Featured
-
-
Article |
 Biomimetic block copolymer particles with gated nanopores and ultrahigh protein sorption capacity
Biomimetic block copolymer particles with gated nanopores and ultrahigh protein sorption capacity
Porous particles can be capable of selectivity encapsulating various guests. Here, the authors report a strategy to make block copolymer microparticles with pH-responsive pores, study and rationalize their assembly process and furthermore demonstrate separation of differently charged proteins.
- Haizhou Yu
- , Xiaoyan Qiu
- & Klaus-Viktor Peinemann
-
Article |
 Using nanoscale and mesoscale anisotropy to engineer the optical response of three-dimensional plasmonic metamaterials
Using nanoscale and mesoscale anisotropy to engineer the optical response of three-dimensional plasmonic metamaterials
The geometry of periodic plasmonic nanostructures in three dimensions can be exploited to give tailored optical properties. Here, the authors study the role of anisotropy on the nano- and mesoscale to provide a framework for designing the optical response of metamaterials formed from plasmonic building blocks.
- Michael B. Ross
- , Martin G. Blaber
- & George C. Schatz
-
Article
| Open Access Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Encapsulation kinetics and dynamics of carbon monoxide in clathrate hydrate
Carbon monoxide clathrate hydrate has been widely studied and although the structure-II gas hydrate is predicted to be thermodynamically favourable, it is the structure-I hydrate that has been observed. Here, the authors synthesize the structure-II carbon monoxide hydrate and probe its structure and formation.
- Jinlong Zhu
- , Shiyu Du
- & Yusheng Zhao
-
Article |
 Graphitic nanostripes in silicon carbide surfaces created by swift heavy ion irradiation
Graphitic nanostripes in silicon carbide surfaces created by swift heavy ion irradiation
Defects alter the properties of silicon carbide structures, but the introduction of these defects in a controlled manner remains a challenge. Here, the authors show that swift heavy ions can create graphitic grooves if the irradiation is at grazing angles of incidence.
- Oliver Ochedowski
- , Orkhan Osmani
- & Marika Schleberger
-
Article
| Open Access All-printable band-edge modulated ZnO nanowire photodetectors with ultra-high detectivity
All-printable band-edge modulated ZnO nanowire photodetectors with ultra-high detectivity
Nanowire photodetectors offer a high sensitivity arising from their geometry that makes them of interest for optoelectronic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate the printable fabrication of ZnO nanowires with high detectivity, making them suitable for high-performance flexible electronics applications.
- Xi Liu
- , Leilei Gu
- & Zhiyong Fan
-
Article |
 Design amphiphilic dipolar π-systems for stimuli-responsive luminescent materials using metastable states
Design amphiphilic dipolar π-systems for stimuli-responsive luminescent materials using metastable states
Some π-conjugated molecules exhibit tunable luminescence—a property that is useful for the next generation of optical devices. Yagai et al. propose a strategy to design these materials on a molecular level, which tailors the emission colour via structural changes in response to mechanical stimuli.
- Shiki Yagai
- , Satoru Okamura
- & Hajime Ito
-
Article |
 Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction
Magnetocaloric effects in a freestanding and flexible graphene-based superlattice synthesized with a spatially confined reaction
Superlattices are made of alternating thin-film layers and offer a broader range of properties than natural materials. Here, the authors present a method for fabricating free-standing graphene–vanadium oxide superlattices, which could be used in smart windows or as temperature sensors.
- Haiou Zhu
- , Chong Xiao
- & Yi Xie
-
Article |
 Rapid fabrication of hierarchically structured supramolecular nanocomposite thin films in one minute
Rapid fabrication of hierarchically structured supramolecular nanocomposite thin films in one minute
There is significant research into fabrication methods for the rapid, scalable preparation of composite nanomaterials. Here, the authors probe the assembly of supramolecular nanocomposites in thin films and are able to optimize parameters to produce hierarchically structured thin films in one minute.
