Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Efficient platform for synthesizing comprehensive heparan sulfate oligosaccharide libraries for decoding glycosaminoglycan–protein interactions
Efficient platform for synthesizing comprehensive heparan sulfate oligosaccharide libraries for decoding glycosaminoglycan–protein interactions
Large collections of defined glycosaminoglycan (GAG) structures have been synthetically challenging to obtain but are required to understand this important class of biomolecules. Now, an efficient platform for synthesizing large libraries of heparan sulfate oligosaccharides has been developed, providing a detailed view into the sulfation code of GAGs.
- Lei Wang
- , Alexander W. Sorum
- & Linda C. Hsieh-Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access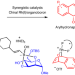 A synergistic Rh(I)/organoboron-catalysed site-selective carbohydrate functionalization that involves multiple stereocontrol
A synergistic Rh(I)/organoboron-catalysed site-selective carbohydrate functionalization that involves multiple stereocontrol
Asymmetric systems for catalytic carbohydrate functionalization are mostly limited to chiral copper complexes and organocatalysts. Now, a synergistic chiral Rh(I)- and organoboron-catalysed site-selective functionalization of carbohydrate polyols has been developed, giving stereocontrolled access to biologically relevant arylhydronaphthalene glycosides. Enantio-, diastereo-, regio- and anomeric control and dynamic kinetic resolution were found to be concomitantly operative.
- V. U. Bhaskara Rao
- , Caiming Wang
- & Charles C. J. Loh
-
Article |
 Synthetic O-acetylated sialosides facilitate functional receptor identification for human respiratory viruses
Synthetic O-acetylated sialosides facilitate functional receptor identification for human respiratory viruses
The specificity of human and animal viruses that engage with O-acetylated sialic acids has now been probed using a collection of O-acetylated sialoglycans obtained by diversification of trisaccharide precursors with viral haemagglutinin–esterases. The results revealed host-specific patterns of receptor recognition and showed that human respiratory viruses uniquely employ 9-O-acetylated α2,8-linked disialosides as receptors.
- Zeshi Li
- , Yifei Lang
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
News & Views |
 Robots command enzymes
Robots command enzymes
Enzymatic approaches to synthesize oligosaccharides offer an alternative to chemical syntheses for the production of homogeneous glycans; however, enzyme-based routes typically require lengthy processes. Now, the design of a water-soluble affinity tag has enabled the automation of multistep enzymatic syntheses of mammalian oligosaccharides.
- Nicola L. B. Pohl
-
Article |
 An automated platform for the enzyme-mediated assembly of complex oligosaccharides
An automated platform for the enzyme-mediated assembly of complex oligosaccharides
An automated platform that can synthesize a wide range of complex glycans could greatly facilitate progress in glycoscience. Now, a fully automated process for enzyme-mediated oligosaccharide synthesis has been developed. This process uses glycosyltransferase-catalysed reactions performed in solution, with product purification being accomplished by solid phase extraction using a sulfonate tag.
- Tiehai Li
- , Lin Liu
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article |
 Streamlining the chemoenzymatic synthesis of complex N-glycans by a stop and go strategy
Streamlining the chemoenzymatic synthesis of complex N-glycans by a stop and go strategy
Preparation of well-defined N-glycans is very demanding, which hampers progress in glycoscience. Now, a biomimetic synthetic approach has been developed in which a readily available bi-antennary glycan can be converted in ten or fewer steps into multi-antennary N-glycans. This approach enables each arm to be uniquely extended by glycosyltransferases to give complex branched N-glycans.
- Lin Liu
- , Anthony R. Prudden
- & Geert-Jan Boons
-
Article |
 A biomimetic receptor for glucose
A biomimetic receptor for glucose
Synthetic receptors can be used to help understand biological systems, but rarely compete in terms of affinity or selectivity. Now, a glucose-binding compound has been prepared that, despite its symmetry and simplicity, can match all but the strongest glucose-binding proteins. The high binding affinity and outstanding selectivity of this receptor may translate into biomedical applications.
