Featured
-
-
Article |
 In situ X-ray diffraction monitoring of a mechanochemical reaction reveals a unique topology metal-organic framework
In situ X-ray diffraction monitoring of a mechanochemical reaction reveals a unique topology metal-organic framework
Ball milling chemical reactions are of interest due to their environmental credentials and potential to achieve new reactions and materials. Here, the authors isolate a metastable material with a previously unknown net topology by in situmonitoring of the mechanosynthesis of a metal organic framework.
- Athanassios D. Katsenis
- , Andreas Puškarić
- & Tomislav Friščić
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic designing of microstructures by chemical gradient-mediated growth
Dynamic designing of microstructures by chemical gradient-mediated growth
While microparticle shape can have significant influence on their properties, simple ways to control shape are difficult to achieve. Here, the authors report a method giving a high degree of control over the shape of such structures by generating gradients of oxygen concentration during photopolymerization.
- Tae Soup Shim
- , Seung-Man Yang
- & Shin-Hyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access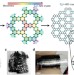 Nitrogenated holey two-dimensional structures
Nitrogenated holey two-dimensional structures
There is currently interest in two-dimensional graphene-like materials incorporating heteroatoms. Here, the authors synthesize a solution-processable, holey two-dimensional network with C2N stoichiometry containing evenly distributed holes and nitrogen atoms, and use it to fabricate a field effect transistor.
- Javeed Mahmood
- , Eun Kwang Lee
- & Jong-Beom Baek
-
Article |
 Crystalline silicon core fibres from aluminium core preforms
Crystalline silicon core fibres from aluminium core preforms
The integration of silicon optoelectronic devices in a fibre platform has great potential, but drawing such fibres is difficult. Using a simple, low cost and scalable method, Hou et al. fabricate a metre-long crystalline silicon-core, silica-clad fibre from a preform not containing elemental silicon.
- Chong Hou
- , Xiaoting Jia
- & Yoel Fink
-
Article |
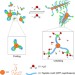 Unfolding a molecular trefoil derived from a zwitterionic metallopeptide to form self-assembled nanostructures
Unfolding a molecular trefoil derived from a zwitterionic metallopeptide to form self-assembled nanostructures
Molecular self-assembly can be influenced by a number of external factors, though solvent effects are less commonly explored. Here, the authors present a three-armed metallopeptide complex that has a folded monomeric conformation in organic solvent, but can self-assemble in water into a supramolecular gel.
- Ye Zhang
- , Ning Zhou
- & Bing Xu
-
Article |
 Hierarchical structural design for fracture resistance in the shell of the pteropod Clio pyramidata
Hierarchical structural design for fracture resistance in the shell of the pteropod Clio pyramidata
The hierarchical structural motifs of biomaterials can lead to advantageous mechanical properties. Here, the authors reveal that a fibre-like helical structure across the shell of a planktonic pteropod suppresses crack propagation and is responsible for a high fracture resistance.
- Ling Li
- , James C. Weaver
- & Christine Ortiz
-
Article |
 De novo design of an RNA tile that self-assembles into a homo-octameric nanoprism
De novo design of an RNA tile that self-assembles into a homo-octameric nanoprism
The rational design of nucleic acid nanostructures requires building blocks that can be predictably combined into a uniform structure. Here, the authors present a designed RNA building block able to self-assemble into a homo-octameric cube.
- Jinwen Yu
- , Zhiyu Liu
- & Chengde Mao
-
Article |
 Ultrasmooth organic–inorganic perovskite thin-film formation and crystallization for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells
Ultrasmooth organic–inorganic perovskite thin-film formation and crystallization for efficient planar heterojunction solar cells
Organic-inorganic metal halide perovskites are of considerable promise for efficient, easy to manufacture solar cells. Here, the authors show that the choice of anions in the perovskite solution can considerably affect the crystal growth and performance of these solar cells.