- Joseph Kao
- , Kari Thorkelsson
- & Ting Xu
-
Article |
 Maximizing omnidirectional light harvesting in metal oxide hyperbranched array architectures
Maximizing omnidirectional light harvesting in metal oxide hyperbranched array architectures
The development of structured electrode architectures is one of the strategies for improving photovoltaic performance. Here, the authors report hierarchical hyperbranced titania materials, composed of nanowires and nanosheets, linked by nanorods, and assess their solar energy conversion efficiency.
- Wu-Qiang Wu
- , Hao-Lin Feng
- & Cheng-Yong Su
-
Article |
 Modular assembly of optical nanocircuits
Modular assembly of optical nanocircuits
Lumped circuit elements provide a simple tool to design complex electronic systems; a similar approach has been proposed for nanophotonics. Here, the authors demonstrate the modularized design and assembly of photonic nanocircuits using metal and dielectric nanoparticles as the constituent lumped elements.
- Jinwei Shi
- , Francesco Monticone
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article |
 A design strategy for the hierarchical fabrication of colloidal hybrid mesostructures
A design strategy for the hierarchical fabrication of colloidal hybrid mesostructures
Achieving a high degree of control over the self-assembly process is a challenging task, but one that can give access to precisely defined structures. Here, the authors show the generation of hybrid materials with controlled morphology and hierarchy based on the assembly of block copolymers on silica cores.
- Lin Jia
- , Guangyao Zhao
- & Mitchell A. Winnik
-
Article
| Open Access Fabrication of crystals from single metal atoms
Fabrication of crystals from single metal atoms
Metal nanocrystals are used in an ever growing list of applications, but precise control and understanding of their formation can be difficult. Here, the authors show a route that allows the controlled formation of metal nanocrystals to be carried out and observed at an atom-by-atom level.
- Nicolas P. E. Barry
- , Anaïs Pitto-Barry
- & Peter J. Sadler
-
Article
| Open Access Electroformation of Janus and patchy capsules
Electroformation of Janus and patchy capsules
Colloidal self-assembly at liquid interfaces has important emulsion applications, for food, household or personal care products, and drug encapsulation. Here, the authors develop a method of forming patchy heterogeneous capsules by electro-coalescence of multiple liquid drops.
- Zbigniew Rozynek
- , Alexander Mikkelsen
- & Jon Otto Fossum
-
Article |
 Rational strategy for shaped nanomaterial synthesis in reverse micelle reactors
Rational strategy for shaped nanomaterial synthesis in reverse micelle reactors
Shape-controlled synthesis of nanoparticles traditionally involves kinetic growth around seed surfaces. Here, the authors are able to fabricate smaller nanoparticles via thermodynamic-driven etching in reverse micelle reactors, yielding monodisperse hollow nanoparticles with concave frameworks and sharp edges.
- Zengyan Wei
- & Hiroshi Matsui
-
Article |
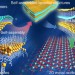 Generalized self-assembly of scalable two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets
Generalized self-assembly of scalable two-dimensional transition metal oxide nanosheets
Two-dimensional metal oxide nanosheets have numerous attractive properties in fields such as photovoltaics and catalysis. Here, the authors show a general approach for the synthesis of these compounds through self-assembly on lamellar reverse micelles.
- Ziqi Sun
- , Ting Liao
- & Shi Xue Dou
-
Article |
 Engineering colloidal quantum dot solids within and beyond the mobility-invariant regime
Engineering colloidal quantum dot solids within and beyond the mobility-invariant regime
Colloidal quantum dots are promising materials for efficient low-cost solar cells and optoelectronics, but their performance does not improve with increased carrier mobility. Here, the authors show instead that the spacing between recombination centres controls the diffusion length.
- David Zhitomirsky
- , Oleksandr Voznyy
- & Edward H. Sargent
-
Article |
 Photochemically colour-tuneable white fluorescence illuminants consisting of conjugated polymer nanospheres
Photochemically colour-tuneable white fluorescence illuminants consisting of conjugated polymer nanospheres
Aromatic conjugated polymers are candidates for optoelectronic applications, but photoswitching of white fluorescence emission has not been realized in these materials. Here, Bu et al.achieve this goal by mixing red, blue and green fluorescent polymer nanospheres in both solutions and films.