- Robert A. Tromans
- , Tom S. Carter
- & Anthony P. Davis
-
Article |
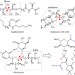 Direct assembly of multiply oxygenated carbon chains by decarbonylative radical–radical coupling reactions
Direct assembly of multiply oxygenated carbon chains by decarbonylative radical–radical coupling reactions
Pentoses and hexoses represent important structural motifs in bioactive secondary metabolites, though their synthesis often requires several elongation steps. Now, a method for radical–radical coupling reactions of sugar derivatives enables the single-step preparation of the oxygenated carbon chains of several natural products, including sagittamide D, maitotoxin and hikizimycin.
- Kengo Masuda
- , Masanori Nagatomo
- & Masayuki Inoue
-
Article |
 Chemical polyglycosylation and nanolitre detection enables single-molecule recapitulation of bacterial sugar export
Chemical polyglycosylation and nanolitre detection enables single-molecule recapitulation of bacterial sugar export
Capsular polysaccharides are a protective layer enveloping pathogenic bacteria. Understanding their export could guide the design of therapeutics that render bacteria vulnerable to attack by the immune system or other therapeutic agents. Now, a synthetic strategy of polyglycosylation has been developed to obtain defined capsular polysaccharide fragments. Subsequent nanolitre detection enables their export to be studied at the single-molecule level.
- Lingbing Kong
- , Andrew Almond
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
Article |
 Modular synthesis of N-glycans and arrays for the hetero-ligand binding analysis of HIV antibodies
Modular synthesis of N-glycans and arrays for the hetero-ligand binding analysis of HIV antibodies
The glycoprotein gp120 is found on the surface of the HIV viron; it is essential for virus entry into cells. Now, an efficient modular synthesis of N-glycans and the preparation of a mixed-glycan array on aluminium-oxide-coated glass slide is described. This is a vital step in understanding the complex compositions of gp120 and thus important for the development of new HIV therapies.
- Sachin S. Shivatare
- , Shih-Huang Chang
- & Chi-Huey Wong
-
Article |
 An antibacterial vaccination strategy based on a glycoconjugate containing the core lipopolysaccharide tetrasaccharide Hep2Kdo2
An antibacterial vaccination strategy based on a glycoconjugate containing the core lipopolysaccharide tetrasaccharide Hep2Kdo2
The presence and linkage of unusual higher sugars in the ‘inner core’ of Gram-negative bacteria makes the core lipopolysacchride tetrasaccharide Hep2Kdo2 a tough target. Now, a 2+2 glycosylation strategy has facilitated the synthesis of this glycoconjugate. Synthesis of Hep2Kdo2 enabled an antibacterial vaccination strategy based on immunization with the glycoconjugate and the subsequent administration of an inhibitor that uncovers the corresponding epitope in pathogenic bacteria.
- Lingbing Kong
- , Balakumar Vijayakrishnan
- & Benjamin G. Davis
-
News & Views |
 Glycosyl cations out on parole
Glycosyl cations out on parole
The reactivity of glycosyl donors is often explained by invoking putative glycosyl cation intermediates but, until now, they have not been observed in the condensed phase.
- Luis Bohé
- & David Crich
-
News & Views |
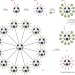 Sweet fullerenes vanquish viruses
Sweet fullerenes vanquish viruses
Fullerene-based dendritic structures coated with 120 sugars can be made in high yields in a relatively short sequence of reactions. The mannosylated compound is shown to inhibit Ebola infection in cells more efficiently than monofullerene-based glycoclusters.
- Sébastien Vidal
-
Article |
 Catching elusive glycosyl cations in a condensed phase with HF/SbF5 superacid
Catching elusive glycosyl cations in a condensed phase with HF/SbF5 superacid
Glycosyl cations are universally accepted as key intermediates in the mechanism of glycosylation—the reaction that covalently links carbohydrates to other molecules—but their high reactivity makes them difficult to characterize. Using HF/SbF5 superacid, two glucosyl cations have been generated and stabilized, then characterized by NMR spectroscopy aided by computation and their conformation elucidated.
