Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Scalable anisotropic cooling aerogels by additive freeze-casting
Scalable anisotropic cooling aerogels by additive freeze-casting
Scaling up anisotropic freeze-casting processes can be challenging due to the temperature gradient farther from the cold source. Here, authors report an additive freeze-casting technique able to produce large-scale aerogel panels and demonstrate it towards practical passive cooling applications.
- Kit-Ying Chan
- , Xi Shen
- & Jang-Kyo Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Self-shrinking soft demoulding for complex high-aspect-ratio microchannels
Self-shrinking soft demoulding for complex high-aspect-ratio microchannels
Microchannels are the essential elements for the design of artificial devices but the fabrication of three dimensional (3D) microchannels with complex geometry and a high aspect ratio remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a simple and solvent-free fabrication method capable of producing monolithic microchannels with complex 3D structures, long length, and small diameter.
- Dongliang Fan
- , Xi Yuan
- & Peiwu Qin
-
Article
| Open Access Replicative manufacturing of metal moulds for low surface roughness polymer replication
Replicative manufacturing of metal moulds for low surface roughness polymer replication
Production of tools for polymer replication in the field of optical applications is still time-consuming and cost-intensive. Here the authors develop an efficient metal casting process, and demonstrate manufacturing of structures of complex shapes with a surface roughness of few nanometres.
- Sebastian Kluck
- , Leonhard Hambitzer
- & Bastian E. Rapp
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-compact MXene fibers by continuous and controllable synergy of interfacial interactions and thermal drawing-induced stresses
Ultra-compact MXene fibers by continuous and controllable synergy of interfacial interactions and thermal drawing-induced stresses
Forming compact layered nanostructures is key to achieving continuous MXene fibers with electrical and mechanical properties. Here, authors demonstrate ultra-compact high-performance MXene fibers via a controllable synergy of interfacial interactions and thermal drawing-induced stresses.
- Tianzhu Zhou
- , Yangzhe Yu
- & Lei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodynamics-guided alloy and process design for additive manufacturing
Thermodynamics-guided alloy and process design for additive manufacturing
Production defects prevent many industrially important materials from being adopted by metal additive manufacturing. Here, the authors propose a universal thermodynamics-guided alloy design approach to assist the discovery of crack-free materials.
- Zhongji Sun
- , Yan Ma
- & Dierk Raabe
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of triboelectric polymer films via repeated rheological forging for ultrahigh surface charge density
Fabrication of triboelectric polymer films via repeated rheological forging for ultrahigh surface charge density
High charge density is the foundation to promote a wide range of applications of triboelectric nanogenerators. Here, authors propose a processing method based on the repeated rheological forging of triboelectric polymers achieving an enhanced triboelectricity and further study its mechanism.
- Zhaoqi Liu
- , Yunzhi Huang
- & Jin-Ping Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Cation-selective two-dimensional polyimine membranes for high-performance osmotic energy conversion
Cation-selective two-dimensional polyimine membranes for high-performance osmotic energy conversion
Two-dimensional (2D) membranes are emerging candidates for osmotic energy conversion but the trade-off between ion selectivity and conductivity remains the key bottleneck. Here, the authors demonstrate a fully crystalline imine-based 2D polymer membrane capable of combining excellent ionic conductivity and high selectivity for osmotic energy conversion.
- Zhen Zhang
- , Preeti Bhauriyal
- & Xinliang Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Multi-scale computer-aided design and photo-controlled macromolecular synthesis boosting uranium harvesting from seawater
Multi-scale computer-aided design and photo-controlled macromolecular synthesis boosting uranium harvesting from seawater
Developing materials for uranium harvesting from seawater with high adsorption capacity remains challenging. Here, the authors develop a new protocol, by combining multi-scale computational simulations with the PET-RAFT polymerization, for rational design and precise synthesis of block copolymers with optimal architectures and atomic economy, achieving a capacity of 11.4 mg/g within 28 days.
