Featured
-
-
News |
 Balancing water supply and wildlife
Balancing water supply and wildlife
Study warns of threats to water security and biodiversity in the world's rivers.
- Natasha Gilbert
-
-
-
-
Books & Arts |
 Environment: Venice's fragile lagoon
Environment: Venice's fragile lagoon
A section of salt marsh in a Biennale pavilion links the city and its environment, notes Colin Martin.
- Colin Martin
-
News & Views |
 A standard for species
A standard for species
Delimitation of species is especially taxing when populations of similar organisms occupy non-overlapping geographical ranges. A new quantitative framework offers a consistent approach for tackling the problem.
- Thomas M. Brooks
- & Kristofer M. Helgen
-
News & Views |
 Beyond infrastructure
Beyond infrastructure
Projects such as building dams and diverting watercourses enhance water security for humans. But they do little to protect the biodiversity of associated ecosystems, and that's a long-term necessity. See Article p.555
- Margaret A. Palmer
-
News & Views |
 Ocean biomes blended
Ocean biomes blended
The ratio of nutrient elements in marine subsurface waters is much the same everywhere, even though biogeochemically distinct ocean biomes exist. A modelling study that includes mixing solves this conundrum. See Article p.550
- Raymond N. Sambrotto
-
News Feature |
 Marine biology: Out of the blue
Marine biology: Out of the blue
The ten-year Census for Marine Life is about to unveil its final results. But how deep did the $650-million project go?
- Daniel Cressey
-
Article |
 Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity
Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity
Water security affects human wellbeing both directly and indirectly, through its effects on biodiversity. Here, a global map has been generated that shows threats to both direct and indirect water security from a full range of potential stressors. Technological investments have also been incorporated. The map shows that nearly 80% of the world's population is exposed to high levels of threat to water security. Investment enables rich nations to offset high stressor levels, but less wealthy nations remain vulnerable.
- C. J. Vörösmarty
- , P. B. McIntyre
- & P. M. Davies
-
Article |
 Ocean nutrient ratios governed by plankton biogeography
Ocean nutrient ratios governed by plankton biogeography
The major nutrients nitrate and phosphate have one of the strongest correlations in the sea, with a slope similar to the average nitrogen to phosphorus content of plankton biomass (16:1). Why this global relationship exists, despite the wide range of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios at the organism level, is unknown. Here, an ocean circulation model and observed nutrient distributions have been used to show that the covariation of dissolved nitrate and phosphate is maintained by ocean circulation.
- Thomas S. Weber
- & Curtis Deutsch
-
News |
 Threats to the world's plants assessed
Threats to the world's plants assessed
Habitat loss is the biggest hazard to plant biodiversity.
- Natasha Gilbert
-
News |
 Looking beyond the glamour of conservation
Looking beyond the glamour of conservation
Mammal ecologists call for greater focus on non-charismatic species.
- Yana Balling
-
News |
 Plants set stage for evolutionary drama
Plants set stage for evolutionary drama
Oxygen increase triggered by vascular plants enabled the development of complex animals.
- Joseph Milton
-
News Q&A |
 Saving species with science
Saving species with science
Coping with climate change is a key priority for conservation in the United States, says new science adviser.
- Amanda Mascarelli
-
Correspondence |
Why the inaction on biodiversity?
- Guillaume Chapron
- , Raphaël Arlettaz
- & Luigi Boitani
-
Research Highlights |
 Animal behaviour: Same-shaped shoals
Animal behaviour: Same-shaped shoals
-
News & Views |
 Foreseeing tipping points
Foreseeing tipping points
Theory suggests that the risk of critical transitions in complex systems can be revealed by generic indicators. A lab study of extinction in plankton populations provides experimental support for that principle. See Letter p. 456
- Marten Scheffer
-
News |
 French bid to save rock art
French bid to save rock art
Revamped conservation effort aims to correct mistakes made in preserving cave paintings.
- Declan Butler
-
News |
 Evolution in the urban jungle
Evolution in the urban jungle
Tuberculosis resistance is most prevalent in city slickers.
- Ewen Callaway
-
-
News |
 Oil-spill bacteria gobbled gases first
Oil-spill bacteria gobbled gases first
Levels of ethane and propane consumed by Gulf microbes spark questions about the oil's fate.
- Amanda Mascarelli
-
Editorial |
An alternative route
A proposed road through the Serengeti can be halted only by providing a viable substitute, not by criticism.
-
Correspondence |
Commodities for export still threaten rainforests in Brazil
- Luiz Antonio Martinelli
- & Paulo Moutinho
-
Research Highlights |
Ecology: Biodiversity balance
-
Opinion |
 Road will ruin Serengeti
Road will ruin Serengeti
Tanzania's iconic national park must not be divided by a highway, say Andrew Dobson, Markus Borner, Tony Sinclair and 24 others. A route farther south would bring greater benefits to development and the environment.