- Jingxhou Bu
- , Kazuyoshi Watanabe
- & Kazuo Akagi
-
Article |
 Carbon enters silica forming a cristobalite-type CO2–SiO2 solid solution
Carbon enters silica forming a cristobalite-type CO2–SiO2 solid solution
Novel materials synthesized under extreme conditions can challenge long-held views of fundamental chemistry. Santoro et al. combine fluid CO2 and solid SiO2to create a new crystalline compound, via experimentation at ultra-high pressures and temperatures, which is stable at ambient conditions.
- Mario Santoro
- , Federico A. Gorelli
- & Julien Haines
-
Article |
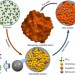 Bottom-up synthesis of high surface area mesoporous crystalline silicon and evaluation of its hydrogen evolution performance
Bottom-up synthesis of high surface area mesoporous crystalline silicon and evaluation of its hydrogen evolution performance
Porous silicon is a technologically important material; however, many top-down etching fabrication processes result in significant material wastage. Here, the authors report a bottom-up self-templating fabrication route and assess the hydrogen evolution performance of the resulting material.
- Fang Dai
- , Jiantao Zai
- & Donghai Wang
-
Article |
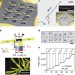 Ultrahigh-speed rotating nanoelectromechanical system devices assembled from nanoscale building blocks
Ultrahigh-speed rotating nanoelectromechanical system devices assembled from nanoscale building blocks
Realising enhanced functionality in nanoelectromechanical systems relies on realising new fabrication and design approaches. Here, the authors report the bottom-up assembly of nanomotors, demonstrating rotation speeds of 18,000 revolutions per minute and continuous rotation for up to 15 h.
- Kwanoh Kim
- , Xiaobin Xu
- & D. L. Fan
-
Article |
 Fabrication and operation of a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a high-voltage microchip
Fabrication and operation of a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a high-voltage microchip
Microfabricated ion traps offer a promising platform for scalable ion quantum computing systems. Sterling et al.realize a two-dimensional ion-trap lattice on a microchip using a new fabrication method that allows very-high voltages to be applied to the chip, enabling very deep ion traps.
- R. C. Sterling
- , H. Rattanasonti
- & W. K. Hensinger
-
Article |
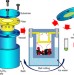 A mechanical-force-driven physical vapour deposition approach to fabricating complex hydride nanostructures
A mechanical-force-driven physical vapour deposition approach to fabricating complex hydride nanostructures
Due to their high reactivity and relatively low thermodynamic stability, direct routes to nanoscale complex hydrides are highly difficult to achieve. Here the authors show a vapour deposition method driven by mechanical force, which allows the formation of complex metal nanorods for hydrogen storage.
- Yuepeng Pang
- , Yongfeng Liu
- & Hongge Pan
-
Article |
 Synthesis of luminescent europium defects in diamond
Synthesis of luminescent europium defects in diamond
Impurities and defects embedded in diamond are a promising platform for spintronics and photonics. Here, Magyar and colleagues incorporate europium defects in diamond, whose optical properties promise their use in quantum information applications.
- Andrew Magyar
- , Wenhao Hu
- & Igor Aharonovich
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering thermal conductance using a two-dimensional phononic crystal
Engineering thermal conductance using a two-dimensional phononic crystal
Controlling thermal transport is commonly achieved by introducing scattering centres. Here, the authors demonstrate that coherent band structure effects can also be used to control phonon transport, viathe use of periodically nanostructured phononic crystals.
- Nobuyuki Zen
- , Tuomas A. Puurtinen
- & Ilari J. Maasilta
-
Article |
 Designing a robustly metallic noncenstrosymmetric ruthenate oxide with large thermopower anisotropy
Designing a robustly metallic noncenstrosymmetric ruthenate oxide with large thermopower anisotropy
Metals with noncentrosymmetric crystal structures are rare, but this class of compounds may have desirable properties for applications. Here, the authors develop a design framework for noncentrosymmetric compounds and predict a new polar ruthenate with robust metallicity and thermopower anisotropy.
