Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Virtual substrate method for nanomaterials characterization
Virtual substrate method for nanomaterials characterization
Quantitative characterization of supported nanomaterials is challenging, because the nanomaterial signals cannot easily be deconvoluted from those of the substrate. Here, the authors introduce an inventive approach to overcome this problem for electron-based surface analysis techniques.
- Bo Da
- , Jiangwei Liu
- & Zejun Ding
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring the orbital angular momentum spectrum of an electron beam
Measuring the orbital angular momentum spectrum of an electron beam
Existing methods of characterizing electron beams carrying orbital angular momentum are inefficient as they allow measuring one OAM state at a time. Here the authors demonstrate an OAM spectrometer capable of analysing multiple OAM states and a potential tool for probing magnetic materials.
- Vincenzo Grillo
- , Amir H. Tavabi
- & Ebrahim Karimi
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule detection of dihydroazulene photo-thermal reaction using break junction technique
Single-molecule detection of dihydroazulene photo-thermal reaction using break junction technique
The conductance across single-molecule junctions is highly dependent on the electronic properties of the molecule in question. Here the authors use this fact to monitor a photo-thermal reaction by analysing break junction data, and observe significant differences compared to solution state behaviour.
- Cancan Huang
- , Martyn Jevric
- & Wenjing Hong
-
Article
| Open Access An in-plane magnetic chiral dichroism approach for measurement of intrinsic magnetic signals using transmitted electrons
An in-plane magnetic chiral dichroism approach for measurement of intrinsic magnetic signals using transmitted electrons
Electron energy-loss magnetic chiral dichroism enables the measurement of the local magnetic properties of a material using a transmission electron microscope, but is limited to signals in the electron-beam direction. Here, the authors demonstrate a method to extend this to in-plane magnetic signals too.
- Dongsheng Song
- , Amir H. Tavabi
- & Jing Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Probing nanoscale oxygen ion motion in memristive systems
Probing nanoscale oxygen ion motion in memristive systems
Ion transport in solid-state materials is a fundamental process for many modern technologies. Utilizing electrostatic force microscopy, Yanget al. directly visualize ion motion and verify the oxygen ion dynamics within HfO2—a common metal-oxide based memristive material.
- Yuchao Yang
- , Xiaoxian Zhang
- & Ru Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity determination of individual surface atoms by atomic force microscopy
Electronegativity is a fundamental concept in chemistry; however it is an elusive quantity to evaluate experimentally. Here, the authors estimate the Pauling electronegativity of individual atoms on a surface via atomic force microscopy using a variety of chemically reactive tips.
- Jo Onoda
- , Martin Ondráček
- & Yoshiaki Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Direct experimental determination of the topological winding number of skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3
Direct experimental determination of the topological winding number of skyrmions in Cu2OSeO3
Experimental demonstrations of topologically nontrivial states in magnetic films currently rely on indirect comparisons of theoretical models with microscopic images. Here the authors show that resonant X-ray scattering provides direct information on the topology of magnetic textures.
- S. L. Zhang
- , G. van der Laan
- & T. Hesjedal
-
Article
| Open Access Portraying entanglement between molecular qubits with four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering
Portraying entanglement between molecular qubits with four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering
Showing the presence of quantum entanglement in a system means it is beyond a classical description, but this is difficult to do experimentally. Here, the authors show how four-dimensional inelastic neutron scattering can quantify entanglement, demonstrating the method on a supramolecular dimer.
- E. Garlatti
- , T. Guidi
- & S. Carretta
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Three-dimensional surface topography of graphene by divergent beam electron diffraction
Graphene, and other 2D materials, do not exist as strictly planar sheets but instead have topographic ripples on the sub-nanometre scale. Here, Latychevskaiaet al. present a method to non-invasively image ripples in 2D materials with a single-shot, wide-area, electron diffraction measurement.