- Zeyu Liu
- , Youshi Lan
- & Gang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access Photo-thermo-induced room-temperature phosphorescence through solid-state molecular motion
Photo-thermo-induced room-temperature phosphorescence through solid-state molecular motion
The development of non-invasive, rapid responsive phosphorescence is highly desirable but has rarely been described. Herein, the authors designed and prepare a series of molecular rotors containing a room temperature phosphorescence active triazine core and three bromobiphenyl units acting as rotors and demonstrate light stimulus triggered phosphorescence.
- Xing Wang Liu
- , Weijun Zhao
- & Ben Zhong Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Solvent-driven fractional crystallization for atom-efficient separation of metal salts from permanent magnet leachates
Solvent-driven fractional crystallization for atom-efficient separation of metal salts from permanent magnet leachates
Rare earth elements are essential to electrified infrastructure and clean energy production. Here, authors show reagent- and energy-efficient separation of lanthanides from secondary feedstock using dimethyl ether-driven fractional crystallization.
- Caleb Stetson
- , Denis Prodius
- & Aaron D. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Sustainable wood electronics by iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization for large-scale applications
Sustainable wood electronics by iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization for large-scale applications
Ecologically friendly wood electronics will help alleviating the shortcomings of state-of-art cellulose-based green electronics. Here, the authors introduce iron-catalyzed laser-induced graphitization (IC-LIG) as an innovative approach for engraving large-scale electrically conductive structures on wood with high quality and efficiency.
- Christopher H. Dreimol
- , Huizhang Guo
- & Guido Panzarasa
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupled temperature and pressure hydrothermal synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres from cellulose
Decoupled temperature and pressure hydrothermal synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres from cellulose
Temperature and pressure are typically dependent parameters in hydrothermal processes. Here, authors devise a hydrothermal system that allows independent control of these parameters and realize low-temperature fast synthesis of carbon sub-micron spheres directly from cellulose at higher pressure.
- Shijie Yu
- , Xinyue Dong
- & Hui Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of the grain arrangements on the thermal stability of polycrystalline nickel-rich lithium-based battery cathodes
Effect of the grain arrangements on the thermal stability of polycrystalline nickel-rich lithium-based battery cathodes
Enhancing the stability of positive electrodes at thermally-abused conditions is vital for next-generation lithium-based batteries. Here, the authors report in situ physicochemical characterizations to improve the fundamental understanding of the degradation mechanism in polycrystalline Ni-rich cathodes.
- Dong Hou
- , Zhengrui Xu
- & Feng Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Tailoring electron beams with high-frequency self-assembled magnetic charged particle micro optics
Electron beam manipulation is important for their application in microscopes, lithography instruments, and colliders. Here the authors report a wafer scale, self-assembled, microcoil electrically-driven magnetic charge particle optic device that can be implemented into different configurations for controlling of electron beams.
- R. Huber
- , F. Kern
- & A. Lubk
-
Comment
| Open Access Computer modeling reveals modalities to actuate mutable, active matter
Computer modeling reveals modalities to actuate mutable, active matter
Catalytic reactions on flexible sheets generate fluid flows that transform the shape of the sheet, which in turn modifies the flow. These complex interactions make computer models vital for designing and harnessing these feedback loops to create soft active matter that autonomously performs self-sustained mechanical work.
- Abhrajit Laskar
- , Raj Kumar Manna
- & Anna C. Balazs
-
Article
| Open Access Twisted oxide lateral homostructures with conjunction tunability
Twisted oxide lateral homostructures with conjunction tunability
It is challenging to construct lateral homostructures with controllable geometry and repeated alternating configurations. Here the authors develop a generic approach for fabricating twisted lateral homostructures with tunable crystal orientation, epitaxial constrain, and phase stability.
