Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Flash freezing route to mesoporous polymer nanofibre networks
Flash freezing route to mesoporous polymer nanofibre networks
Mesoporous polymeric materials are good candidates for advanced separation materials, though their low-cost production remains challenging. Here, the authors report a microphase separation technique for the fabrication of nanoporous networks from frozen solutions of common polymers.
- Sadaki Samitsu
- , Rui Zhang
- & Izumi Ichinose
-
Article |
 Formation of nanodiamonds at near-ambient conditions via microplasma dissociation of ethanol vapour
Formation of nanodiamonds at near-ambient conditions via microplasma dissociation of ethanol vapour
Nanodiamonds are small clusters of carbon that are of use in various nanotechnology applications such as spintronics, but are difficult to synthesize. Here Kumar et al. achieve the fabrication of nanodiamonds 2–5 nm in size at near-ambient conditions by a microplasma process.
- Ajay Kumar
- , Pin Ann Lin
- & R. Mohan Sankaran
-
Article |
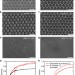 Three-dimensional self-assembled photonic crystals with high temperature stability for thermal emission modification
Three-dimensional self-assembled photonic crystals with high temperature stability for thermal emission modification
Photonic crystal structures can be used to control the spectral distribution of thermal emission. Here, Arpin et al. demonstrate three-dimensional tungsten and hafnium diboride photonic crystals to control high-temperature thermal emission for solar thermophotovoltaic energy devices.
- Kevin A. Arpin
- , Mark D. Losego
- & Paul V. Braun
-
Article |
 Dispersant-free conducting pastes for flexible and printed nanocarbon electrodes
Dispersant-free conducting pastes for flexible and printed nanocarbon electrodes
The realization of highly conductive, dispersant-free pastes based on nanocarbon materials has been hindered by agglomeration of particles. Han et al. demonstrate conducting pastes that do not agglomerate due to quadruple hydrogen-bonding motifs among the nanocarbon particles.
- Joong Tark Han
- , Bo Hwa Jeong
- & Geon-Woong Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Growth of carbon nanotubes via twisted graphene nanoribbons
Growth of carbon nanotubes via twisted graphene nanoribbons
Carbon nanotubes can be considered as rolled-up small sheets of graphene. Here Lim and colleagues demonstrate this process, by fabricating carbon nanotubes through a thermally induced process of self-intertwining of graphene nanoribbons.
- Hong En Lim
- , Yasumitsu Miyata
- & Hisanori Shinohara
-
Article
| Open Access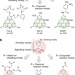 A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
A platform for designing hyperpolarized magnetic resonance chemical probes
Hyperpolarization of chemical nuclei is known to greatly increase sensitivity to characterization by magnetic resonance imaging. Here a new platform that allows for the design of a number of hyperpolarized probes for chemical sensing applications is demonstrated.
- Hiroshi Nonaka
- , Ryunosuke Hata
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article |
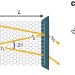 Ballistic interferences in suspended graphene
Ballistic interferences in suspended graphene
Exploiting the optics-like dynamics of low-energy electronic excitations in graphene requires the challenging combination of ballistic transport and complex gating. Here the fabrication and characterization of suspended graphene p–njunctions is reported, paving the way for future electron optics experiments.
- Peter Rickhaus
- , Romain Maurand
- & Christian Schönenberger
-
Article |
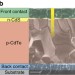 Doping of polycrystalline CdTe for high-efficiency solar cells on flexible metal foil
Doping of polycrystalline CdTe for high-efficiency solar cells on flexible metal foil
Flexible CdTe solar cells on metal foil substrates are promising for low-cost roll-to-roll fabrication, but their efficiency is usually low because of their inverted structure. By controlling the doping of the CdTe layer with copper, Kranz et al. show that efficiencies up to 13.6% can be obtained.
- Lukas Kranz
- , Christina Gretener
- & Ayodhya N. Tiwari
-
Article |
 Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Disk-cylinder and disk-sphere nanoparticles via a block copolymer blend solution construction
Compositionally and geometrically complex nano-objects are an important goal in medicinal, photonic and electronic materials research. Here, the authors fabricate disk-sphere and disk-cylinder nanoparticles with defined multicompartments from binary mixtures of block copolymers.