- Tatiana Latychevskaia
- , Wei-Hao Hsu
- & Ing-Shouh Hwang
-
Article
| Open Access Electron–acoustic phonon coupling in single crystal CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites revealed by coherent acoustic phonons
Electron–acoustic phonon coupling in single crystal CH3NH3PbI3 perovskites revealed by coherent acoustic phonons
Carrier mobility is a basic semiconductor property. Manteet al., use femtosecond lasers to investigate coherent acoustic phonons and relate their deformation potentials to estimate the intrinsic electron and hole mobilities of CH3NH3PbI3 single crystals to be 2,800 and 9,400 cm2 V−1 s−1, respectively.
- Pierre-Adrien Mante
- , Constantinos C. Stoumpos
- & Arkady Yartsev
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Interfacial Ca2+ environments in nanocrystalline apatites revealed by dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced 43Ca NMR spectroscopy
Solid-state NMR can in principle be used to study calcium environments in biomaterials such as bones/teeth, but43Ca lacks receptivity. Here the authors present an approach to acquire 43Ca data for hydroxyapatite at its natural isotopic abundance, distinguishing between core and surface Ca sites.
- Daniel Lee
- , César Leroy
- & Gaël De Paëpe
-
Article
| Open Access Purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory
Purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory
Magnetoelectric coupling allows switching of magnetic states via gate voltage pulses. Here the authors propose and demonstrate a purely antiferromagnetic magnetoelectric random access memory based on Cr2O3, reporting 50-fold reduction of writing threshold compared to ferromagnetic counterparts.
- Tobias Kosub
- , Martin Kopte
- & Denys Makarov
-
Article
| Open Access Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Electronic single-molecule identification of carbohydrate isomers by recognition tunnelling
Carbohydrates are common biological molecules, but display huge stereochemical complexity that often cannot be elucidated by mass spectrometry. Here the authors show that recognition tunnelling can distinguish individual stereoisomers, utilizing picomole quantities of analytes.
- JongOne Im
- , Sovan Biswas
- & Peiming Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Interrogation of bimetallic particle oxidation in three dimensions at the nanoscale
Understanding bimetallic alloy oxidation is key to design of hollow-structured binary oxides and their optimization for applications, e.g., as catalysts. Here the authors combine real-time imaging and chemically-sensitive electron tomography to uncover unexpected complexity in possible morphological outcomes of bimetallic oxidation.
- Lili Han
- , Qingping Meng
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article
| Open Access Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Phase transformation strengthening of high-temperature superalloys
Nanoscale processes may directly impact macroscopic mechanical behaviour. Here authors describe a ‘phase-transformation strengthening’ mechanism in nickel-based high temperature alloys, allowing suppression of deleterious deformation processes at elevated temperatures by specific alloying elements.
- T. M. Smith
- , B. D. Esser
- & M. J. Mills
-
Article
| Open Access Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Origin and structure of polar domains in doped molecular crystals
Doping can introduce structural distortions in a molecular crystal in the form of polar domains. Here, the authors combine pyroelectric measurements and computation to reveal the molecular structure of such domains in centrosymmetric α-glycine crystals doped with L-amino acids.
- E. Meirzadeh
- , I. Azuri
- & I. Lubomirsky
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Atomic intercalation to measure adhesion of graphene on graphite
Analysis of the mechanical properties of two-dimensional materials is important for device development. Here, the authors report a microscopic method for measuring the adhesion of graphene on top of highly ordered pyrolytic graphite, which exploits atomic-scale blisters formed upon neon atom intercalation.
- Jun Wang
- , Dan C. Sorescu
- & Petro Maksymovych
-
Article
| Open Access Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with low-repetition-rate pulsed light source through phase-domain sampling
Low repetition rate lasers are suitable for studying nonlinear optical phenomena, while near-field microscopy allows high spatial resolution for nanomaterial characterisation. Here, Wang et al. enable scattering-type near-field microscopy with low repetition rate lasers through phase-domain sampling.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Nanoscale probing of electron-regulated structural transitions in silk proteins by near-field IR imaging and nano-spectroscopy
Silk protein fibres are exceptionally strong, owing to their high β-sheet nanocrystal content. Here, the authors use an electron beam to guide silk β-sheet crystals through structural transitions, and visualize the changes by infrared near-field optics, achieving close to molecular-level resolution.