- Danilo Puggioni
- & James M. Rondinelli
-
Article |
 Colour-tunable fluorescent multiblock micelles
Colour-tunable fluorescent multiblock micelles
Controlling the colour and pattern of emission in nanoscale objects is still a challenging goal. Here the authors report segmented micelles where the emission from each individual section can be precisely controlled, giving nanomaterials capable of producing colours throughout the visible range.
- Zachary M. Hudson
- , David J. Lunn
- & Ian Manners
-
Article |
 Linking experiment and theory for three-dimensional networked binary metal nanoparticle–triblock terpolymer superstructures
Linking experiment and theory for three-dimensional networked binary metal nanoparticle–triblock terpolymer superstructures
Three-dimensional superstructures of binary nanoparticles offer a flexible design approach towards materials with designable properties. Here, Li et al.study metal nanoparticle–triblock terpolymer superstructures, where an experimental and theoretical understanding can lead to their application in fields such as catalysis.
- Zihui Li
- , Kahyun Hur
- & Ulrich Wiesner
-
Article
| Open Access Enantioselective recognition at mesoporous chiral metal surfaces
Enantioselective recognition at mesoporous chiral metal surfaces
Chemical synthesis of chiral materials with enantioselective properties is an ongoing challenge. Here, the authors fabricate a chirally imprinted mesoporous metal from the electrochemical reduction of platinum salts in the presence of a liquid crystal phase and chiral templating molecules.
- Chularat Wattanakit
- , Yémima Bon Saint Côme
- & Alexander Kuhn
-
Article |
 Design rules for self-assembled block copolymer patterns using tiled templates
Design rules for self-assembled block copolymer patterns using tiled templates
Sparse templates can be used to direct the assembly of block copolymers into patterned structures. Here the authors report a small set of template tiles that can be combined in different arrangements and orientations to form a variety of non-trivial patterns.
- Jae-Byum Chang
- , Hong Kyoon Choi
- & Karl K. Berggren
-
Article |
 Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
Novel polymer-free iridescent lamellar hydrogel for two-dimensional confined growth of ultrathin gold membranes
The structure of hydrogels is normally isotropic, but anisotropic hydrogels with a periodic lamellar structure can also be synthesized. Here the confined water layers in a lamellar hydrogel are used to guide the growth of large area, single-crystalline gold membranes with two-dimensional properties.
- Jian Niu
- , Dong Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article |
 Microsphere-assisted fabrication of high aspect-ratio elastomeric micropillars and waveguides
Microsphere-assisted fabrication of high aspect-ratio elastomeric micropillars and waveguides
Obtaining poly(dimethylsiloxane) micropillar arrays with high aspect-ratios has been challenging. Here, the authors report a direct drawing-based fabrication technique for obtaining upright micropillars with millimeter-scale heights, and demonstrate an airflow sensor based on them.
- Jungwook Paek
- & Jaeyoun Kim
-
Article |
 Toward atomically-precise synthesis of supported bimetallic nanoparticles using atomic layer deposition
Toward atomically-precise synthesis of supported bimetallic nanoparticles using atomic layer deposition
Synthesis of supported bimetallic nanoparticles often results in mixtures containing one or two metals. Here, the authors report a highly controlled method where one metal particle is initially formed on a support and the second metal is then grown exclusively on this metal surface.
- Junling Lu
- , Ke-Bin Low
- & Jeffrey W. Elam
-
Article |
 Fractal design concepts for stretchable electronics
Fractal design concepts for stretchable electronics
Stretchable electrodes provide the foundation for many applications but optimising the architecture to balance performance and flexibility is challenging. Here, the authors show that fractal designs offer new opportunities to tune the mechanical properties of such structures.