- Ping-Chun Wu
- , Chia-Chun Wei
- & Jan-Chi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Well-defined nanostructuring with designable anodic aluminum oxide template
Well-defined nanostructuring with designable anodic aluminum oxide template
Well-defined nanostructuring is a feasible concept to achieve nanostructured arrays with unique properties. Here the authors report fabrication of designable anodic aluminum oxide templates with controllable in-plane and out-of-plane shapes, sizes, spatial configurations, and pore combinations.
- Rui Xu
- , Zhiqiang Zeng
- & Yong Lei
-
Article
| Open Access Direct sound printing
Direct sound printing
Photo- and thermo-activated polymerization and melting processes are dominant in Additive Manufacturing (AM) while ultrasound activated sonochemical reactions have not been explored for AM so far. Here, the authors demonstrate 3D printing of structures using acoustic cavitation produced directly by focused ultrasound which creates sonochemical reactions in highly localized cavitation regions.
- Mohsen Habibi
- , Shervin Foroughi
- & Muthukumaran Packirisamy
-
Article
| Open Access Wafer-scale epitaxial modulation of quantum dot density
Wafer-scale epitaxial modulation of quantum dot density
Nucleation control of self-assembled quantum dots is challenging. Here, the authors employ conventional molecular beam epitaxy to achieve wafer-scale density modulation of high-quality quantum dots with tunable periodicity on unpatterned substrates.
- N. Bart
- , C. Dangel
- & A. Ludwig
-
Article
| Open Access Topoarchitected polymer networks expand the space of material properties
Topoarchitected polymer networks expand the space of material properties
Synthesizing architected materials with strong adhesion has been challenging. Here the authors fabricate architected polymer networks by sequential polymerization and photolithography, and attain adherent interface by topological entanglement.
- Xiao Liu
- , Jingping Wu
- & Jian Hu
-
Article
| Open Access λ/30 inorganic features achieved by multi-photon 3D lithography
λ/30 inorganic features achieved by multi-photon 3D lithography
Stereolithography has progressed over the years but resolution and feature size is still limited by the properties of materials and resins. Here, the authors demonstrate femtosecond laser direct writing of a hydrogen silsesquioxane photoresist using a 780 nm femtosecond laser demonstrating feature sizes of 26 nm.
- Feng Jin
- , Jie Liu
- & Xuan-Ming Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient Kerr soliton comb generation in micro-resonator with interferometric back-coupling
Efficient Kerr soliton comb generation in micro-resonator with interferometric back-coupling
Increasing the conversion efficiency of soliton crystals will enable further application of optical frequency comb. Here the authors engineer an hybrid Mach-Zehnder micro-ring resonator to achieve 80% pump-to-comb conversion efficiency based on dissipative Kerr solitons.
- J. M. Chavez Boggio
- , D. Bodenmüller
- & T. Hansson
-
Article
| Open Access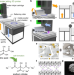 A general fruit acid chelation route for eco-friendly and ambient 3D printing of metals
A general fruit acid chelation route for eco-friendly and ambient 3D printing of metals
Additive manufacturing of metals has revolutionized production and personalization of commodities. Here, authors demonstrate its feasibility of becoming a green technology, by developing an eco-friendly fruit-acid-based chelation approach.
- Soo Young Cho
- , Dong Hae Ho
- & Jeong Ho Cho
-
Article
| Open Access A self-driving laboratory advances the Pareto front for material properties
A self-driving laboratory advances the Pareto front for material properties
Useful materials must satisfy multiple objectives. The Pareto front expresses the trade-offs of competing objectives. This work uses a self-driving laboratory to map out the Pareto front for making highly conductive coatings at low temperatures.
- Benjamin P. MacLeod
- , Fraser G. L. Parlane
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ transfer vat photopolymerization for transparent microfluidic device fabrication
In-situ transfer vat photopolymerization for transparent microfluidic device fabrication
Despite many advantages of vat photopolymerization in microfluidic device fabrication, well-controlled μm-sized (< 100 μm) channels in the layer building direction remains a challenge. Here, authors present a general high resolution and low-cost 3D printing process that can produce devices within the 10 μm scale.
