Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A spin-crossover framework endowed with pore-adjustable behavior by slow structural dynamics
A spin-crossover framework endowed with pore-adjustable behavior by slow structural dynamics
Host-guest interactions can play a critical role in achieving switchable porous materials, but controlling them remains challenging. Here the authors report an atypical pore rearrangement in a magnetic 2D porous framework upon water adsorption; the structural transformation affects the magnetic properties of the material.
- Jin-Peng Xue
- , Yang Hu
- & Jun Tao
-
Article
| Open Access Plasma-induced surface cooling
Plasma-induced surface cooling
When a plasma interacts with a surface, different thermal effects may arise. Here, the authors explore plasma interactions with a surface that produce a surface cooling effect.
- John A. Tomko
- , Michael J. Johnson
- & Patrick E. Hopkins
-
Article
| Open Access Frenkel-defected monolayer MoS2 catalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
Frenkel-defected monolayer MoS2 catalysts for efficient hydrogen evolution
While material defect sites are active for chemical reactions, it is important to understand how different defect types impact reactivity. Here, authors prepare Frenkel-defected MoS2 monolayers and demonstrate improved performances for H2 evolution electrocatalysis than pristine or doped MoS2.
- Jie Xu
- , Gonglei Shao
- & Zhen Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Reaching the highest efficiency of spin Hall effect of light in the near-infrared using all-dielectric metasurfaces
Reaching the highest efficiency of spin Hall effect of light in the near-infrared using all-dielectric metasurfaces
Here, Junsuk Rho and co-workers propose and experimentally demonstrate a metasurface supporting a large and efficient spin Hall effect of light in optical wavelength. The spin Hall shifts reaching ten wavelengths with efficiencies over 70% are observed.
- Minkyung Kim
- , Dasol Lee
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the energy level alignment at donor/acceptor interfaces in non-fullerene organic solar cells
Mapping the energy level alignment at donor/acceptor interfaces in non-fullerene organic solar cells
Energy level alignment (ELA) at donor-acceptor heterojunctions is of vital importance yet largely undetermined in organic solar cells. Here, authors determine the heterojunction ELA with (mono) layer-by-layer precision to understand the co-existence of efficient charge.
- Xian’e Li
- , Qilun Zhang
- & Mats Fahlman
-
Article
| Open Access Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR as a tool to probe guest binding and exchange in metallohosts
Paramagnetic relaxation enhancement NMR as a tool to probe guest binding and exchange in metallohosts
Paramagnetic metallohost systems are difficult to characterize. Here the authors report that the paramagnetic relaxation enhancement effect can be used to prove by nuclear magnetic resonance experiments that Mn(III) porphyrin cage compounds can bind and thread low molecular weight and polymeric guests.
- Anne Swartjes
- , Paul B. White
- & Roeland J. M. Nolte
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral structures of electric polarization vectors quantified by X-ray resonant scattering
Chiral structures of electric polarization vectors quantified by X-ray resonant scattering
The polar chiral texture of the vortex or skyrmion structure in ferroelectric oxide PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice attracts attention. Here, the authors report a theoretical framework to probe emergent chirality of electrical polarization textures.
- Kook Tae Kim
- , Margaret R. McCarter
- & Dong Ryeol Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant neutron reflectometry for hydrogen detection
Resonant neutron reflectometry for hydrogen detection
The detection and quantification of hydrogen is becoming increasingly important in research on electronic materials and devices. Here the authors show that waveguide resonances enhance the sensitivity of neutron reflectometry, enabling fast, direct, and nondestructive measurements of hydrogen incorporation in thin-film structures.
- L. Guasco
- , Yu. N. Khaydukov
- & B. Keimer
-
Article
| Open Access In situ infrared nanospectroscopy of the local processes at the Li/polymer electrolyte interface
In situ infrared nanospectroscopy of the local processes at the Li/polymer electrolyte interface
Solid-state batteries remain promising but essential insights into electrode-electrolyte interface are required. Here, the authors report in situ infrared nanospectroscopy of the lithium-polymer-electrolyte interface to reveal its intrinsic molecular, structural, and chemical heterogeneities.