- Jonathan A. Fan
- , Woon-Hong Yeo
- & John A. Rogers
-
Article |
 Dynamic urea bond for the design of reversible and self-healing polymers
Dynamic urea bond for the design of reversible and self-healing polymers
The design of dynamic covalent bonds is crucial to self-healing polymer materials, but the reaction normally occurs in the presence of heat or/and catalysts. Ying et al.report a catalyst-free design of dynamic urea bonds that are capable of autonomous repairing at low temperature.
- Hanze Ying
- , Yanfeng Zhang
- & Jianjun Cheng
-
Article |
 Graphene radio frequency receiver integrated circuit
Graphene radio frequency receiver integrated circuit
Graphene transistors are attractive for many applications but making integrated circuits without degrading their characteristics is proving challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate a radio frequency integrated receiver using a graphene-last approach compatible with conventional processing methods.
- Shu-Jen Han
- , Alberto Valdes Garcia
- & Wilfried Haensch
-
Article
| Open Access Designing quantum dots for solotronics
Designing quantum dots for solotronics
Single-atom dopants embedded in a semiconductor matrix are of potential use for optical, spintronics as well as information storage applications. Here, Kobak et al.realize CdTe and CdSe quantum dots with single cobalt and manganese ions and show how the quantum dot design influences single-spin relaxation time.
- J. Kobak
- , T. Smoleński
- & W. Pacuski
-
Article |
 Polystyrene sulphonic acid resins with enhanced acid strength via macromolecular self-assembly within confined nanospace
Polystyrene sulphonic acid resins with enhanced acid strength via macromolecular self-assembly within confined nanospace
Solid acid catalysts allow easy separation and reduction in waste not easily achievable with mineral acids. Here the authors report polystyrene sulphonic acid resins whose acid strength and catalytic performance can be tuned by changing their morphology within a confined nanospace.
- Xiaomin Zhang
- , Yaopeng Zhao
- & Qihua Yang
-
Article |
 Replication of flexible polymer membranes with geometry-controllable nano-apertures via a hierarchical mould-based dewetting
Replication of flexible polymer membranes with geometry-controllable nano-apertures via a hierarchical mould-based dewetting
Free-standing membranes are widely used as device templates, but their fabrication is limited to silicon-based materials nowadays. Cho et al. introduce a hierarchical mould-based dewetting approach to generate soft polymeric membranes with controllable multiple levels of nano-apertures over large areas.
- Hyesung Cho
- , Junsoo Kim
- & Kahp-Yang Suh
-
Article |
 A nanocomposite superstructure of metal oxides with effective charge transfer interfaces
A nanocomposite superstructure of metal oxides with effective charge transfer interfaces
Mesocrystals are periodic arrangements of nanoparticles that allow for a tuning of the superstructure properties via its constituents. Here Bian et al. combine the properties of different nanocrystalline materials and fabricate a superstructure of two metal oxides with n- and p-type polarity.
- Zhenfeng Bian
- , Takashi Tachikawa
- & Tetsuro Majima
-
Article |
 Ultrathin rhodium nanosheets
Ultrathin rhodium nanosheets
Single-layered materials such as graphene are well known, but metallic elements tend to favour three-dimensional clusters. Here the authors report the synthesis of rhodium nanosheets—a supported, single-layered metallic material with rare δ-bonding.
- Haohong Duan
- , Ning Yan
- & Yadong Li
-
Article |
 Ultra-high mobility transparent organic thin film transistors grown by an off-centre spin-coating method
Ultra-high mobility transparent organic thin film transistors grown by an off-centre spin-coating method
One of the advantages of organic over inorganic semiconductors is they can be grown from solution, but their electrical mobility is often poor. Yuan et al. report a technique for fabricating organic transistors with mobilities far beyond that of amorphous silicon and close to that of polycrystalline silicon.
- Yongbo Yuan
- , Gaurav Giri
- & Zhenan Bao
-
Article |
 Wafer-scale design of lightweight and transparent electronics that wraps around hairs
Wafer-scale design of lightweight and transparent electronics that wraps around hairs
Realising flexible, lightweight and transparent electronics is a continuous challenge. Here, the authors report a process to create such transistor devices, which can be transferred onto various flexible substrates, and continue to function when wrapped around human hairs.