- Wei Zhang
- , Michael Saliba
- & Henry J. Snaith
-
Article |
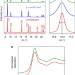 Redox response of actinide materials to highly ionizing radiation
Redox response of actinide materials to highly ionizing radiation
Understanding the degradation of materials subject to energetic radiation is important for the development of technologies based on nuclear fission. Here, the authors show that redox reactions of actinide compounds play an important role in their response to energetic radiation and their radiation tolerance.
- Cameron L. Tracy
- , Maik Lang
- & Rodney C. Ewing
-
Article |
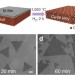 Synthesis of large single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains on Cu–Ni alloy
Synthesis of large single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains on Cu–Ni alloy
High nucleation density has thus far limited the quality and grain size of CVD-grown hexagonal boron nitride. Here, by optimizing the Ni ratio in Cu–Ni substrates, the authors successfully reduce nucleation density and report single-crystal hexagonal boron nitride grains up to 7500 μm2.
- Guangyuan Lu
- , Tianru Wu
- & Mianheng Jiang
-
Article |
 Growth of high-density horizontally aligned SWNT arrays using Trojan catalysts
Growth of high-density horizontally aligned SWNT arrays using Trojan catalysts
Single-walled carbon nanotube arrays have been proposed for use in electronics, but getting the tubes aligned and in high density is a very challenging task. Hu et al. show that catalyst particles dissolved in a substrate can slowly be brought to the surface, allowing continued controlled growth of nanotubes.
- Yue Hu
- , Lixing Kang
- & Jin Zhang
-
Article |
 Three-dimensionally bonded spongy graphene material with super compressive elasticity and near-zero Poisson’s ratio
Three-dimensionally bonded spongy graphene material with super compressive elasticity and near-zero Poisson’s ratio
The incorporation of the desirable properties of graphene into three-dimensional materials remains challenging. Here, the authors report the scalable self-assembly of graphene sheets into spongy materials with very low densities, and near-zero and largely strain-independent Poisson's ratios in all directions.
- Yingpeng Wu
- , Ningbo Yi
- & Yongsheng Chen
-
Article |
 Probing the limits of gate-based charge sensing
Probing the limits of gate-based charge sensing
Reading out the state of quantum bits is an essential requirement that any quantum computer implementation must satisfy. Gonzalez-Zalba et al. now show that in situresonant gate-based detection can be a more sensitive approach than external electrometers while reducing the qubit architecture’s complexity.
- M. F. Gonzalez-Zalba
- , S. Barraud
- & A. C. Betz
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular nematic liquid crystalline material for high-performance organic photovoltaics
A molecular nematic liquid crystalline material for high-performance organic photovoltaics
There is a trade-off between increasing thickness of active layers in organic photovoltaic cells to be compatible with modern printing techniques and decreasing it to improve the device performance. Sun et al.report a nematic liquid crystalline molecular electron donor material used in thick layers.
- Kuan Sun
- , Zeyun Xiao
- & David J. Jones
-
Article
| Open Access The evolution of cyclopropenium ions into functional polyelectrolytes
The evolution of cyclopropenium ions into functional polyelectrolytes
Cationic polyelectrolytes have a broad range of applications, including membranes for fuel cells. Here, the authors report a family of cationic polyelectrolytes based on the highly modular cyclopropenium ion building block, which show high ionic conductivity and tunable physical properties.
- Yivan Jiang
- , Jessica L. Freyer
- & Luis M. Campos
-
Article |
 A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
A strain-absorbing design for tissue–machine interfaces using a tunable adhesive gel
Biocompatibility is a limiting factor in the use of electronic sensors in physiological applications. Here, the authors present a flexible and conductive polymer gel as an adhesive interface material for electronic biosensors, also demonstrating in vivoheart attachment and monitoring.
- Sungwon Lee
- , Yusuke Inoue
- & Takao Someya
-
Article |
 Bottom-up formation of endohedral mono-metallofullerenes is directed by charge transfer
Bottom-up formation of endohedral mono-metallofullerenes is directed by charge transfer
An understanding of the formation mechanism of endohedral metallofullerenes may pave the way towards targeted synthesis of these nanomaterials. Here, the authors investigate their bottom-up synthesis and determine that charge transfer plays a key role in their formation.