- Yang Xu
- , Fangjie Qi
- & Yong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid digital light 3D printing enabled by a soft and deformable hydrogel separation interface
Rapid digital light 3D printing enabled by a soft and deformable hydrogel separation interface
The commercial application of 3D printing is limited by time constraints and current efforts to speed the process are economically inefficient. Here the authors report on the use of a green and inexpensive hydrogel to separate the interface and cured components in common stereolithographic processes to allow for rapid printing.
- Jingjun Wu
- , Jing Guo
- & Qian Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-coherent nanomechanical resonators based on inverse design
Ultra-coherent nanomechanical resonators based on inverse design
Nanomechanical resonators can be improved through rational design. Using an inverse design approach the authors achieve ultra-coherent resonators and pave the way towards the engineering of high performance micro- and nanomechanical resonators.
- Dennis Høj
- , Fengwen Wang
- & Ulrik Lund Andersen
-
Article
| Open Access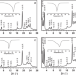 Tempering of cocoa butter and chocolate using minor lipidic components
Tempering of cocoa butter and chocolate using minor lipidic components
In chocolate production, a complicated tempering process is used to guide the crystallization of cocoa butter towards its most desirable polymorph, which gives the chocolate proper melting behavior, gloss, and snap—hallmarks of good quality chocolate. Here, the authors find that simply adding a specific phospholipid also directs crystallization towards this polymorph, producing chocolate with comparable microstructure and properties to tempered chocolate.
- Jay Chen
- , Saeed M. Ghazani
- & Alejandro G. Marangoni
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
The limited strength of green parts have been a major hurdle in the Binder Jet Additive Manufacturing. Here the authors apply polyethyleneimine binder to print silica sand structures with double the flexural strength of green parts and 8-fold increase in the strength upon reactive infiltration.
- Dustin B. Gilmer
- , Lu Han
- & Tomonori Saito
-
Article
| Open Access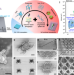 3D electron-beam writing at sub-15 nm resolution using spider silk as a resist
3D electron-beam writing at sub-15 nm resolution using spider silk as a resist
Electron beam lithography (EBL) is renowned to provide fabrication resolution in the deep nanometer scale but their incapability of arbitrary 3D nanofabrication poses a major limitation to the technique. Here, the authors demonstrate a manufacturing technique of functional 3d nanostructures at a resolution of sub-15 nm using voltage-regulated 3d EBL.
- Nan Qin
- , Zhi-Gang Qian
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access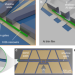 Shadow-wall lithography of ballistic superconductor–semiconductor quantum devices
Shadow-wall lithography of ballistic superconductor–semiconductor quantum devices
Advanced fabrication techniques enable a wide range of quantum devices, such as the realization of a topological qubit. Here, the authors introduce an on-chip fabrication technique based on shadow walls to implement topological qubits in an InSb nanowire without fabrication steps such as lithography and etching.
- Sebastian Heedt
- , Marina Quintero-Pérez
- & Leo P. Kouwenhoven
-
Article
| Open Access Photopatterned microswimmers with programmable motion without external stimuli
Photopatterned microswimmers with programmable motion without external stimuli
Maragoni microswimmers show the advantage of self-propulsion but their development is limited by fabrication techniques. Here, the authors use a photopatterning method which allows for a high throughput production of maragoni microswimmers with multiple functional parts and distinct materials properties.
- Yeongjae Choi
- , Cheolheon Park
- & Wook Park
-
Article
| Open Access Large-area patterning of full-color quantum dot arrays beyond 1000 pixels per inch by selective electrophoretic deposition
Large-area patterning of full-color quantum dot arrays beyond 1000 pixels per inch by selective electrophoretic deposition
Colloidal quantum dots are promising for next-generation displays, yet the technology to realise high-resolution and uniform patterning is still scarce. Here, the authors report full-colour QD large area patterning by combining photolithography and selective electrophoretic deposition technique.