- Xin He
- , Jonathan M. Larson
- & Robert Kostecki
-
Article
| Open Access Growing single crystals of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks enabled by intermediate tracing study
Growing single crystals of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks enabled by intermediate tracing study
Resolving single-crystal structures of two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks (2D COFs) is a great challenge. Here, the authors identify two different growth mechanisms of COFs, enabling the growth and structure determination of micron-sized 2D single-crystalline COFs.
- Chengjun Kang
- , Kuiwei Yang
- & Dan Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access A dual-function liquid electrolyte additive for high-energy non-aqueous lithium metal batteries
A dual-function liquid electrolyte additive for high-energy non-aqueous lithium metal batteries
Lithium metal batteries suffer from poor (electro)chemical stability of the electrodes during prolonged cycling. Here, the authors report a dual function liquid electrolyte additive to form protective interphases on both electrodes to produce lab-scale high energy lithium metal batteries.
- Yuji Zhang
- , Yuan Wu
- & Chengxin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Demonstration of non-destructive and isotope-sensitive material analysis using a short-pulsed laser-driven epi-thermal neutron source
Demonstration of non-destructive and isotope-sensitive material analysis using a short-pulsed laser-driven epi-thermal neutron source
High-power laser beams can be used to accelerate neutron beams. Here the authors demonstrate the application of laser-driven neutron beams to neutron resonance spectroscopy and neutron resonance imaging.
- Marc Zimmer
- , Stefan Scheuren
- & Markus Roth
-
Article
| Open Access Optical sensors for operando stress monitoring in lithium-based batteries containing solid-state or liquid electrolytes
Optical sensors for operando stress monitoring in lithium-based batteries containing solid-state or liquid electrolytes
Chemo-mechanical stress within Li-based batteries detrimentally affects the performance and lifetime of these devices. Here, the authors propose an operando technique using optical fibers embedded in electrodes for internal stress monitoring of cells containing either solid or liquid electrolytes.
- Laura Albero Blanquer
- , Florencia Marchini
- & Jean-Marie Tarascon
-
Article
| Open Access Improving the oxygen redox reversibility of Li-rich battery cathode materials via Coulombic repulsive interactions strategy
Improving the oxygen redox reversibility of Li-rich battery cathode materials via Coulombic repulsive interactions strategy
Tailoring the oxygen redox reactivity in Li-rich cathode is crucial for developing high-energy batteries. Here, the authors report a strategy to obtain a flexible crystal structure and enhance the oxygen redox reversibility.
- Qingyuan Li
- , De Ning
- & Xiangfeng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access A self-driving laboratory advances the Pareto front for material properties
A self-driving laboratory advances the Pareto front for material properties
Useful materials must satisfy multiple objectives. The Pareto front expresses the trade-offs of competing objectives. This work uses a self-driving laboratory to map out the Pareto front for making highly conductive coatings at low temperatures.
- Benjamin P. MacLeod
- , Fraser G. L. Parlane
- & Curtis P. Berlinguette
-
Article
| Open Access Nontrivial nanostructure, stress relaxation mechanisms, and crystallography for pressure-induced Si-I → Si-II phase transformation
Nontrivial nanostructure, stress relaxation mechanisms, and crystallography for pressure-induced Si-I → Si-II phase transformation
Crystallographic theory suggests austenite-twinned martensite interfaces at specific orientations, but this is not the case for Si-I → Si-II phase transformation. Here the authors show the classically forbidden microstructure by combined experiments, simulations and crystallographic theory.
- Hao Chen
- , Valery I. Levitas
- & Nenad Velisavljevic
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced corrosion resistance by engineering crystallography on metals
Enhanced corrosion resistance by engineering crystallography on metals
Passive films on metal surfaces provide better corrosion resistance, but they can degrade in long-term service. Here the authors demonstrate a strategy to engineer crystallographic configuration at the metal/film interface to further improve corrosion resistance.
