture technique, CATCH, which can be used to identify and characterize complex genomic interaction networks.
- Ryan J. Bourgo
- , Hari Singhal
- & Geoffrey L. Greene
-
Article
| Open Access Laser capture microscopy coupled with Smart-seq2 for precise spatial transcriptomic profiling
Laser capture microscopy coupled with Smart-seq2 for precise spatial transcriptomic profiling
Laser capture microscopy (LCM) coupled with global transcriptome profiling requires relatively large numbers of cells. Here, the authors show that LCM coupled with full-length mRNA-sequencing (LCM-seq) can sequence single cells, and that LCM-seq can provide biological insight on highly similar neuronal populations.
- Susanne Nichterwitz
- , Geng Chen
- & Eva Hedlund
-
Article
| Open Access Prosaposin is a regulator of progranulin levels and oligomerization
Prosaposin is a regulator of progranulin levels and oligomerization
Increasing progranulin (PGRN) levels is a promising approach for treating frontotemporal dementia and other neurodegenerative diseases. Here Nicholson et al.show that the prosaposin (PSAP) locus is associated with plasma PGRN levels and demonstrate that PSAP can alter PGRN levels and its oligomerization.
- Alexandra M. Nicholson
- , NiCole A. Finch
- & Rosa Rademakers
-
Article
| Open Access Rebalancing gene haploinsufficiency in vivo by targeting chromatin
Rebalancing gene haploinsufficiency in vivo by targeting chromatin
Deficit in transcription factor Tbx1 causes heart defects in humans and mice. Here the authors show that Tbx1 regulates gene expression by recruiting histone methyltransferases that affect chromatin marks, and that a drug inhibiting histone demethylation ameliorates the cardiovascular phenotype in Tbx1 haploinsufficient or hypomorphic mice.
- Filomena Gabriella Fulcoli
- , Monica Franzese
- & Antonio Baldini
-
Article
| Open Access A uniform survey of allele-specific binding and expression over 1000-Genomes-Project individuals
A uniform survey of allele-specific binding and expression over 1000-Genomes-Project individuals
Using variants from the 1000 Genomes Project, RNA-seq and ChIP-seq data from related projects, this study describes a resource and survey of allele-specific binding and gene expression. A catalogue of allelic SNPs and annotation elements is available as an online resource at alleledb.gersteinlab.org.
- Jieming Chen
- , Joel Rozowsky
- & Mark Gerstein
-
Article
| Open Access Atlas of prostate cancer heritability in European and African-American men pinpoints tissue-specific regulation
Atlas of prostate cancer heritability in European and African-American men pinpoints tissue-specific regulation
Over one hundred loci have been identified to be associated with the familial risk of prostate cancer but the functional effects are poorly understood. Here the authors use single-nucleotide variant and epigentic data to show an underlying genetic architecture marked by histone modification.
- Alexander Gusev
- , Huwenbo Shi
- & Bogdan Pasaniuc
-
Article
| Open Access Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon genomes from East England reveal British migration history
Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon genomes from East England reveal British migration history
This study examines ancient genomes of individuals from the late Iron Age to the middle Anglo-Saxon period in the East of England. Using a newly devised analytic algorithm, the author also estimate the relative ancestry of East English genome derived from Anglo-Saxon migrations and to the rest of Europe.
- Stephan Schiffels
- , Wolfgang Haak
- & Richard Durbin
-
Article
| Open Access ChIP-seq reveals broad roles of SARD1 and CBP60g in regulating plant immunity
ChIP-seq reveals broad roles of SARD1 and CBP60g in regulating plant immunity
SARD1 and CBP60g are two plant transcription factors that regulate salicylic acid biosynthesis in response to pathogens. Here, Sun et al.show that they bind a wide array of loci related to multiple defence signalling pathways suggesting a broader role as regulators of the plant immune response.
- Tongjun Sun
- , Yaxi Zhang
- & Yuelin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A new tool called DISSECT for analysing large genomic data sets using a Big Data approach
A new tool called DISSECT for analysing large genomic data sets using a Big Data approach
Availability of computing power can limit computational analysis of large genetic and genomic datasets. Here, Canela-Xandri, et al. describe a software called DISSECT that is capable of analyzing large-scale genetic data by distributing the work across thousands of networked computers.