- Jiahua Zhu
- , Shiyi Zhang
- & Darrin J. Pochan
-
Article
| Open Access Mouldable all-carbon integrated circuits
Mouldable all-carbon integrated circuits
The incorporation of electronic circuits into various plastic products and devices is limited by the brittle nature of silicon wafers. Here, Sun et al.demonstrate flexible and high-performance all-carbon-based transistor circuits that can be thermo-moulded into various shapes.
- Dong-Ming Sun
- , Marina Y. Timmermans
- & Yutaka Ohno
-
Article |
 Transparency and damage tolerance of patternable omniphobic lubricated surfaces based on inverse colloidal monolayers
Transparency and damage tolerance of patternable omniphobic lubricated surfaces based on inverse colloidal monolayers
It is challenging to design transparent, water-repellent and mechanical robust coatings for a broad range of technological applications. Vogel et al. develop a lubricant-infused surface coating, which satisfies all these requirements and is compatible with conventional patterning processes.
- Nicolas Vogel
- , Rebecca A. Belisle
- & Joanna Aizenberg
-
Article |
 Silicon-in-silica spheres via axial thermal gradient in-fibre capillary instabilities
Silicon-in-silica spheres via axial thermal gradient in-fibre capillary instabilities
Silicon nanospheres could be of interest for applications in electronics and optoelectronics. Here, Gumenniket al. demonstrate a nanosphere fabrication process based on an optical fibre drawing technique that is able to produce p and n-type spheres paired into rectifying bispherical junctions.
- Alexander Gumennik
- , Lei Wei
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity
Nano-structured smart hydrogels with rapid response and high elasticity
Smart hydrogels are 3D networks composed of cross-linked polymer chains that can alter their shape and properties in response to environmental stimuli. Xiaet al.demonstrate a smart hydrogel with rapid response and high elasticity, due to its nano-scale structure.
- Lie-Wen Xia
- , Rui Xie
- & Liang-Yin Chu
-
Article
| Open Access Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Conducting linear chains of sulphur inside carbon nanotubes
Elemental sulphur is an insulator in the bulk phase, although it may become conducting under ultrahigh-pressure conditions. Here, the authors report a one-dimensional conducting form of sulphur formed by encapsulation inside single-walled and double-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Toshihiko Fujimori
- , Aarón Morelos-Gómez
- & Katsumi Kaneko
-
Article |
 Chemical vapour deposition growth of large single crystals of monolayer and bilayer graphene
Chemical vapour deposition growth of large single crystals of monolayer and bilayer graphene
The growth of high-quality graphene over large areas is essential for the realization of graphene-based electronic devices. Zhou et al.report a new pathway to grow single crystalline graphene of up to 5 mm in size, with very good electronic performance and high uniformity.
- Hailong Zhou
- , Woo Jong Yu
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article |
 Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers
Postsynthetic modulation of the structural properties of hydrogels is desirable for a range of biomaterials applications. Here, the authors fabricate photolatently modulable polymer hydrogels crosslinked by titania nanosheets, which may be micropatterned with high spatial and temporal resolution.
- Mingjie Liu
- , Yasuhiro Ishida
- & Takuzo Aida
-
Article |
 Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Layer-by-layer assembly of vertically conducting graphene devices
Vertically assembled graphene devices have received less attention than the typical two dimensional arrangements. Chen et al. show that an Au/graphene/Au assembly exhibits a large magnetoresistance ratio of up to 400%, while a Co/graphene/Co device displays a spin valve effect at room temperature.
- Jing-Jing Chen
- , Jie Meng
- & Da-Peng Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Top–down fabrication of sub-nanometre semiconducting nanoribbons derived from molybdenum disulfide sheets
Top–down fabrication of sub-nanometre semiconducting nanoribbons derived from molybdenum disulfide sheets
Fabricating semiconductor devices with dimensions below 10 nm presents significant challenges. Here, Liu et al. use controlled electron irradiation to remove atoms in an MoS2 sheet, creating Mo5S4nanoribbons with a uniform width of 0.35 nm and a theoretical band gap of 0.77 eV.