- X. X. Wei
- , B. Zhang
- & X. L. Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Multiphase flow detection with photonic crystals and deep learning
Multiphase flow detection with photonic crystals and deep learning
Photonic crystal (PC)-based sensing is an attractive approach for achieving accurate environmental sensing applications due to its band structure. Here, the authors utilize microwave transmission through PCs and deep learning physics-based data analytics to characterize flowing fluid mixtures.
- Lang Feng
- , Stefan Natu
- & John J. Valenza
-
Article
| Open Access Stochastic fluctuations of bosonic dark matter
Stochastic fluctuations of bosonic dark matter
Direct dark matter searches need to take into account whether the total observation time is lower than the characteristic coherence time of the DM field. Analysing this generally overlooked scenario, here the authors quantify the impact on DM limits of the stochastic nature of the virialised ultralight field.
- Gary P. Centers
- , John W. Blanchard
- & Andrei Derevianko
-
Article
| Open Access Time-resolved study of holeboring in realistic experimental conditions
Time-resolved study of holeboring in realistic experimental conditions
Experimental measurements involving multiple laser and plasma parameters are useful in understanding the relativistic laser-plasma interactions. Here the authors extend the model of holeboring for arbitrary profiles of laser pulse and plasma scale lengths.
- J. Hornung
- , Y. Zobus
- & V. Bagnoud
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time ultrafast oscilloscope with a relativistic electron bunch train
Real-time ultrafast oscilloscope with a relativistic electron bunch train
A travelling wave inside a metal slit can reveal its own waveform by probing deflecting motions of charged particles. Here, a real-time THz oscilloscope was demonstrated by utilizing the relativistic electrons and the subwavelength slit waveguide.
- In Hyung Baek
- , Hyun Woo Kim
- & Young Uk Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Defect engineering on V2O3 cathode for long-cycling aqueous zinc metal batteries
Defect engineering on V2O3 cathode for long-cycling aqueous zinc metal batteries
Aqueous Zn metal batteries are a promising system for high-power electrochemical energy storage. Here, the authors investigate a defective V2O3 cathode via neutron and X-ray techniques and test the material in Zn metal cell configuration for 30k cycles.
- Kefu Zhu
- , Shiqiang Wei
- & Li Song
-
Article
| Open Access Evolving contact mechanics and microstructure formation dynamics of the lithium metal-Li7La3Zr2O12 interface
Evolving contact mechanics and microstructure formation dynamics of the lithium metal-Li7La3Zr2O12 interface
All-solid-state batteries are promising alternatives to Li-ion batteries. Here, the authors investigate the chemo-mechanical changes at the lithium metal/solid electrolyte interface via operando acoustic transmission and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Wesley Chang
- , Richard May
- & Daniel Steingart
-
Article
| Open Access Uncovering the out-of-plane nanomorphology of organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction by GTSAXS
Uncovering the out-of-plane nanomorphology of organic photovoltaic bulk heterojunction by GTSAXS
Morphology of organic thin film, including the in-plane and out-of-plane directions, plays a crucial role in determining the performance of organic solar cells, yet the characterisation is challenging for the out-of-plane direction. Here, the authors use GTSAXS to uncover the nanomorphology in this dimension, and show how it affects exciton dissociation and charge transfer.
- Xinxin Xia
- , Tsz-Ki Lau
- & Xinhui Lu
-
Article
| Open Access In-situ spectroscopic observation of dynamic-coupling oxygen on atomically dispersed iridium electrocatalyst for acidic water oxidation
In-situ spectroscopic observation of dynamic-coupling oxygen on atomically dispersed iridium electrocatalyst for acidic water oxidation
Uncovering the dynamics of active sites in the working conditions is important yet challenging. Here the authors identify dynamic-coupling oxygen on atomically dispersed iridium sites during oxygen evolution reaction using in situ techniques.
- Hui Su
- , Wanlin Zhou
- & Shiqiang Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Stroboscopic operando spectroscopy of the dynamics in heterogeneous catalysis by event-averaging
Stroboscopic operando spectroscopy of the dynamics in heterogeneous catalysis by event-averaging
To follow in situ and in real time how catalyst surfaces respond to gas composition changes is a challenge. This study reports on an eventaveraging method, based on cyclic gas pulsing and software-based image recognition, that overcomes the challenge for large photoelectron spectroscopy datasets.
