Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Liquid-state quantitative SERS analyzer on self-ordered metal liquid-like plasmonic arrays
Liquid-state quantitative SERS analyzer on self-ordered metal liquid-like plasmonic arrays
The design and application of a liquid interfacial plasmonic platform promises for practical applications of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Here, the authors report a reversible chloroform/water encasing strategy to self-assemble metal liquid-like 3D gold nanorod arrays with attractive SERS capability.
- Li Tian
- , Mengke Su
- & Weihong Tan
-
Article
| Open Access Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
Anomalous twin boundaries in two dimensional materials
All materials subjected to mechanical deformation form low energy interfaces known as twin boundaries. Here, the authors investigate a variety of structural features that form upon bending atomically thin 2D-crystals, and predict distinct classes of post deformation microstructure based on their atomic arrangement, bend angle and flake thickness.
- A. P. Rooney
- , Z. Li
- & S. J. Haigh
-
Article
| Open Access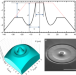 Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Single crystal toroidal diamond anvils for high pressure experiments beyond 5 megabar
Static pressures exceeding 4 million atmospheres are extremely challenging to achieve, but are necessary for the study of matter that exists under these conditions in natural environments. Here, diamonds anvils with a toroidal design are demonstrated to sustain over 6 million atmospheres in a diamond anvil cell.
- Zs. Jenei
- , E. F. O’Bannon
- & W. J. Evans
-
Article
| Open Access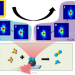 Active site localization of methane oxidation on Pt nanocrystals
Active site localization of methane oxidation on Pt nanocrystals
The structural changes at low-coordination sites of nanocatalysts such as edges, remain poorly understood. Here, the authors report observations of high-lattice distortion at edges of Pt nanocrystals during heterogeneous catalytic methane oxidation by using in situ 3D Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction imaging.
- Dongjin Kim
- , Myungwoo Chung
- & Hyunjung Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Morphology and structure of ZIF-8 during crystallisation measured by dynamic angle-resolved second harmonic scattering
Angle-resolved monitoring of structure parameters during crystal growth is often slow owing to mechanical movements. Here, the authors use second harmonic scattering and Fourier-plane imaging to dynamically monitor size, shape and concentration of ZIF-8 in situ during the growth process.
- Stijn Van Cleuvenbergen
- , Zachary J. Smith
- & Monique A. van der Veen
-
Article
| Open Access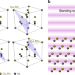 Element- and momentum-resolved electronic structure of the dilute magnetic semiconductor manganese doped gallium arsenide
Element- and momentum-resolved electronic structure of the dilute magnetic semiconductor manganese doped gallium arsenide
The knowledge of the electronic structure of composite material is essential for tailoring their properties. The authors introduce a method based on standing wave angle-resolved hard X-ray photoemission to determine the element- and momentum-resolved electronic band structure simultaneously.
- Slavomír Nemšák
- , Mathias Gehlmann
- & Charles S. Fadley
-
Article
| Open Access Surveying silicon nitride nanopores for glycomics and heparin quality assurance
Surveying silicon nitride nanopores for glycomics and heparin quality assurance
The complexity of polysaccharides significantly complicates their analysis in comparison to other biopolymers. Here, the authors demonstrate that solid-state silicon nitride nanopore sensors can be used to reliably detect native polysaccharides and to perform a simple quality assurance assay on a polysaccharide therapeutic, heparin.
- Buddini Iroshika Karawdeniya
- , Y. M. Nuwan D. Y. Bandara
- & Jason R. Dwyer
-
Article
| Open Access Optical emission near a high-impedance mirror
Optical emission near a high-impedance mirror
Light emission of molecules can be largely impacted (enhanced or quenched) by nearby surfaces. Here, Esfandyarpour et al. engineer a high-impedance mirror that increases light emission of adjacent molecules by enhancing the coupling between the molecule and free space.