- Paul W. Dunk
- , Marc Mulet-Gas
- & Harold W. Kroto
-
Article |
 High electron mobility in thin films formed via supersonic impact deposition of nanocrystals synthesized in nonthermal plasmas
High electron mobility in thin films formed via supersonic impact deposition of nanocrystals synthesized in nonthermal plasmas
Surface defects in nanomaterials can trap electrons and thereby limit the performance of electronic devices. Thimsen et al. show that the conductivity of films comprising ZnO nanocrystals can be increased by coating with Al2O3.
- Elijah Thimsen
- , Melissa Johnson
- & Eray S. Aydil
-
Article |
 Enabling complex nanoscale pattern customization using directed self-assembly
Enabling complex nanoscale pattern customization using directed self-assembly
Block copolymers are frequently used as self-assembling materials for nanoscale patterns, but controlling assembly for complex patterning is challenging. Here, the authors integrate masking features into organic–inorganic guide patterns, enabling precise pattern customization by directed self-assembly.
- Gregory S. Doerk
- , Joy Y. Cheng
- & Daniel P. Sanders
-
Article |
 Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality
Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality
Materials with ultra-low densities can display a range of useful properties, ranging from compressibility to sound absorption. Here, the authors report the fabrication of ultra-lightweight materials by the assembly of electrospun nanofibres into an aerogel and examine the mechanical properties.
- Yang Si
- , Jianyong Yu
- & Bin Ding
-
Article |
 Steric engineering of metal-halide perovskites with tunable optical band gaps
Steric engineering of metal-halide perovskites with tunable optical band gaps
The performance of solar cells based on metal-halide perovskites has improved rapidly in recent years. First principles calculations and experiments performed by Filip et al.suggest new routes to controlling the band gap of these materials, which could enable further improvements in their performance.
- Marina R. Filip
- , Giles E. Eperon
- & Feliciano Giustino
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic fossilization of soft biological tissues and their shape-preserving transformation into silica or electron-conductive replicas
Synthetic fossilization of soft biological tissues and their shape-preserving transformation into silica or electron-conductive replicas
Imaging biological tissues has long been an issue, particularly with regard to manipulation and dissection for SEM. Here, the authors present a simple technique for the stabilization of biological tissues via a synthetic fossilization process, requiring minimal expertise or equipment and involving few steps.
- Jason L. Townson
- , Yu-Shen Lin
- & Bryan Kaehr
-
Article |
 Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
Kinetically tuned dimensional augmentation as a versatile synthetic route towards robust metal–organic frameworks
The synthesis of ultra-stable, single crystalline metal–organic frameworks is challenging. Here, the authors describe a kinetically tuned augmentation synthetic route for the preparation of a range of robust crystalline materials from preformed trimetallic components.
- Dawei Feng
- , Kecheng Wang
- & Hong-Cai Zhou
-
Article |
 Photocatalytic colour switching of redox dyes for ink-free light-printable rewritable paper
Photocatalytic colour switching of redox dyes for ink-free light-printable rewritable paper
Printing text and images is a significant cause of paper and ink waste, leading to an increased focus on reusable alternatives. Here, the authors show that films of commercial dyes can be photoactivated with UV light and catalysts and, with an appropriate stabilizer, can be used as a rewritable display system.
- Wenshou Wang
- , Ning Xie
- & Yadong Yin
-
Article |
 Soft epitaxy of nanocrystal superlattices
Soft epitaxy of nanocrystal superlattices
Epitaxial crystal growth is widely used in electronics for the rational design of efficient devices. Here, Rupich et al. find a universal law for island size scaling, which outlines similarities and differences between self-assembly of nanocrystals and atomic epitaxial growth.
