Featured
-
-
Article |
 Brilliant femtosecond-laser-driven hard X-ray flashes from carbon nanotube plasma
Brilliant femtosecond-laser-driven hard X-ray flashes from carbon nanotube plasma
Compact laser-wakefield-driven X-ray sources show promise but suffer from poor conversion efficiency. New research demonstrates high-yield, hard X-rays generated by using carbon nanotube targets, instead of gases.
- Yinren Shou
- , Pengjie Wang
- & Wenjun Ma
-
Article |
 Bright short-wavelength infrared organic light-emitting devices
Bright short-wavelength infrared organic light-emitting devices
Organic LEDs based on acceptor–donor–acceptor molecules Y11, IDSe-4Cl and COTIC-4F are shown to be highly effective emitters of short-wave infrared light.
- Yuan Xie
- , Wansheng Liu
- & Yong Cao
-
Article |
 Continuous transition between weak and ultrastrong coupling through exceptional points in carbon nanotube microcavity exciton–polaritons
Continuous transition between weak and ultrastrong coupling through exceptional points in carbon nanotube microcavity exciton–polaritons
A microcavity exciton–polariton system based on aligned and packed single-walled carbon nanotubes exhibits ultrastrong coupling. The coupling strength is polarization sensitive. The record high value of vacuum Rabi splitting, 329 meV, is reported.
- Weilu Gao
- , Xinwei Li
- & Junichiro Kono
-
-
News & Views |
 Nanotube chemistry tunes light
Nanotube chemistry tunes light
Room-temperature single-photon emission at several wavelengths in the near-infrared, including the telecom window, is realized by organic colour centres chemically implanted on chirality-defined single-walled carbon nanotubes.
- Kartik Srinivasan
- & Ming Zheng
-
Article |
 Tunable room-temperature single-photon emission at telecom wavelengths from sp3 defects in carbon nanotubes
Tunable room-temperature single-photon emission at telecom wavelengths from sp3 defects in carbon nanotubes
Single-photon emission with 99% purity is generated from sp3 defects in carbon nanotubes (CNTs) by optical excitation at room temperature. By increasing the CNT diameter from 0.76 nm to 0.94 nm, the emission wavelength can be changed from 1,100 nm to 1,600 nm.
- Xiaowei He
- , Nicolai F. Hartmann
- & Stephen K. Doorn
-
Article |
 A flexible and wearable terahertz scanner
A flexible and wearable terahertz scanner
A flexible and wearable terahertz scanner based on carbon nanotubes is demonstrated at room temperature over a frequency range 0.14 THz to 39 THz. The terahertz photothermoelectricity is enhanced by using different electrode materials.
- D. Suzuki
- , S. Oda
- & Y. Kawano
-
Article |
 Fully integrated quantum photonic circuit with an electrically driven light source
Fully integrated quantum photonic circuit with an electrically driven light source
Single photons are generated from electrically driven semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes embedded in a photonic circuit. Pronounced antibunching is observed when photon correlation is measured at cryogenic temperatures.
- Svetlana Khasminskaya
- , Felix Pyatkov
- & Wolfram H. P. Pernice
-
Article |
 Cavity-enhanced light emission from electrically driven carbon nanotubes
Cavity-enhanced light emission from electrically driven carbon nanotubes
Carbon nanotubes in a nanocavity offer a route to narrow-linewidth on-chip light emitters.
- Felix Pyatkov
- , Valentin Fütterling
- & Wolfram H. P. Pernice
-
News & Views |
 Liquid quantum photonics
Liquid quantum photonics
Researchers have observed light propagation in which photons glide smoothly along a one-dimensional chain of electrons known as a Luttinger liquid — a many-body interacting quantum system held within a single-walled carbon nanotube.
- Mark Tame
-
Article |
 Through-skull fluorescence imaging of the brain in a new near-infrared window
Through-skull fluorescence imaging of the brain in a new near-infrared window
Near-infrared photoluminescence from carbon nanotubes makes it possible to optically image the vasculature in the brain directly through the skull.
- Guosong Hong
- , Shuo Diao
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 Efficient real-time detection of terahertz pulse radiation based on photoacoustic conversion by carbon nanotube nanocomposite
Efficient real-time detection of terahertz pulse radiation based on photoacoustic conversion by carbon nanotube nanocomposite
By integrating a photoacoustic transmitter based on a carbon nanotube nanocomposite and an optical microring resonator as an ultrasonic sensor, a low-noise terahertz pulse detection system is demonstrated at room temperature. The response time and the noise-equivalent detectability energy are on the order of 0.1 µs and 220 pJ, respectively.