- Xiaofei Liu
- , Tao Xu
- & Wanlin Guo
-
Article
| Open Access A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporous Al(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels
Hierarchically porous metal-organic monoliths are potential materials for mass transfer applications. Here, the authors synthesize metal-organic aerogels via the gelation of metal-organic frameworks, and are able to tune their porosity exploiting the properties of both crystalline and aerogel materials.
- Lei Li
- , Shenglin Xiang
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article |
 Shaping colloids for self-assembly
Shaping colloids for self-assembly
Creating new materials requires novel approaches to design and synthesize small building particles. Sacanna et al. develop a versatile synthetic strategy to design and mass-produce colloidal building blocks starting from two different colloids that leads to selectively functionalized surface areas.
- Stefano Sacanna
- , Mark Korpics
- & Gi-Ra Yi
-
Article
| Open Access Design principle for increasing charge mobility of π-conjugated polymers using regularly localized molecular orbitals
Design principle for increasing charge mobility of π-conjugated polymers using regularly localized molecular orbitals
Polymers are good potential processable materials for electronic components; however, their charge mobilities are quite low. Here, the authors show that wrapping polymers with macrocycles and localization of π-orbitals realizes an ideal orbital alignment for charge hopping with subsequently increased mobility.
- Jun Terao
- , Akihisa Wadahama
- & Yasushi Tsuji
-
Article |
 Stepwise self-assembly of C60 mediated by atomic scale moiré magnifiers
Stepwise self-assembly of C60 mediated by atomic scale moiré magnifiers
A promising route towards molecular devices is the self-assembly of atoms or molecules on a surface. Here, Gruznev et al. show that the synthesis of unique geometries of C60molecules on gold–indium-covered crystalline silicon is governed by moiré interference.
- D.V. Gruznev
- , A.V. Matetskiy
- & Y.L. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors
In vivo recordings of brain activity using organic transistors
Flexible organic electronic devices have the potential to serve as biosensors in living animals. Khodagholy et al. show that organic transistors can be used to record brain activity in rats and demonstrate that they have a superior signal-to-noise ratio compared with electrodes due to local signal amplification.
- Dion Khodagholy
- , Thomas Doublet
- & George G. Malliaras
-
Article |
 A low-temperature method to produce highly reduced graphene oxide
A low-temperature method to produce highly reduced graphene oxide
The chemical reduction of graphene oxide can provide large quantities of reduced graphene oxide for potential application in electronics and composite materials. Feng et al. report a highly efficient low-temperature one-pot reduction of graphene oxide that uses sodium-ammonia solution as the reducing agent.
- Hongbin Feng
- , Rui Cheng
- & Jinghong Li
-
Article |
 A synthetic nanomaterial for virus recognition produced by surface imprinting
A synthetic nanomaterial for virus recognition produced by surface imprinting
The recognition of viruses by synthetic materials is historically difficult. Here, a templating procedure using silica nanoparticles coated with organosilanes is used to form virus-imprinted particles, possessing both shape and chemical imprints, capable of virus recognition at picomolar concentrations.
- Alessandro Cumbo
- , Bernard Lorber
- & Patrick Shahgaldian
-
Article |
 Scalable fabrication of high-power graphene micro-supercapacitors for flexible and on-chip energy storage
Scalable fabrication of high-power graphene micro-supercapacitors for flexible and on-chip energy storage
Microscale supercapacitors are promising alternative energy-storage devices; however, their use has been limited by the need for complicated fabrication techniques. This work reports the scalable fabrication of graphene supercapacitors with planar geometry that achieve power densities of up to 200 W cm−3.
- Maher F. El-Kady
- & Richard B. Kaner
-
Article |
 Engineering the architectural diversity of heterogeneous metallic nanocrystals
Engineering the architectural diversity of heterogeneous metallic nanocrystals
Engineering heterogeneous metallic nanocrystals could produce diverse materials with tunable properties. Here the authors develop a strategy for the rational and independent programming of each architecture-determining element, such as the shape, size and spatial relationship of the component nanocrystals.