- Andrew P. Dobson
- , Markus Borner
- & Eric Wolanski
-
News |
 Can conservation cut poverty?
Can conservation cut poverty?
Experts differ on the effects of biodiversity projects on improvements in living standards.
- Natasha Gilbert
-
Correspondence |
A call for action to curb invasive species in South America
- Karina Speziale
- & Sergio Lambertucci
-
Research Highlights |
 Marine biology: Charismatic carbon
Marine biology: Charismatic carbon
-
-
Research Highlights |
 Palaeontology: Leaf-like history of lacewings
Palaeontology: Leaf-like history of lacewings
-
News & Views |
 A glacial test of timing
A glacial test of timing
Meticulous reconstruction of the former extent of a glacier high in the mountains of New Zealand will help in interpreting global-scale climatic adjustments that occurred at the end of the last glaciation.
- Martin P. Kirkbride
-
News & Views |
 Communication and speciation
Communication and speciation
An electrifying evolutionary radiation has evidently occurred among elephant fish in Africa's Ivindo basin. An implication is that open niches for communication can result in species diversification.
- Manuel Leal
- & Jonathan B. Losos
-
Letter |
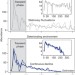 Early warning signals of extinction in deteriorating environments
Early warning signals of extinction in deteriorating environments
Populations that become extinct because of environmental degradation pass a tipping point, after which extinction is inevitable. But theory predicts that the population's dynamics indicate what is coming beforehand, through the phenomenon of critical slowing down. It has now been shown that critical slowing down can be used to anticipate extinction in experimental populations of Daphnia magna.
- John M. Drake
- & Blaine D. Griffen
-
News |
 Aquatic conservation efforts pay off
Aquatic conservation efforts pay off
Clean-up of Potomac River offers hope to environmentalists worldwide.
- Richard A. Lovett
-
News |
 Canada sees shock salmon glut
Canada sees shock salmon glut
Some 34 million of the fish are thronging British Columbia's Fraser River.
- Kate Larkin
-
News Q&A |
 What lies beneath Antarctic ice
What lies beneath Antarctic ice
Rodolfo del Valle and his team are heading to the Southern Ocean to measure a methane leak.
- Ana Belluscio
-
Letter |
 Bacterial charity work leads to population-wide resistance
Bacterial charity work leads to population-wide resistance
Bacteria regularly evolve antibiotic resistance, but little is known about this process at the population level. Here, a continuous culture of Escherichia coli facing increasing antibiotic levels is followed. Most isolates taken from this population are less antibiotic resistant than the population as a whole. A few highly resistant mutants provide protection to the less resistant constituents, in part by producing the signalling molecule indole, which serves to turn on drug efflux pumps and oxidative-stress protective mechanisms.
- Henry H. Lee
- , Michael N. Molla
- & James J. Collins
-
News |
 Cold blamed for Bolivia's mass fish deaths
Cold blamed for Bolivia's mass fish deaths
Extreme weather wreaks havoc in the rivers.
- Anna Petherick
-
Research Highlights |
Ecology: Tree death count
-
News |
 Ecologists fear Antarctic krill crisis
Ecologists fear Antarctic krill crisis
Fishing industry threatens to destabilize stocks.
- Quirin Schiermeier
-
Opinion |
 Seafood stewardship in crisis
Seafood stewardship in crisis
The main consumer-targeted certification scheme for sustainable fisheries is failing to protect the environment and needs radical reform, say Jennifer Jacquet, Daniel Pauly and colleagues.
- Jennifer Jacquet
- , Daniel Pauly
- & Jeremy Jackson
-
Books & Arts |
 Soil map digs under the tundra
Soil map digs under the tundra
An ambitious atlas that charts the composition of frozen northern soils highlights their contribution to climate change, finds Philippe Ciais.
- Philippe Ciais
-
News Feature |
 Deepwater Horizon: After the oil
Deepwater Horizon: After the oil
When oil stopped gushing into the Gulf of Mexico, the ecosystems under assault started on a long road to recovery. Amanda Mascarelli meets the researchers assessing their chances.
- Amanda Mascarelli
-
News |
 Where conflict meets conservation
Where conflict meets conservation
Animals as hidden victims of war are the focus of a groundbreaking initiative launched at King's College London.
- Rhiannon Smith
-
News |
 Cold empties Bolivian rivers of fish
Cold empties Bolivian rivers of fish
Antarctic cold snap kills millions of aquatic animals in the Amazon.
- Anna Petherick
-
-
-
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

 Virus-like particles speed bacterial evolution
Virus-like particles speed bacterial evolution How stress shapes ecosystems
How stress shapes ecosystems Mosquitoes: schemes to render them extinct are impracticable
Mosquitoes: schemes to render them extinct are impracticable