- Jinyang Zhao
- , Lixuan Chen
- & Xiao Wei Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Six-photon upconverted excitation energy lock-in for ultraviolet-C enhancement
Six-photon upconverted excitation energy lock-in for ultraviolet-C enhancement
Photon upconversion with near-infrared excitation and ultraviolet emission has many applications, but suffers from low quantum efficiency. Here, the authors report a six-photon upconversion process in nanoparticles with heterogeneous core-multishell structure, that regulate the energy transfer pathway.
- Qianqian Su
- , Han-Lin Wei
- & Dayong Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Large-area synthesis of nanoscopic catalyst-decorated conductive MOF film using microfluidic-based solution shearing
Large-area synthesis of nanoscopic catalyst-decorated conductive MOF film using microfluidic-based solution shearing
The immobilization of catalysts within the pores of conductive metal-organic frameworks (C-MOFs) via facile and scalable methodologies remains challenging. Here the authors report a microfluidic channel-embedded solution shearing process that enables the high throughput, large-area, single-step preparation of Pt nanocatalyst-embedded C-MOF thin films.
- Jin-Oh Kim
- , Won-Tae Koo
- & Steve Park
-
Article
| Open Access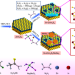 Interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution
Interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution
The construction of Z-scheme heterostructures is of great significance for realizing efficient photocatalytic water splitting. Here, the authors report an interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-Scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution.
- Xuehua Wang
- , Xianghu Wang
- & Zhenjiang Li
-
Article
| Open Access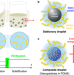 Static-state particle fabrication via rapid vitrification of a thixotropic medium
Static-state particle fabrication via rapid vitrification of a thixotropic medium
Upscale fabrication of functionalized microparticles is a pending challenge. Here, Kim et al. exploit the rheology of a thixotropic medium to grind sizeable amounts of raw material into well-defined colloidal dispersions, physically stabilized for further production steps.
- Sang Yup Kim
- , Shanliangzi Liu
- & Rebecca Kramer-Bottiglio
-
Article
| Open Access Digital electronics in fibres enable fabric-based machine-learning inference
Digital electronics in fibres enable fabric-based machine-learning inference
Implementation of digital electronics into fibres can enable real time monitoring of human physiological functions. Loke et al. show how digital functionalities can be incorporated into thin flexible polymeric fibre strands and applied for on-body machine-learning and intelligent textiles.
- Gabriel Loke
- , Tural Khudiyev
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article
| Open Access Versatile non-luminescent color palette based on guest exchange dynamics in paramagnetic cavitands
Versatile non-luminescent color palette based on guest exchange dynamics in paramagnetic cavitands
Host-guest supramolecular chemistry can be used as a tool to develop multicolor displays. Here, the authors present a system based on lanthanide-cradled cyclodextrins that allows to construct MRI-readable and erasable artificial non-luminescent color palettes.
- Elad Goren
- , Liat Avram
- & Amnon Bar-Shir
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-printed self-healing hydrogels via Digital Light Processing
3D-printed self-healing hydrogels via Digital Light Processing
Self-healing hydrogels can mimic the damage repair behaviour of living tissues, but such hydrogels have only been processed via extrusion-based additive manufacturing technology. Here, the authors demonstrate a rapidly self-healing hydrogel which can be processed by DLP printing.
- Matteo Caprioli
- , Ignazio Roppolo
- & Shlomo Magdassi
-
Article
| Open Access Sea urchin-like microstructure pressure sensors with an ultra-broad range and high sensitivity
Sea urchin-like microstructure pressure sensors with an ultra-broad range and high sensitivity
Pressure sensors with high sensitivity and large pressure range is crucial to their various applications in electronic engineering. Here, Wang et al. propose a new design based on a ternary nanocomposite material and show high pressure sensitivity of 680 kPa−1 and fast response of 10 ms up to 150 kPa.