- Jan Knudsen
- , Tamires Gallo
- & Joachim Schnadt
-
Article
| Open Access Wigner solids of domain wall skyrmions
Wigner solids of domain wall skyrmions
Skyrmions, a topological spin texture, have been found in a variety of magnetic systems, including quantum hall ferromagnets. Here, Yang et al demonstrate the existence of skyrmions in domain walls in a quantum Hall ferromagnet, and suggest that these skyrmions form a 1D Wigner crystal.
- Kaifeng Yang
- , Katsumi Nagase
- & Hongwu Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Turn-key constrained parameter space exploration for particle accelerators using Bayesian active learning
Turn-key constrained parameter space exploration for particle accelerators using Bayesian active learning
Characterizing an unknown, complex system, like an accelerator, in multi-dimensional space is a challenging task. Here the authors report a Bayesian active learning method - Constrained Proximal Bayesian Exploration - for the characterization of a complex, constrained measurement as a function of multiple free parameters.
- Ryan Roussel
- , Juan Pablo Gonzalez-Aguilera
- & Auralee Edelen
-
Article
| Open Access Direct measurement of ferroelectric polarization in a tunable semimetal
Direct measurement of ferroelectric polarization in a tunable semimetal
Free carriers and electrical polarization coexist in ferroelectric metals. Here, the authors use a capacitive method to probe the electronic compressibility of free carriers in a tunable semimetal, extract the polarized contribution, and study the carrier dependence of the ferroelectric state.
- Sergio C. de la Barrera
- , Qingrui Cao
- & Benjamin M. Hunt
-
Comment
| Open Access The need for robust characterization of nanomaterials for nanomedicine applications
The need for robust characterization of nanomaterials for nanomedicine applications
Robust and precise characterization of the interactions between nanoengineered materials and biosystems is vital for the development of safe, efficient diagnostic and therapeutic nanomedicines. This comment discusses the key aspects of nanoparticle characteristics affecting the interpretation of nano-bio interface data.
- Morteza Mahmoudi
-
Article
| Open Access Artificial sodium-selective ionic device based on crown-ether crystals with subnanometer pores
Artificial sodium-selective ionic device based on crown-ether crystals with subnanometer pores
Artificial sodium channels open up the way to new separation technologies but remains highly challenging. In this work, the authors report an artificial sodium-selective ionic device, built on porous crown-ether crystals with a sodium ion selectivity against calcium ions exceeding that one of biological ion channel counterparts.
- Tingyan Ye
- , Gaolei Hou
- & Jun Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
Additive manufacturing of strong silica sand structures enabled by polyethyleneimine binder
The limited strength of green parts have been a major hurdle in the Binder Jet Additive Manufacturing. Here the authors apply polyethyleneimine binder to print silica sand structures with double the flexural strength of green parts and 8-fold increase in the strength upon reactive infiltration.
- Dustin B. Gilmer
- , Lu Han
- & Tomonori Saito
-
Article
| Open Access Inertial and viscous flywheel sensing of nanoparticles
Inertial and viscous flywheel sensing of nanoparticles
Balances for nanoparticles such as resonating fluid-filled cantilevers usually probe only mass through changes in oscillation frequency. Katsikis and Collis et al. tap information from previously ignored rotational motion to simultaneously measure particle mass and volume.
- Georgios Katsikis
- , Jesse F. Collis
- & Scott R. Manalis
-
Article
| Open Access Superior photo-carrier diffusion dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites revealed by spatiotemporal conductivity imaging
Superior photo-carrier diffusion dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid perovskites revealed by spatiotemporal conductivity imaging
Spatiotemporal dynamic of charge carriers is commonly studied with optical or photoconductivity measurements, yet these techniques come with their own limitations. To circumvent these limits, the authors probe the free-carrier diffusion dynamics of microsecond lifetimes via laser-illuminated microwave impedance microscopy.