- Nan Qin
- , Shaoqing Zhang
- & Tiger H. Tao
-
Article
| Open Access The mechanism of eutectic growth in highly anisotropic materials
The mechanism of eutectic growth in highly anisotropic materials
The origins of non-periodic growth features observed in irregular eutectics have been a source of controversy. Here authors use time-resolved X-ray microtomography during eutectic growth of an alloy to show how competing models can be extended and reconciled.
- Ashwin J. Shahani
- , Xianghui Xiao
- & Peter W. Voorhees
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Two-dimensional flow nanometry of biological nanoparticles for accurate determination of their size and emission intensity
Size and molecular composition of biological nanoparticles dictate their function, but cannot be simultaneously determined accurately. Here, Höök and others have subjected constrained biological nanoparticles on a lipid bilayer to hydrodynamic flow to quantify accurately both size and emission intensity.
- Stephan Block
- , Björn Johansson Fast
- & Fredrik Höök
-
Article
| Open Access Primary thermometry triad at 6 mK in mesoscopic circuits
Primary thermometry triad at 6 mK in mesoscopic circuits
Mesoscopic electrical circuits are an ideal platform to explore quantum phenomena, but this requires cooling the electrons to very low temperature, which is challenging. Here, the authors employ three different in situthermometers to report electronic quantum transport at 6mK in a micrometer-scale circuit.
- Z. Iftikhar
- , A. Anthore
- & F. Pierre
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping surface charge density of lipid bilayers by quantitative surface conductivity microscopy
Mapping surface charge density of lipid bilayers by quantitative surface conductivity microscopy
Surface charges on lipid bilayers deeply influence the way proteins interact with cellular membranes, yet their precise quantification has proven challenging. Here, the authors report on a quantitative method to map and evaluate surface charge densities under physiological conditions.
- Lasse Hyldgaard Klausen
- , Thomas Fuhs
- & Mingdong Dong
-
Article
| Open Access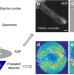 Simultaneous atomic-resolution electron ptychography and Z-contrast imaging of light and heavy elements in complex nanostructures
Simultaneous atomic-resolution electron ptychography and Z-contrast imaging of light and heavy elements in complex nanostructures
The use of ptychography with electrons has been limited. Here, Yang et al. demonstrate that the combination of Z-contrast and phase imaging reveals the structure of complex nanomaterials. This practical tool can be used to solve the structure of a beam-sensitive carbon nanostructure at atomic-resolution.
- H. Yang
- , R. N. Rutte
- & P. D. Nellist
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
Revealing the planar chemistry of two-dimensional heterostructures at the atomic level
The properties of 2D materials such as graphene can vary according to the quality and, for vertical devices, the interfaces between materials. Here, the authors report a method using TOF-SIMS, micro-Raman spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy to give high levels of detail of vertical 2D heterostructures.
- Harry Chou
- , Ariel Ismach
- & Andrei Dolocan
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Imaging screw dislocations at atomic resolution by aberration-corrected electron optical sectioning
Although screw dislocations impact on the properties of various engineering materials, their investigation on the atomic scale has been challenging. Here, the authors use optical sectioning in a scanning transmission electron microscope to achieve direct imaging of screw displacements around a screw dislocation core in GaN.