- Oriol Canela-Xandri
- , Andy Law
- & Albert Tenesa
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic pan-cancer analysis of tumour purity
Systematic pan-cancer analysis of tumour purity
The importance of the tumour microenvironment has now been realised, however the presence of non-tumour cells in cancer samples can complicate genomic analyses. Here, the authors estimate tumour purity in 10,000 samples from the TCGA dataset and can detect a signature of T cell activation.
- Dvir Aran
- , Marina Sirota
- & Atul J. Butte
-
Article
| Open Access Capture Hi-C reveals novel candidate genes and complex long-range interactions with related autoimmune risk loci
Capture Hi-C reveals novel candidate genes and complex long-range interactions with related autoimmune risk loci
There is evidence that a proportion of the polymorphisms identified by genome-wide association studies lie in enchancer regions. Here the authors use Capture Hi-C to investigate the interaction with targets in autoimmune disease, showing interactions can be long range and cell-type specific.
- Paul Martin
- , Amanda McGovern
- & Steve Eyre
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide analysis of the genetic regulation of gene expression in human neutrophils
Genome-wide analysis of the genetic regulation of gene expression in human neutrophils
Neutrophils are abundant immune cells important for antimicrobial defence and in autoimmunity. Here, by mapping expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) in neutrophils of Chinese ethnicity from Singapore, Andiappan et al.provide a resource for understanding immune-related trait associated genetic variants.
- Anand Kumar Andiappan
- , Rossella Melchiotti
- & Olaf Rotzschke
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci for variation in human ear morphology
A genome-wide association study identifies multiple loci for variation in human ear morphology
The shape of the pinna varies widely in the general human population but the genetic basis of this variation is unknown. Here Adhikari et al. conduct a genome-wide association study in Latin Americans and discover seven gene regions influencing pinna morphology, including EDAR and TBX15.
- Kaustubh Adhikari
- , Guillermo Reales
- & Andrés Ruiz-Linares
-
Article
| Open Access Single molecule-level detection and long read-based phasing of epigenetic variations in bacterial methylomes
Single molecule-level detection and long read-based phasing of epigenetic variations in bacterial methylomes
Bacterial DNA methylation is involved in many processes, from host defense to antibiotic resistance, however current methods for examining methylated genomes lack single-cell resolution. Here Beaulaurier et al. present Single Molecule Modification Analysis of Long Reads, a new tool for de novodetection of epigenetic heterogeneity.
- John Beaulaurier
- , Xue-Song Zhang
- & Gang Fang
-
Article
| Open Access Proteins that bind regulatory regions identified by histone modification chromatin immunoprecipitations and mass spectrometry
Proteins that bind regulatory regions identified by histone modification chromatin immunoprecipitations and mass spectrometry
The protein factors that bind to regulatory regions in the genome have not been systematically mapped. Here the authors performed chromatin immunoprecipitations for histone modifications associated with promoters, enhancers or heterochromatin in mouse embryonic stem cells and assigned a genome location to many factors important for pluripotency.
- Erik Engelen
- , Johannes H. Brandsma
- & Raymond A. Poot
-
Article
| Open Access Contrasting host–pathogen interactions and genome evolution in two generalist and specialist microsporidian pathogens of mosquitoes
Contrasting host–pathogen interactions and genome evolution in two generalist and specialist microsporidian pathogens of mosquitoes
Microsporidia are intracellular parasitic fungi that infect diverse animal hosts including humans. Here, Desjardins et al.present genomic and transcriptomic data for two microsporidia that infect disease-transmitting mosquitoes, highlighting differences in potential host interplay mechanisms.
- Christopher A. Desjardins
- , Neil D. Sanscrainte
- & Christina A Cuomo
-
Article |
 MiR-125a targets effector programs to stabilize Treg-mediated immune homeostasis
MiR-125a targets effector programs to stabilize Treg-mediated immune homeostasis
Compromised function of regulatory T cells can lead to autoimmunity. Here the authors show that miR-125a stabilizes regulatory T-cell function and is downregulated in lupus and Crohn’s disease, as well as autoimmune mouse models, and that a chemical miR-125a analogue reverts established disease in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis.
- Wen Pan
- , Shu Zhu
- & Nan Shen

 High throughput error corrected Nanopore single cell transcriptome sequencing
High throughput error corrected Nanopore single cell transcriptome sequencing