- Xuejian Ma
- , Fei Zhang
- & Keji Lai
-
Article
| Open Access X-ray studies bridge the molecular and macro length scales during the emergence of CoO assemblies
X-ray studies bridge the molecular and macro length scales during the emergence of CoO assemblies
The understanding of nucleation and growth of nanostructures plays a key role in complex materials design. Here, the authors illustrate how X-ray in situ studies link transformation at the molecular- and macro- length scales during the emergence of cobalt oxide assemblies.
- Lukas Grote
- , Cecilia A. Zito
- & Dorota Koziej
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal and electronic facet analysis of ultrafine Ni2P particles by solid-state NMR nanocrystallography
Crystal and electronic facet analysis of ultrafine Ni2P particles by solid-state NMR nanocrystallography
Structural and morphological control of crystalline nanoparticles is crucial in heterogeneous catalysis. Applying DFT-assisted solid-state NMR spectroscopy, we determine the surface crystal and electronic structure of Ni2P nanoparticles, unveiling NMR nanocrystallography as an emerging tool in facet-engineered nanocatalysts.
- Wassilios Papawassiliou
- , José P. Carvalho
- & Andrew J. Pell
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional atomic mapping of ligands on palladium nanoparticles by atom probe tomography
Three-dimensional atomic mapping of ligands on palladium nanoparticles by atom probe tomography
Despite the important role of ligands in designing nanoparticles, directly imaging them on the nanoparticle surface remains a challenge. Here, the authors use atom probe tomography to map the spatial distribution of ligands on nanoparticles and reveal that the interplay between halide and cetrimonium ligands decides the oxidation resistance and shape of Pd nanoparticles.
- Kyuseon Jang
- , Se-Ho Kim
- & Pyuck-Pa Choi
-
Article
| Open Access Interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution
Interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution
The construction of Z-scheme heterostructures is of great significance for realizing efficient photocatalytic water splitting. Here, the authors report an interfacial chemical bond and internal electric field modulated Z-Scheme Sv-ZnIn2S4/MoSe2 photocatalyst for efficient hydrogen evolution.
- Xuehua Wang
- , Xianghu Wang
- & Zhenjiang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Atomically-resolved interlayer charge ordering and its interplay with superconductivity in YBa2Cu3O6.81
Atomically-resolved interlayer charge ordering and its interplay with superconductivity in YBa2Cu3O6.81
Charge ordering and superconductivity are known to compete in layered cuprates; however, precise real-space characterization of their interplay has been lacking. Here, the authors address this using atomically-resolved cross-sectional scanning tunnelling microscopy and spectroscopy on cryogenically cleaved YBa2Cu3O6.81.
- Chun-Chih Hsu
- , Bo-Chao Huang
- & Ya-Ping Chiu
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution and expansion of Li concentration gradient during charge–discharge cycling
Evolution and expansion of Li concentration gradient during charge–discharge cycling
Quantification of Li ions in local area is key to understand the degradation of Li ion batteries. Here the authors report Li compositional gradient evolution in the cathode after charge-discharge cycles using a complementary study via atom probe tomography and scanning transmission electron microscopy.
- Byeong-Gyu Chae
- , Seong Yong Park
- & Woo Sung Jeon
-
Comment
| Open Access Correlating advanced microscopies reveals atomic-scale mechanisms limiting lithium-ion battery lifetime
Correlating advanced microscopies reveals atomic-scale mechanisms limiting lithium-ion battery lifetime
The longevity of a lithium-ion battery is limited by cathode degradation. Combining atom probe tomography and scanning transmission electron microscopy reveals that the degradation results from atomic-scale irreversible structural changes once lithium leaves the cathode during charging, thereby inhibiting lithium intercalation back into the cathode as the battery discharges. This information unveils possible routes for improving the lifetime of lithium-ion batteries.
- Baptiste Gault
- & Jonathan D. Poplawsky
-
Article
| Open Access Mesoscale structure development reveals when a silkworm silk is spun
Mesoscale structure development reveals when a silkworm silk is spun
Studying the development of silk structure is important for understanding material properties and biomimetics. Here, the authors use ex vivo processing to characterise the stages of silk spinning and identify a consolidation phase where transient water pockets emerge due to multiple factors leading to nanofibril coalescence.