- Sara M. Rupich
- , Fernando C. Castro
- & Dmitri V. Talapin
-
Article |
 Sponge-like molecular cage for purification of fullerenes
Sponge-like molecular cage for purification of fullerenes
Mixtures of various size fullerenes are available as a component of fullerene soot, but isolating pure fullerenes is a challenging task. Here, the authors use a porphyrin-based supramolecular cage that encapsulates fullerenes with high selectivity and releases C60by a simple washing technique.
- Cristina García-Simón
- , Marc Garcia-Borràs
- & Xavi Ribas
-
Article |
 Wavefront modulation and subwavelength diffractive acoustics with an acoustic metasurface
Wavefront modulation and subwavelength diffractive acoustics with an acoustic metasurface
Metasurfaces are subwavelength structures that manipulate impinging waves into desired output waveforms, but building them for acoustic applications remains challenging. Exploiting tapered labyrinthine structures, Xie et al.present an acoustic metasurface that manipulates sound waves in a variety of ways.
- Yangbo Xie
- , Wenqi Wang
- & Steven A. Cummer
-
Article |
 Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties
Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties
Graphene quantum dots (GQDs) have a wide range of potential applications, yet current cutting methods produce GQDs in low amounts and with poor optical properties. Here, the authors demonstrate, via a facile molecular fusion route, the synthesis of GQDs at the gram-scale and report excellent optical properties.
- Liang Wang
- , Yanli Wang
- & Minghong Wu
-
Article |
 Ordered three-dimensional interconnected nanoarchitectures in anodic porous alumina
Ordered three-dimensional interconnected nanoarchitectures in anodic porous alumina
Three-dimensional nanostructures have numerous applications and are normally fabricated via templating strategies. Here, the authors present a current-limited hard anodization approach for tunable, homogeneous anodic aluminium oxide, which can be used to template a range of periodic nanowire networks.
- Jaime Martín
- , Marisol Martín-González
- & Olga Caballero-Calero
-
Article |
 Towards intrinsic charge transport in monolayer molybdenum disulfide by defect and interface engineering
Towards intrinsic charge transport in monolayer molybdenum disulfide by defect and interface engineering
Impurities in molybdenum disulfide are known to reduce charge mobility to below its intrinsic limit. Here, the authors demonstrate that impurities are associated with lattice defects and that a chemical route can repair sulfur vacancies and improve interface quality with a substrate, enhancing device performance.
- Zhihao Yu
- , Yiming Pan
- & Xinran Wang
-
Article |
 Stimuli-sensitive intrinsically disordered protein brushes
Stimuli-sensitive intrinsically disordered protein brushes
Polymer brush surface coatings are important biomaterials for the reduction of biomolecule and cell adhesion. Here, the authors use a recombinantly expressed, intrinsically disordered protein to form a stimuli-responsive and enzyme-active polymer brush surface.
- Nithya Srinivasan
- , Maniraj Bhagawati
- & Sanjay Kumar
-
Article |
 Thermally robust and porous noncovalent organic framework with high affinity for fluorocarbons and CFCs
Thermally robust and porous noncovalent organic framework with high affinity for fluorocarbons and CFCs
There is significant research into using metal-organic frameworks for gas storage and separation, however, discrete molecule-based systems are rarer. Here, the authors report a small organic molecule that organizes into a relatively stable noncovalent organic framework, capable of adsorbing greenhouse species.
- Teng-Hao Chen
- , Ilya Popov
- & Ognjen Š. Miljanić
-
Article |
 Engineering polar discontinuities in honeycomb lattices
Engineering polar discontinuities in honeycomb lattices
It has been predicted that when a polar discontinuity occurs in honeycomb lattices, wires of electrons or holes would appear. Here, the authors suggest different and realistic routes to engineer such wires in current two-dimensional materials, and validate these with first-principles calculations.