- Majid Esfandyarpour
- , Alberto G. Curto
- & Mark L. Brongersma
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly by thermal hysteresis
Complex assembly pathways often involve transient, partly-formed intermediates that are challenging to characterize. Here, the authors present a simple and rapid spectroscopic thermal hysteresis method for mapping the energy landscapes of supramolecular assembly.
- Robert W. Harkness V
- , Nicole Avakyan
- & Anthony K. Mittermaier
-
Article
| Open Access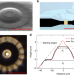 Toroidal diamond anvil cell for detailed measurements under extreme static pressures
Toroidal diamond anvil cell for detailed measurements under extreme static pressures
Extreme static pressures exceeding a million atmospheres exist in a variety of natural environments, but obtaining such pressures in a laboratory is still a challenge. Here, the authors develop a toroidal diamond anvil design that allows for the generation of 600 GPa (6 million atmospheres) in routinely used diamond anvil cells.
- Agnès Dewaele
- , Paul Loubeyre
- & Mohamed Mezouar
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-level insight into super-efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution on iron and vanadium co-doped nickel (oxy)hydroxide
Atomic-level insight into super-efficient electrocatalytic oxygen evolution on iron and vanadium co-doped nickel (oxy)hydroxide
While splitting water could provide a renewable way to produce fuel, highly active catalysts are needed to overcome water oxidation’s sluggish kinetics. Here, authors gain atomic-level insight on metal ion synergetic interactions that boost water oxidation performances in co-doped nickel hydroxide.
- Jian Jiang
- , Fanfei Sun
- & Mei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Self-hydrogenated shell promoting photocatalytic H2 evolution on anatase TiO2
Self-hydrogenated shell promoting photocatalytic H2 evolution on anatase TiO2
Photocatalytic water splitting on TiO2 is a promising route to H2 fuel production, but the mechanistic pathway at the water–TiO2 interface remains poorly understood. Here, using liquid environmental TEM and first-principles calculations, the authors unveil the formation of a self-hydrogenated shell on the TiO2 surface that further promotes H2 production.
- Yue Lu
- , Wen-Jin Yin
- & Man-Ling Sui
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetostatic twists in room-temperature skyrmions explored by nitrogen-vacancy center spin texture reconstruction
Magnetostatic twists in room-temperature skyrmions explored by nitrogen-vacancy center spin texture reconstruction
The Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) is crucial to the stabilization of skyrmions but the contribution is not well understood. Here, the authors provide a methodology using the single electron spin of a nitrogen-vacancy center to image the fine structure of skyrmions which is attributed to the competition between the DMI and stray fields.
- Y. Dovzhenko
- , F. Casola
- & A. Yacoby
-
Article
| Open Access Structure determination from single molecule X-ray scattering with three photons per image
Structure determination from single molecule X-ray scattering with three photons per image
Existing methods to extract structural information from single-molecule scattering measurements require large number of photons per image. Here the authors discuss a method to reconstruct the structure of a molecule from X-ray scattering data by using only three photons per image.
- Benjamin von Ardenne
- , Martin Mechelke
- & Helmut Grubmüller
-
Article
| Open Access Structural resolution of inorganic nanotubes with complex stoichiometry
Structural resolution of inorganic nanotubes with complex stoichiometry
Structural determination of inorganic nanotubes has lagged far behind that of their carbon-based counterparts. Here, the authors present a transferable methodology, combining wide angle X-ray scattering and computation, to quantitatively resolve the atomic structure of inorganic nanotubes with complex stoichiometry.
- Geoffrey Monet
- , Mohamed S. Amara
- & Pascale Launois
-
Article
| Open Access Tomographic and multimodal scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with peak force tapping mode
Tomographic and multimodal scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy with peak force tapping mode
Scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) offers nanometer-scale spatial resolution, but generally does not retain tomographic information. Here, Wang et al. develop peak-force SNOM to section scattered fields and improve imaging resolution.