- Xiu-man Wang
- , Lu-qi Tao
- & ChingPing Wong
-
Article
| Open Access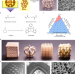 3D printing of inherently nanoporous polymers via polymerization-induced phase separation
3D printing of inherently nanoporous polymers via polymerization-induced phase separation
3D printing offers flexibility in fabrication of polymer objects but fabrication of large polymer structures with micrometer-sized geometrical features are challenging. Here, the authors introduce a method combining advantages of 3D printing and polymerization-induced phase separation, which enables formation of 3D polymer structures with controllable inherent porosity.
- Zheqin Dong
- , Haijun Cui
- & Pavel A. Levkin
-
Article
| Open Access Laser photonic-reduction stamping for graphene-based micro-supercapacitors ultrafast fabrication
Laser photonic-reduction stamping for graphene-based micro-supercapacitors ultrafast fabrication
Microfabrication for cost-effective miniaturized energy storage devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a spatially shaped femtosecond laser method, which is ultrafast, one-step, high resolution and large-scale, for use in patterning flexible high-performance micro-supercapacitors.
- Yongjiu Yuan
- , Lan Jiang
- & Tianhong Cui
-
Article
| Open Access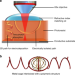 Mechanically interlocked 3D multi-material micromachines
Mechanically interlocked 3D multi-material micromachines
Mechanically interlocking dissimilar materials, such as metals and polymers, is a challenging yet promising pathway for designing and fabricating complex systems on the small scale. Here, the authors report a novel interlocking fabrication scheme and showcase the fabrication of microrobots via 3D-lithography.
- C. C. J. Alcântara
- , F. C. Landers
- & S. Pané
-
Article
| Open Access 3D-printed integrative probeheads for magnetic resonance
3D-printed integrative probeheads for magnetic resonance
Here, the authors combine 3D printing and liquid metal filling techniques to fabricate customised probeheads for magnetic resonance experiments. They demonstrate in situ electrochemical nuclear magnetic resonance analysis, reaction monitoring with continues-flow separation and small-sample imaging.
- Junyao Xie
- , Xueqiu You
- & Zhong Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural and electronic switching of a single crystal 2D metal-organic framework prepared by chemical vapor deposition
Structural and electronic switching of a single crystal 2D metal-organic framework prepared by chemical vapor deposition
The realization of advanced devices from metal-organic frameworks requires the preparation of uniform and crystalline thin-films of these materials. Here the authors use chemical vapor deposition to grow single-crystal frameworks that exhibit a reversible structural transition and large conductivity response.
- F. James Claire
- , Marina A. Solomos
- & Thomas J. Kempa
-
Article
| Open Access A universal method for depositing patterned materials in situ
A universal method for depositing patterned materials in situ
Complexity and harsh working conditions pose limitations for fabrication of patterned materials. Here the authors report a single-step method for in situ deposition of materials that is based on semiconductor nanoparticle assisted photon-induced chemical reduction and optical trapping.
- Yifan Chen
- , Siu Fai Hung
- & Sen Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Metal 3D printing technology for functional integration of catalytic system
Metal 3D printing technology for functional integration of catalytic system
Metal 3D printing is a very promising technology to revolutionize catalytic systems. Here the authors show that metal 3D printing products themselves can simultaneously serve as chemical reactors and catalysts for conversion of C1 molecules into high value-added chemicals.
- Qinhong Wei
- , Hangjie Li
- & Noritatsu Tsubaki
-
Article
| Open Access Designer patterned functional fibers via direct imprinting in thermal drawing
Designer patterned functional fibers via direct imprinting in thermal drawing
Creating micro/nanostructures on fibers is beneficial to many fiber-based devices, which remains a challenge in large-scale fabrication due to elongation and reflow. Here, the authors demonstrate a method for generating high-resolution, arbitrarily designed surface patterns on fiber during the thermal drawing process.
- Zhe Wang
- , Tingting Wu
- & Lei Wei

 Digitally-enhanced lubricant evaluation scheme for hot stamping applications
Digitally-enhanced lubricant evaluation scheme for hot stamping applications