- Marco Gibertini
- , Giovanni Pizzi
- & Nicola Marzari
-
Article |
 Dry-air-stable lithium silicide–lithium oxide core–shell nanoparticles as high-capacity prelithiation reagents
Dry-air-stable lithium silicide–lithium oxide core–shell nanoparticles as high-capacity prelithiation reagents
Anode prelithiation is used to treat the initial capacity loss and low Coulombic efficiency in lithium-ion batteries, but existing methods are not effective. Here, the authors report lithium silicide–lithium oxide core–shell nanoparticles as a promising prelithiation reagent.
- Jie Zhao
- , Zhenda Lu
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Bottom-up approach for the low-cost synthesis of graphene-alumina nanosheet interfaces using bimetallic alloys
Bottom-up approach for the low-cost synthesis of graphene-alumina nanosheet interfaces using bimetallic alloys
Graphene-dielectric interfaces play a crucial role in many electronic devices, but electronic properties of graphene are inevitably degraded when the interfaces are produced. Omiciuolo et al.solve this problem using a low-cost approach based on epitaxial growth of graphene on dielectric alloys.
- Luca Omiciuolo
- , Eduardo R. Hernández
- & Alessandro Baraldi
-
Article |
 Rational design of all organic polymer dielectrics
Rational design of all organic polymer dielectrics
The selection of polymeric dielectric materials for energy storage applications is not trivial, as several criteria must be satisfied simultaneously. Here, Sharma et al.present a high-throughput hierarchical strategy using the band gap and dielectric constant to screen and identify good candidates.
- Vinit Sharma
- , Chenchen Wang
- & Rampi Ramprasad
-
Article |
 Cephalopod-inspired design of electro-mechano-chemically responsive elastomers for on-demand fluorescent patterning
Cephalopod-inspired design of electro-mechano-chemically responsive elastomers for on-demand fluorescent patterning
Cephalopods change colour by mechanically activating chromatophores via muscle contraction. Here, the authors use a similar concept for flexible displays, where electric field control over elastomer strain allows activation of mechanophores and provides on-demand and variable fluorescent patterns.
- Qiming Wang
- , Gregory R. Gossweiler
- & Xuanhe Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
Self-propagating high-temperature synthesis for compound thermoelectrics and new criterion for combustion processing
The existing methods to synthesize thermoelectric materials remain constrained to multi-step processes that are usually time and energy consuming. Here, Su et al.use a fast, one-step combustion approach to synthesize various compounds, which holds promise for scalable industrial processing.
- Xianli Su
- , Fan Fu
- & Ctirad Uher
-
Article |
 Sculpting carbon bonds for allotropic transformation through solid-state re-engineering of –sp2 carbon
Sculpting carbon bonds for allotropic transformation through solid-state re-engineering of –sp2 carbon
Inter-allotropic transformation of carbon is of immense fundamental and technological interest, but requires extreme conditions. Here, the authors report a method to transform single-walled carbon nanotubes into other carbon structures with high reproducibility by controlling alternating-voltage pulses.
- Hyun Young Jung
- , Paulo T. Araujo
- & Yung Joon Jung
-
Article |
 Controlled thermal oxidative crosslinking of polymers of intrinsic microporosity towards tunable molecular sieve membranes
Controlled thermal oxidative crosslinking of polymers of intrinsic microporosity towards tunable molecular sieve membranes
Organic frameworks with well-defined micropore structures are attractive materials for mass transfer and catalytic applications. Here, the authors demonstrate that polymers of intrinsic microporosity can be thermal-oxidatively crosslinked yielding robust materials with high molecular-sieving selectivity.
- Qilei Song
- , Shuai Cao
- & Easan Sivaniah
-
Article |
 Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis
Hierarchical synthesis of non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures and enabled plasmon-driven photocatalysis
The continued development of hybrid nanostructures is important for a range of applications. Here, the authors fabricate non-centrosymmetric hybrid nanostructures of programmable composition, and demonstrate that they are capable of plasmon enhanced photocatalysis.