- Quan Wan
- , Mei Yang
- & Mingying Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Laser-excited elastic guided waves reveal the complex mechanics of nanoporous silicon
Laser-excited elastic guided waves reveal the complex mechanics of nanoporous silicon
Assessing mechanics of nanoporous silicon is challenging, but important for new applications. Here, the authors use non-destructive laser-excited elastic guided waves detected contactless, to study dry and liquid-infused single-crystalline porous silicon, revealing its complex mechanics and significant deviations from bulk silicon.
- Marc Thelen
- , Nicolas Bochud
- & Patrick Huber
-
Article
| Open Access Structural-profiling of low molecular weight RNAs by nanopore trapping/translocation using Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A
Structural-profiling of low molecular weight RNAs by nanopore trapping/translocation using Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A
Nanopores have been used for direct observation of RNA structure in native environments but have limited RNA differentiation capabilities. Here, the authors report on the use of Mycobacterium smegmatis porin A nanopores for the trapping and translocation identification of microRNA, siRNA, tRNA and ribosomal RNA.
- Yuqin Wang
- , Xiaoyu Guan
- & Shuo Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Atomistic insights into the nucleation and growth of platinum on palladium nanocrystals
Atomistic insights into the nucleation and growth of platinum on palladium nanocrystals
Creating predictable, controllable nanoparticles relies on a mechanistic understanding of their synthesis. Here, through integrated in situ liquid microscopy and first-principles calculations, the authors elucidate the atomistic details involved in the formation of colloidal core-shell nanoparticles.
- Wenpei Gao
- , Ahmed O. Elnabawy
- & Miaofang Chi
-
Article
| Open Access Label-free characterization of organic nanocarriers reveals persistent single molecule cores for hydrocarbon sequestration
Label-free characterization of organic nanocarriers reveals persistent single molecule cores for hydrocarbon sequestration
In-situ methods are important for investigating the local structure and function in molecular nanostructures but such investigations often involve laborious labeling methods that can disrupt behavior or are not fast enough to capture stimuli-responsive phenomena. Here, the authors use X-rays resonant with molecular bonds to demonstrate an in-situ nanoprobe that eliminates the need for labels and enables data collection times within seconds.
- Terry McAfee
- , Thomas Ferron
- & Brian A. Collins
-
Article
| Open Access Event generation and statistical sampling for physics with deep generative models and a density information buffer
Event generation and statistical sampling for physics with deep generative models and a density information buffer
Here, the authors report buffered-density variational autoencoders for the generation of physical events. This method is computationally less expensive over other traditional methods and beyond accelerating the data generation process, it can help to steer the generation and to detect anomalies.
- Sydney Otten
- , Sascha Caron
- & Rob Verheyen
-
Article
| Open Access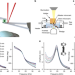 Rheology of rounded mammalian cells over continuous high-frequencies
Rheology of rounded mammalian cells over continuous high-frequencies
While rheology studies have contributed to the understanding of the viscoelastic properties of living cells, the use of higher frequencies promises elucidate the link between cellular and molecular properties. Here authors introduce a rheological assay that measures the cell mechanical response across a continuous frequency range ≈ 1 – 40 kHz.
- Gotthold Fläschner
- , Cosmin I. Roman
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access In situ correlation between metastable phase-transformation mechanism and kinetics in a metallic glass
In situ correlation between metastable phase-transformation mechanism and kinetics in a metallic glass
The competition between the formation of different phases and their kinetics need to be clearly understood to make materials with on-demand and multifaceted properties. Here, the authors reveal, by a combination of complementary in situ techniques, the mechanism of a Cu-Zr-Al metallic glass’s high propensity for metastable phase formation, which is partially through a kinetic mechanism of Al partitioning.
- Jiri Orava
- , Shanoob Balachandran
- & Ivan Kaban

 Compositional dependence of the fragility in metallic glass forming liquids
Compositional dependence of the fragility in metallic glass forming liquids