- H. Yang
- , J. G. Lozano
- & P. D. Nellist
-
Article |
 Concentration and chemical-state profiles at heterogeneous interfaces with sub-nm accuracy from standing-wave ambient-pressure photoemission
Concentration and chemical-state profiles at heterogeneous interfaces with sub-nm accuracy from standing-wave ambient-pressure photoemission
Heterogeneous chemical processes are vital for many applications, but the crucial interfaces involved are difficult to probe experimentally with elemental and chemical-state specificity. Here, the authors present a photoelectron spectroscopy-based method for studying such interfaces with sub-nanometre accuracy and under realistic pressure conditions
- Slavomír Nemšák
- , Andrey Shavorskiy
- & Charles S. Fadley
-
Article |
 Thermally robust and porous noncovalent organic framework with high affinity for fluorocarbons and CFCs
Thermally robust and porous noncovalent organic framework with high affinity for fluorocarbons and CFCs
There is significant research into using metal-organic frameworks for gas storage and separation, however, discrete molecule-based systems are rarer. Here, the authors report a small organic molecule that organizes into a relatively stable noncovalent organic framework, capable of adsorbing greenhouse species.
- Teng-Hao Chen
- , Ilya Popov
- & Ognjen Š. Miljanić
-
Article |
 Temperature-dependent elastic anisotropy and mesoscale deformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy
Temperature-dependent elastic anisotropy and mesoscale deformation in a nanostructured ferritic alloy
Nanostructured ferritic alloys offer many attractive properties that make them suitable for use in extreme environments. Here, the authors use neutron diffraction to determine single-crystal elastic constants of nanoscale ferrite grains, observing a large temperature-induced elastic anisotropy.
- G.M. Stoica
- , A.D. Stoica
- & D. Ma
-
Article |
 Quantitative characterization of nanoscale polycrystalline magnets with electron magnetic circular dichroism
Quantitative characterization of nanoscale polycrystalline magnets with electron magnetic circular dichroism
Electron magnetic circular dichroism gives element-selective information on spin and orbital magnetic moments, but its low intensity has limited its use for nanoscale studies. Using a statistical analysis method, Muto et al.show that this can be overcome with nanometre-sized electron beams.
- Shunsuke Muto
- , Ján Rusz
- & Claus M. Schneider
-
Article |
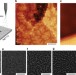 Solid-source growth and atomic-scale characterization of graphene on Ag(111)
Solid-source growth and atomic-scale characterization of graphene on Ag(111)
The integration of graphene with silver offers the promise of combining the electronic and plasmonic properties of both materials. Here, Kiraly et al.achieve the growth of graphene on a silver substrate, with the graphene electronic structure only minimally affected by the silver.
- Brian Kiraly
- , Erin V. Iski
- & Nathan P. Guisinger
-
Article |
 X-ray micro-beam characterization of lattice rotations and distortions due to an individual dislocation
X-ray micro-beam characterization of lattice rotations and distortions due to an individual dislocation
Dislocations are materials defects that have a major influence on structural and functional properties. Here, Hofmann et al.quantify the strain field due to an individual dislocation using X-ray micro-beam Laue diffraction, validating textbook elasticity theories.
- Felix Hofmann
- , Brian Abbey
- & Yuzi Liu
-
Article |
 Tensile testing of ultra-thin films on water surface
Tensile testing of ultra-thin films on water surface
The mechanical testing of thin films is non-trivial, due to their very fine dimensions. Kim et al. use the inherent surface tension of water as a platform for the frictionless tensile testing of gold films, with a thickness as fine as 55 nm.
- Jae-Han Kim
- , Adeel Nizami
- & Taek-Soo Kim
-
Article |
 Quantitative experimental determination of site-specific magnetic structures by transmitted electrons
Quantitative experimental determination of site-specific magnetic structures by transmitted electrons
Understanding magnetic materials at the nanoscale is important for the development of novel applications, but has been hampered by a lack of suitable experimental techniques. Here, the use of transmitted electrons permits the determination of atomic site-specific magnetic information.
- Z.Q. Wang
- , X.Y. Zhong
- & J. Zhu

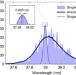 Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser
Attosecond interferometry with self-amplified spontaneous emission of a free-electron laser