- Lin Weng
- , Hui Zhang
- & Min Ouyang
-
Article |
 Giant spin Hall effect in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition
Giant spin Hall effect in graphene grown by chemical vapour deposition
Manipulating spin currents in graphene by the spin–orbit interaction is important for many technological developments. Here, the authors show that the presence of residual metallic adatoms in chemical vapour deposition graphene enhances its spin–orbit coupling by three orders of magnitude.
- Jayakumar Balakrishnan
- , Gavin Kok Wai Koon
- & Barbaros Özyilmaz
-
Article |
 Designed synthesis of large-pore crystalline polyimide covalent organic frameworks
Designed synthesis of large-pore crystalline polyimide covalent organic frameworks
Covalent organic frameworks are a potentially useful class of materials, although they are currently synthesized using relatively few reactions. Here, the authors show that the imidization reaction can be used to prepare a series of large pore polyimide frameworks with high surface area and thermal stability.
- Qianrong Fang
- , Zhongbin Zhuang
- & Yushan Yan
-
Article |
 Atom manipulation on an insulating surface at room temperature
Atom manipulation on an insulating surface at room temperature
Atomic manipulation can be used to fabricate unique structures at the atomic level but has previously been limited to conductive surfaces, mainly at low temperatures. Here, the authors present a systematic manipulation on an insulating surface using atomic force microscopy to construct complex patterns.
- Shigeki Kawai
- , Adam S. Foster
- & Ernst Meyer
-
Article |
 Enantioselective control of lattice and shape chirality in inorganic nanostructures using chiral biomolecules
Enantioselective control of lattice and shape chirality in inorganic nanostructures using chiral biomolecules
Inorganic structured nanomaterials with chiral symmetry groups may have interesting optical activities. Here, the authors use biomolecules to synthesize chiral tellurium and selenium nanostructures, which exhibit visible optical and chiroptical responses and may be used as templates for mixed metal structures.
- Assaf Ben-Moshe
- , Sharon Grayer Wolf
- & Gil Markovich
-
Article |
 Functional ferroic heterostructures with tunable integral symmetry
Functional ferroic heterostructures with tunable integral symmetry
Crystal symmetries play an important role in the properties of materials, but allow little dynamic control once the materials have been grown. Here, the authors show that conducting oxides sandwiched between independently switchable ferroelectric films achieve tunable symmetry for controllable properties.
- C. Becher
- , M. Trassin
- & D. Meier
-
Article |
 Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
Ultra-high aspect ratio high-resolution nanofabrication for hard X-ray diffractive optics
The increasing use of hard X-ray sources for scientific and biomedical imaging applications requires the development of suitable optical devices to focus and shape these high-energy beams. Here, Chang and Sakdinawat have fabricated ultra-high aspect ratio nanostructures for hard X-ray focusing.
- Chieh Chang
- & Anne Sakdinawat
-
Article |
 Stress-induced phase transformation and optical coupling of silver nanoparticle superlattices into mechanically stable nanowires
Stress-induced phase transformation and optical coupling of silver nanoparticle superlattices into mechanically stable nanowires
Silver nanowires are commonly synthesized via chemical routes. Here, the authors report nanowire formation via a physical method involving stress-induced phase transformation and sintering of spherical silver nanoparticle superlattices.
- Binsong Li
- , Xiaodong Wen
- & Hongyou Fan
-
Article |
 An elasto-mechanical unfeelability cloak made of pentamode metamaterials
An elasto-mechanical unfeelability cloak made of pentamode metamaterials
Cloaking of a range of stimuli have been demonstrated in various metamaterials recently. Here, the authors report mechanical cloaking in a pentamode structure, leading to ‘unfeelability’ of a core in an elasto-mechanical core-shell system.
- T. Bückmann
- , M. Thiel
- & M. Wegener

 Formation of nickel cobalt sulfide ball-in-ball hollow spheres with enhanced electrochemical pseudocapacitive properties
Formation of nickel cobalt sulfide ball-in-ball hollow spheres with enhanced electrochemical pseudocapacitive properties