- Haomin Wang
- , Le Wang
- & Xiaoji G. Xu
-
Article
| Open Access High spatial resolution nanoslit SERS for single-molecule nucleobase sensing
High spatial resolution nanoslit SERS for single-molecule nucleobase sensing
Direct and real-time identification of nucleobases in DNA strands is still limited by the sensitivity and spatial resolution of the established solid-state nanopore devices. Here, the authors use CMOS compatible, plasmonic nanoslits to locally enable SERS for identifying nucleobases, both individual and incorporated in DNA strands.
- Chang Chen
- , Yi Li
- & Pol Van Dorpe
-
Article
| Open Access Self-cleaning and surface chemical reactions during hafnium dioxide atomic layer deposition on indium arsenide
Self-cleaning and surface chemical reactions during hafnium dioxide atomic layer deposition on indium arsenide
Atomic layer deposition of high-quality thin oxide layers is crucial for many modern semiconductor electronic devices. Here, the authors explore the surface chemistry during the initial deposition and observe a previously unknown two-step process, with promise for an improved self-cleaning effect.
- Rainer Timm
- , Ashley R. Head
- & Anders Mikkelsen
-
Article
| Open Access Quantitative 3D determination of self-assembled structures on nanoparticles using small angle neutron scattering
Quantitative 3D determination of self-assembled structures on nanoparticles using small angle neutron scattering
The ligand shell of a nanoparticle remains difficult to resolve, as the available characterization methods provide only qualitative information. Here, the authors introduce an approach based on small-angle neutron scattering that can quantitatively reveal the organization of ligands in mixed-monolayer nanoparticles.
- Zhi Luo
- , Domenico Marson
- & Francesco Stellacci
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear disarmament verification via resonant phenomena
Nuclear disarmament verification via resonant phenomena
Authenticating a nuclear warhead without revealing its design is a challenge. Here the authors discuss a nuclear disarmament verification method based on neutron resonance analysis which is sensitive to the isotopic composition of the materials used in warheads.
- Jake J. Hecla
- & Areg Danagoulian
-
Article
| Open Access Electron heating and thermal relaxation of gold nanorods revealed by two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Electron heating and thermal relaxation of gold nanorods revealed by two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy
Electron dynamics in plasmonic nanoparticles are often studied with transient absorption spectroscopy. Here, Lietard et al. apply two-dimensional electronic spectroscopy, a method generally used for molecular spectroscopy, to study ultrafast nonlinear dynamics of electrons in excited gold nanorods.
- Aude Lietard
- , Cho-Shuen Hsieh
- & Minhaeng Cho
-
Article
| Open Access A non-invasive method to directly quantify surface heterogeneity of porous materials
A non-invasive method to directly quantify surface heterogeneity of porous materials
Surface heterogeneity significantly influences the properties of porous materials, but remains extremely difficult to characterize. Here, the authors extend Porod’s scattering law from homogeneous to heterogeneous porous materials, allowing for surface variation to be non-invasively probed.
- Wei-Shan Chiang
- , Daniel Georgi
- & Yun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Inference of field reversed configuration topology and dynamics during Alfvenic transients
Inference of field reversed configuration topology and dynamics during Alfvenic transients
It is important to understand the fast plasma dynamics in the operation of fusion plasma devices. Here the authors demonstrate the inference on the internal field reversed configuration magnetic topology and their occurrence during fast Alfvenic transient phenomena in C-2U device.
- J. A. Romero
- , S. A. Dettrick
- & Y. Mok
-
Article
| Open Access Probing electrochemical reactions in organic cathode materials via in operando infrared spectroscopy
Probing electrochemical reactions in organic cathode materials via in operando infrared spectroscopy
Metal-organic batteries are gaining traction as versatile, low-cost, and sustainable devices, although there are still few ways to probe internal behavior during use. Here, the authors explore organic-molecule structural changes within several battery systems by in operando infrared spectroscopy.
- Alen Vizintin
- , Jan Bitenc
- & Robert Dominko
-
Article
| Open Access Laser-accelerated particle beams for stress testing of materials
Laser-accelerated particle beams for stress testing of materials
Recently, there has been significant progress on the application of laser-generated proton beams in material science. Here the authors demonstrate the benefit of employing such beams in stress testing different materials by examining their mechanical, optical, electrical, and morphological properties.