- Yue Yu
- , Qingbo Zhang
- & Jim Yang Lee
-
Article |
 New diluted ferromagnetic semiconductor with Curie temperature up to 180 K and isostructural to the ‘122’ iron-based superconductors
New diluted ferromagnetic semiconductor with Curie temperature up to 180 K and isostructural to the ‘122’ iron-based superconductors
Diluted magnetic semiconductors are promising spintronic materials, however the simultaneous doping of charge and magnetic moment has prevented synthesis of bulk samples. This work reports the synthesis of a bulk magnetic semiconductor (Ba1−xKx)(Zn1−yMny)2As2with Curie temperatures up to 180 K.
- K. Zhao
- , Z. Deng
- & C. Q. Jin
-
Article |
 Solution-phase epitaxial growth of noble metal nanostructures on dispersible single-layer molybdenum disulfide nanosheets
Solution-phase epitaxial growth of noble metal nanostructures on dispersible single-layer molybdenum disulfide nanosheets
The ‘wet’ chemical epitaxial growth of nanostructures on semiconducting surfaces is usually hindered by surface defects. Here, the authors show that large surface area single-layer molybdenum disulphide is an ideal substrate for epitaxial growth of a range of metallic nanoparticles.
- Xiao Huang
- , Zhiyuan Zeng
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 The essential role of carefully optimized synthesis for elucidating intrinsic material properties of (Ga,Mn)As
The essential role of carefully optimized synthesis for elucidating intrinsic material properties of (Ga,Mn)As
The electronic band structure of (Ga,Mn)As has been debated due to contrasting reports of experimental findings from samples differently synthesized. Nĕmec et al.show that a careful optimization of the synthesis protocol is necessary to evaluate the intrinsic semiconducting and magnetic properties of (Ga,Mn)As.
- P. Nĕmec
- , V. Novák
- & T. Jungwirth
-
Article |
 Holographic detection of the orbital angular momentum of light with plasmonic photodiodes
Holographic detection of the orbital angular momentum of light with plasmonic photodiodes
Sub-wavelength structures can be used to convert between light and plasmon polaritons. Genevetet al. design holographic plasmonic interfaces that couple vortex light beams to surface plasmons, allowing them to detect the orbital angular momentum of the beam with a simple silicon photodiode.
- Patrice Genevet
- , Jiao Lin
- & Federico Capasso
-
Review Article |
 Moving from static to dynamic complexity in hydrogel design
Moving from static to dynamic complexity in hydrogel design
Hydrogels are water-containing polymer networks that have been applied in various biological settings. Burdick and Murphy review recent advances in the development of dynamic hydrogels whose properties and mechanics change in response to biological signals.
- Jason A. Burdick
- & William L. Murphy
-
Article |
 A general method for the large-scale synthesis of uniform ultrathin metal sulphide nanocrystals
A general method for the large-scale synthesis of uniform ultrathin metal sulphide nanocrystals
Ultrathin metal sulphides are attractive components for electronic and optical devices and are promising anode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Here, a universal, soft colloidal templating strategy is employed for the large-scale synthesis of uniform, ultrathin metal sulphide nanomaterials.
- Yaping Du
- , Zongyou Yin
- & Hua Zhang
-
Article |
 Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers
Fabrication of flexible and freestanding zinc chalcogenide single layers
Ultrathin inorganic materials hold promise for a variety of applications, including flexible electronics. This work presents a fabrication method that permits the synthesis of large and flexible freestanding layers of zinc selenide that display a high-photocurrent density.
- Yongfu Sun
- , Zhihu Sun
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Organic transistors with high thermal stability for medical applications
Organic transistors with high thermal stability for medical applications
Organic electronic devices are promising for many applications, particularly in biomedical research, but are hindered by thermal instability and low melting points. Now, organic thin-film transistors are shown with excellent thermal properties that can withstand medical sterilization processes.
- Kazunori Kuribara
- , He Wang
- & Takao Someya
-
Article |
 Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Ionic polypeptides with unusual helical stability
Water-soluble peptides with stable α-helical conformations are desirable for a range of applications, but incorporating charged residues to improve solubility usually leads to reduced helical stability. Here, polypeptides produced from amino acids with elongated charged side chains are found to be water soluble and exhibit very high helical stability.
- Hua Lu
- , Jing Wang
- & Jianjun Cheng

 Molecular actuators driven by cooperative spin-state switching
Molecular actuators driven by cooperative spin-state switching