- Sung-Liang Chen
- , You-Chia Chang
- & L. Jay Guo
-
-
Letter |
 Voltage-switchable photocurrents in single-walled carbon nanotube–silicon junctions for analog and digital optoelectronics
Voltage-switchable photocurrents in single-walled carbon nanotube–silicon junctions for analog and digital optoelectronics
A photodiode-based logic device employing scalable heterojunctions of carbon nanotubes and silicon whose output currents can be manipulated by both optical and electrical inputs is developed. Bidirectional phototransistors and novel clock-triggerable logic elements, such as a mixed optoelectronic AND gate, a 2-Bit optoelectronic ADDER/OR gate and a 4-Bit optoelectronic D/A converter, are also demonstrated.
- Young Lae Kim
- , Hyun Young Jung
- & Swastik Kar
-
Article |
 Triplet–triplet exciton dynamics in single-walled carbon nanotubes
Triplet–triplet exciton dynamics in single-walled carbon nanotubes
Little is known about triplet excitons in semiconducting single-walled nanotubes, despite their importance in various applications. The pump–probe and spin-sensitive photoluminescence of such nanotubes is studied, and the quantum yield of triplet formation, triplet lifetime and triplet exciton size are found to be 5 ± 2%, 30 ± 10 µs and 0.65 nm, respectively.
- Dominik Stich
- , Florian Späth
- & Tobias Hertel
-
Letter |
 Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes
Photocurrent generation in semiconducting and metallic carbon nanotubes
Clear evidence is presented for the origins of photocurrent generation in metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes — photocurrent is found to be mainly generated by photothermal and photovoltaic effects in metallic and semiconducting carbon nanotubes, respectively. This finding will enable the engineering of highly efficient carbon-based photodetectors and energy-harvesting devices.
- Maria Barkelid
- & Val Zwiller
-
Article |
 Giant Raman scattering from J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes for multispectral imaging
Giant Raman scattering from J-aggregated dyes inside carbon nanotubes for multispectral imaging
The use of Raman spectroscopy for high-resolution optical imaging is severely limited by the inherent weakness of the Raman effect. Now, a giant resonant Raman effect is demonstrated from J-aggregated dye molecules encapsulated in single-walled carbon nanotubes, and it is used to realize multispectral Raman imaging.
- E. Gaufrès
- , N. Y.-Wa Tang
- & R. Martel
-
Commentary |
 Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotube and graphene saturable absorbers for fibre lasers
Nanotubes and graphene have emerged as promising materials for use in ultrafast fibre lasers. Their unique electrical and optical properties enable them to be used as saturable absorbers that have fast responses and broadband operation and that can be easily integrated in fibre lasers.
- Amos Martinez
- & Zhipei Sun
-
Letter |
 Brightening of excitons in carbon nanotubes on dimensionality modification
Brightening of excitons in carbon nanotubes on dimensionality modification
Artificially reducing the effective dimensionality of carbon nanotubes from one to zero dimensions increases the luminescence quantum yield of excitons confined in zero-dimensional-like states to ∼18%, which is over one order of magnitude larger than that of intrinsic one-dimensional excitons (∼1%). This finding will help realize future nanoscale photonic devices.
- Yuhei Miyauchi
- , Munechiyo Iwamura
- & Kazunari Matsuda
-
-
Article |
 Charge-compensated, semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube thin film as an electrically configurable optical medium
Charge-compensated, semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotube thin film as an electrically configurable optical medium
A simple two-terminal device containing a semiconducting single-walled-nanotube thin-film is reported that generates an extremely high density of holes when it comes in contact with an ionic liquid, inducing strong electromodulation of the interband and excitonic transitions as a result of the position-dependent shift of the single-walled-nanotube Fermi level.
- Feihu Wang
- , Mikhail E. Itkis
- & Robert C. Haddon
-
-
-
-
Letter |
 Efficient photovoltage multiplication in carbon nanotubes
Efficient photovoltage multiplication in carbon nanotubes
Photovoltages generated from semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes are often too small for most practical solar-energy-harvesting applications. Here, researchers demonstrate that virtual contacts can be used to multiply photovoltages from around 0.2 V to 1.0 V.
- Leijing Yang
- , Sheng Wang
- & Lian-Mao Peng
-
Editorial |
 Carbon optimism
Carbon optimism
The use of diamond, graphene and carbon nanotubes is becoming increasingly common in photonic applications, and several recent notable achievements suggest that carbon has a bright future in photonics.
-
News & Views |
 Breaking Kasha's rule
Breaking Kasha's rule
The emission of visible light from a dye encapsulated within a carbon nanotube gives great hope and new opportunities for the design of nanoscale optoelectronic devices.
- Kazuhiro Yanagi
- & Hiromichi Kataura
-
News & Views |
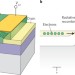 A brighter future
A brighter future
The demonstration of an LED made from a single electrostatically doped carbon nanotube p–n junction with dramatically improved light-emission efficiency marks an important advance for carbon nanotube photonics.
- Tobias Hertel

 Efficient tin-based perovskite solar cells with trans-isomeric fulleropyrrolidine additives
Efficient tin-based perovskite solar cells with trans-isomeric fulleropyrrolidine additives Black forest
Black forest Nanotube shock
Nanotube shock