- M. Barberio
- , M. Scisciò
- & P. Antici
-
Article
| Open Access Picometer polar atomic displacements in strontium titanate determined by resonant X-ray diffraction
Picometer polar atomic displacements in strontium titanate determined by resonant X-ray diffraction
It is a challenge to measure changes in the crystal structures in picometer scale and the associated phase. Here the authors demonstrate the lattice expansion and polar distortions of oxygen deficient SrTiO3 using a resonance X-ray scattering technique.
- Carsten Richter
- , Matthias Zschornak
- & Dirk C. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale geochemical and geomechanical characterization of organic matter in shale
Nanoscale geochemical and geomechanical characterization of organic matter in shale
Solid organic matter (OM) plays a key role in the production of hydrocarbons in shale formations, yet information on OM heterogeneity at a nanoscale is lacking. Here, the authors use atomic force microscopy-based infrared spectroscopy to document the evolution of individual organic macerals with maturation.
- Jing Yang
- , Javin Hatcherian
- & Andrew E. Pomerantz
-
Article
| Open Access Probing defect dynamics in monolayer MoS2 via noise nanospectroscopy
Probing defect dynamics in monolayer MoS2 via noise nanospectroscopy
The intrinsic properties of atomically thin MoS2 are believed to be strongly affected by the presence of structural defects; however, the underlying physical mechanism of such link is not fully understood. Here, the authors combine noise-current analysis with atomic force microscopy to explore the relationship between point defects and the anomalous physical properties of MoS2 monolayers.
- Seung Hyun Song
- , Min-Kyu Joo
- & Young Hee Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Atomic-resolution three-dimensional hydration structures on a heterogeneously charged surface
Local hydration structures at solid-liquid interfaces are important in catalytic, electrochemical, and biological processes. Here, the authors demonstrate atomic-scale 3D hydration structures around the boundary on a heterogeneous mineral surface using atomic force microscopy experiments and molecular dynamics simulations.
- Kenichi Umeda
- , Lidija Zivanovic
- & Hirofumi Yamada
-
Article
| Open Access Spectroscopic identification of active sites for the oxygen evolution reaction on iron-cobalt oxides
Spectroscopic identification of active sites for the oxygen evolution reaction on iron-cobalt oxides
Optimization of electrocatalysts requires an understanding of all active reaction sites. Here, the authors combine X-ray absorption spectroscopy and electrochemistry to identify cobalt atoms with different coordination geometries and probe their contribution to electrocatalytic water oxidation.
- Rodney D. L. Smith
- , Chiara Pasquini
- & Holger Dau
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled spin switching in a metallocene molecular junction
Controlled spin switching in a metallocene molecular junction
Manipulating spin states of molecules in a controllable manner is essential to develop the molecule-based spintronics technologies. Here, Ormaza et al. show how to use the interaction between a single metallocene molecule and a metallic surface to reversibly switch spin from 1 to ½ in a junction.
- M. Ormaza
- , P. Abufager
- & L. Limot
-
Article
| Open Access Adhesion toughness of multilayer graphene films
Adhesion toughness of multilayer graphene films
The reason why the surface adhesion of a graphene monolayer is much greater than that of graphene multilayers remains unclear. Here, the authors build a model to show interlayer sliding and fracture mode mixity cause the decrease in adhesion toughness of multilayer graphene.
- Joseph D. Wood
- , Christopher M. Harvey
- & Simon Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Bending and breaking of stripes in a charge ordered manganite
Bending and breaking of stripes in a charge ordered manganite
Charge-lattice coupling plays a central role in the exotic behaviors of multiferroic complex oxides, such as manganites, however, obtaining a microscopic picture is challenging. Here, Savitzky et al. map periodic lattice displacement fields at the picometer scale to study local order-disorder competition.