- Giovanni A. Salvatore
- , Niko Münzenrieder
- & Gerhard Tröster
-
Article |
 Development of an ultra-thin film comprised of a graphene membrane and carbon nanotube vein support
Development of an ultra-thin film comprised of a graphene membrane and carbon nanotube vein support
Graphene has great potential in various electronic devices, but obtaining large-area suspended graphene is problematic. Here, the authors use carbon nanotubes as supports for graphene, enabling large areas of strong and 90% electron transparent suspended graphene to be realized.
- Xiaoyang Lin
- , Peng Liu
- & Kaili Jiang
-
Article |
 A facile soft-template synthesis of mesoporous polymeric and carbonaceous nanospheres
A facile soft-template synthesis of mesoporous polymeric and carbonaceous nanospheres
The controlled synthesis of monodisperse nanospheres faces a number of difficulties, such as extensive crosslinking during hydrothermal processes. Here, the authors show a route for the controlled synthesis of mesoporous polymer nanospheres, which can be further converted into carbon nanospheres through carbonization.
- Jian Liu
- , Tianyu Yang
- & Shi Zhang Qiao
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional strutted graphene grown by substrate-free sugar blowing for high-power-density supercapacitors
Three-dimensional strutted graphene grown by substrate-free sugar blowing for high-power-density supercapacitors
Three-dimensional graphene offers an ideal sheet-to-sheet connectivity of assembled graphenes, but often suffers from poor electrochemical performance. Wang et al. present a sugar-blowing technique to prepare a 3D graphene, which overcomes such problems and shows potential in supercapacitor applications.
- Xuebin Wang
- , Yuanjian Zhang
- & Yoshio Bando
-
Article |
 Synergistic interaction between redox-active electrolyte and binder-free functionalized carbon for ultrahigh supercapacitor performance
Synergistic interaction between redox-active electrolyte and binder-free functionalized carbon for ultrahigh supercapacitor performance
Using redox-active electrolytes can promote faradaic reactions in supercapactors. Mai et al.report a copper chloride solution electrolyte, which, when combined with a surface-functionalized carbon-based binder-free electrode, exhibits ultrahigh supercapacitor performance.
- Li-Qiang Mai
- , Aamir Minhas-Khan
- & Xu Xu
-
Article |
 High-capacity antimony sulphide nanoparticle-decorated graphene composite as anode for sodium-ion batteries
High-capacity antimony sulphide nanoparticle-decorated graphene composite as anode for sodium-ion batteries
Anode materials used for sodium-ion batteries often suffer from poor stability and rate capability in electrochemical reactions. Yu et al.report a nanocomposite anode consisting of stibnite and reduced graphene oxide, which exhibits excellent cycle stability and rate performance.
- Denis Y. W. Yu
- , Petr V. Prikhodchenko
- & Ovadia Lev
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen-induced nanotunnel opening within semiconductor subsurface
Hydrogen-induced nanotunnel opening within semiconductor subsurface
Silicon carbide surfaces offer many interesting properties induced by surface strain relief. Soukiassian et al.report hydrogen-induced self-organized nano-voids below a silicon carbide surface, and suggest the resultant nanotunnel may be used as a template to capture atoms or molecules.
- Patrick Soukiassian
- , Erich Wimmer
- & Mario Rocca
-
Article |
 Solid-source growth and atomic-scale characterization of graphene on Ag(111)
Solid-source growth and atomic-scale characterization of graphene on Ag(111)
The integration of graphene with silver offers the promise of combining the electronic and plasmonic properties of both materials. Here, Kiraly et al.achieve the growth of graphene on a silver substrate, with the graphene electronic structure only minimally affected by the silver.
- Brian Kiraly
- , Erin V. Iski
- & Nathan P. Guisinger

 Visible-frequency asymmetric transmission devices incorporating a hyperbolic metamaterial
Visible-frequency asymmetric transmission devices incorporating a hyperbolic metamaterial