- Benjamin H. Savitzky
- , Ismail El Baggari
- & Lena F. Kourkoutis
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Mapping microscale wetting variations on biological and synthetic water-repellent surfaces
Real-world surfaces exhibit spatially varying wettability, which affects water repellency and droplet behaviour on such surfaces. Here, the authors use scanning droplet adhesion microscopy to create wetting maps that visualize variations in wettability with a spatial resolution down to 10 μm.
- Ville Liimatainen
- , Maja Vuckovac
- & Robin H. A. Ras
-
Article
| Open Access The influence of the solid to plasma phase transition on the generation of plasma instabilities
The influence of the solid to plasma phase transition on the generation of plasma instabilities
Exploring the plasma processes in the pre-plasma state that lead to instabilities is challenging. Here the authors probe the evolution of the plasma phase change and the instabilities in plasma created by an exploding copper wire in Z-pinch geometry using shadowgraphy.
- E. Kaselouris
- , V. Dimitriou
- & M. Tatarakis
-
Article
| Open Access Complex three-dimensional self-assembly in proxies for atmospheric aerosols
Complex three-dimensional self-assembly in proxies for atmospheric aerosols
Nearly all atmospheric aerosols contain surface-active organic compounds; however, the nature of how they arrange remains poorly understood. Here, the authors show that fatty acids in atmospheric aerosol proxies self-assemble into highly ordered, viscous 3D nanostructures that undergo changes upon exposure to humidity and ozone.
- C. Pfrang
- , K. Rastogi
- & A. M. Squires
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale tomography reveals the deactivation of automotive copper-exchanged zeolite catalysts
Nanoscale tomography reveals the deactivation of automotive copper-exchanged zeolite catalysts
Cu-exchanged zeolite chabazite has superior stability over other catalysts in automotive NOx reduction. Here, the authors use atom probe tomography to create 3D nanoscale reconstructions of two Cu-containing zeolite catalysts, providing a complete picture of their deactivation mechanisms during aging.
- Joel E. Schmidt
- , Ramon Oord
- & Bert M. Weckhuysen
-
Article
| Open Access In situ real-time gravimetric and viscoelastic probing of surface films formation on lithium batteries electrodes
In situ real-time gravimetric and viscoelastic probing of surface films formation on lithium batteries electrodes
The solid-electrolyte interphase formed on Li-battery electrodes strongly affects their cycling performance, however the mechanical properties of the surface films are not well-known. Here the authors report a sensitive gravimetric/viscoelastic method to probe surface film formation on composite electrodes, coupled with Li-ion intercalation.
- Vadim Dargel
- , Netanel Shpigel
- & Doron Aurbach
-
Article
| Open Access Nonlinear dynamic characterization of two-dimensional materials
Nonlinear dynamic characterization of two-dimensional materials
The mechanical resonances of atomically thin membranes show nonlinear responses at driving forces in the picoNewton range. Here, the authors develop a contactless method to extract the Young’s modulus of 2D materials from the nonlinear dynamic response of these nanomechanical resonators.
- D. Davidovikj
- , F. Alijani
- & P. G. Steeneken
-
Article
| Open Access Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy
Piezo-generated charge mapping revealed through direct piezoelectric force microscopy
Piezoelectrics and ferroelectrics are important for everyday applications, but methods to characterize these materials at the nanoscale are lacking. Here the authors present direct piezoelectric force microscopy, an AFM mode that can measure charges generated by the direct piezoelectric effect with nanoscale resolution.
- A. Gomez
- , M. Gich
- & X. Obradors
-
Article
| Open Access Grain boundary mediated hydriding phase transformations in individual polycrystalline metal nanoparticles
Grain boundary mediated hydriding phase transformations in individual polycrystalline metal nanoparticles
Grain boundaries are thought to significantly mediate phase transformations in nanoparticles. Here, the authors combine multichannel plasmonic nanospectroscopy and transmission Kikuchi diffraction to study the role of grain boundaries in hydriding reactions of Pd nanoparticles on a single-particle level.
- Svetlana Alekseeva
- , Alice Bastos da Silva Fanta
- & Christoph Langhammer
-
Article
| Open Access Anomeric memory of the glycosidic bond upon fragmentation and its consequences for carbohydrate sequencing
Anomeric memory of the glycosidic bond upon fragmentation and its consequences for carbohydrate sequencing
Establishing generic carbohydrate sequencing methods is both a major scientific challenge and a strategic priority. Here the authors show a hybrid analytical approach integrating molecular spectroscopy and mass spectrometry to resolve carbohydrate isomerism, anomeric configuration, regiochemistry and stereochemistry.
- Baptiste Schindler
- , Loïc Barnes
- & Isabelle Compagnon
-
Article
| Open Access Lifshitz transition from valence fluctuations in YbAl3
Lifshitz transition from valence fluctuations in YbAl3
How the electronic structure of a mixed-valence system changes with respect to local chemical environment remains elusive. Here, Chatterjee et al. show that valence fluctuations of YbAl3 can lead to dramatic changes in the Fermi surface topology in reciprocal space.
- Shouvik Chatterjee
- , Jacob P. Ruf
- & Kyle M. Shen
-
Article
| Open Access In situ atomic-scale observation of oxygen-driven core-shell formation in Pt3Co nanoparticles
In situ atomic-scale observation of oxygen-driven core-shell formation in Pt3Co nanoparticles
Core-shell platinum alloy nanoparticles are promising catalysts for oxygen reduction, however a deeper understanding of core-shell formation is still required. Here the authors report oxygen-driven formation of core-shell Pt3Co nanoparticles, seen at the atomic scale with in situ electron microscopy at ambient pressure.
- Sheng Dai
- , Yuan You
- & Xiaoqing Pan
-
Article
| Open Access In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
In situ stable crack growth at the micron scale
To improve mechanical properties in ceramics through grain boundary engineering, precise mechanical characterization of individual boundaries is vital yet difficult to achieve. Here authors perform experiments using an in situ scanning electron microscopy based double cantilever beam test, allowing to directly view and measure stable crack growth in silicon carbide.
- Giorgio Sernicola
- , Tommaso Giovannini
- & Finn Giuliani
-
Article
| Open Access Auger electron emission initiated by the creation of valence-band holes in graphene by positron annihilation
Auger electron emission initiated by the creation of valence-band holes in graphene by positron annihilation
Auger processes are at the core of electron emission in solid-state physics, however measuring the spectra of electrons emitted solely as a result of Auger transitions remains a challenge. Here, the authors measure the electron energy spectrum in graphene and observe the prominence of Auger-like processes in its valence band.
- V. A. Chirayath
- , V. Callewaert
- & A. H. Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access Exploring the hidden interior of the Earth with directional neutrino measurements
Exploring the hidden interior of the Earth with directional neutrino measurements
The detection of Earth’s anti neutrino emission from potassium and the mantle remain elusive. Here the authors propose a method for measuring potassium and mantle geo-neutrinos by detecting their elastic scattering on electrons with direction-sensitive detectors.
- Michael Leyton
- , Stephen Dye
- & Jocelyn Monroe
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental neutron scattering evidence for proton polaron in hydrated metal oxide proton conductors
Experimental neutron scattering evidence for proton polaron in hydrated metal oxide proton conductors
Hydration of oxygen vacancies could form hydroxyl groups with interstitial structural protons. Here a quasi-elastic neutron scattering study reveals proton polarons in proton-conducting ceramic electrolytes, and the proton transport turns out to be a cooperative process.
- Artur Braun
- & Qianli Chen
-
Article
| Open Access All-optical observation and reconstruction of spin wave dispersion
All-optical observation and reconstruction of spin wave dispersion
Observation of the entire dispersion relation for spin waves remains a challenge which prevents the full understanding of many intriguing magnetic properties. Here, the authors develop a table-top all-optical approach to map out the dispersion curve of pure-magnetostatic waves in magnetic films.
- Yusuke Hashimoto
- , Shunsuke Daimon
- & Eiji Saitoh

 Triboelectric microplasma powered by mechanical stimuli
Triboelectric microplasma powered by mechanical stimuli