- A. Martin
- , A. Arda
- & Y. Blériot
-
Article |
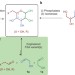 Asymmetric assembly of aldose carbohydrates from formaldehyde and glycolaldehyde by tandem biocatalytic aldol reactions
Asymmetric assembly of aldose carbohydrates from formaldehyde and glycolaldehyde by tandem biocatalytic aldol reactions
Forged by evolution, the natural enzymatic pathways to aldose carbohydrates are complex. Now, a biocatalytic stereoselective one-pot assembly of these carbohydrates from formaldehyde and glycolaldehyde using engineered D-fructose-6-phosphate aldolase (FSA) variants has been developed that circumvents this complexity.
- Anna Szekrenyi
- , Xavier Garrabou
- & Pere Clapés
-
News & Views |
 Molecular editing of carbohydrates
Molecular editing of carbohydrates
Deoxygenation reactions have been used to convert biomass-derived carbohydrates into useful platform chemicals. Now, a method has been described that can selectively excise C–O bonds to produce valuable chiral synthons.
- Andrew McNally
-
Article |
 Chemoselective conversion of biologically sourced polyols into chiral synthons
Chemoselective conversion of biologically sourced polyols into chiral synthons
Biorenewable carbohydrate feedstocks can be efficiently converted into a diverse set of oxygen-functionalized chiral synthons using a combination of a tertiary silane and the catalyst B(C6F5)3. The deoxygenation mechanism involves cyclic intermediates, which provide a means of controlling chemo- and diastereoselectivity.
- Laura L. Adduci
- , Trandon A. Bender
- & Michel R. Gagné
-
Article |
 Development of a minimal saponin vaccine adjuvant based on QS-21
Development of a minimal saponin vaccine adjuvant based on QS-21
Adjuvants are used to increase the immune response to molecular vaccines. A minimal synthetic variant of the saponin natural product QS-21 has been developed as a potent, non-toxic adjuvant, enabling dissection of structural requirements in the triterpene domain and in vivo biodistribution studies to probe mechanisms of action.
- Alberto Fernández-Tejada
- , Eric K. Chea
- & David Y. Gin
-
-
Article |
 Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Discrimination of epimeric glycans and glycopeptides using IM-MS and its potential for carbohydrate sequencing
Identification of glycosylation patterns is complicated by the lack of sensitive analytical techniques that can distinguish between epimeric carbohydrates. It has now been shown that ion-mobility tandem mass spectrometry of ions derived from glycopeptides and oligosaccharides enables glycan stereochemistry to be determined, highlighting the potential of this technique for sequencing complex carbohydrates on cell surfaces.
- P. Both
- , A. P. Green
- & C. E. Eyers
-
Article |
 Component-based syntheses of trioxacarcin A, DC-45-A1 and structural analogues
Component-based syntheses of trioxacarcin A, DC-45-A1 and structural analogues
The trioxacarcins are polyoxygenated natural products that potently inhibit the growth of cultured human cancer cells. Here, the syntheses of trioxacarcin A, DC-45-A1 and structural analogues are described — the majority of which were found to be active in antiproliferative assays. A convergent, component-based route comprising sequential stereoselective glycosylation reactions allows assembly of these analogues in 11 steps or fewer.
- Thomas Magauer
- , Daniel J. Smaltz
- & Andrew G. Myers
-
News & Views |
 Exploiting intramolecularity
Exploiting intramolecularity
Selective reaction of one alcohol among many in complex molecules can be achieved by the use of a catalyst that forms a single covalent bond to a nearby functional group.
- André M. Beauchemin
-
Article |
 Catalyst recognition of cis-1,2-diols enables site-selective functionalization of complex molecules
Catalyst recognition of cis-1,2-diols enables site-selective functionalization of complex molecules
The manipulation of complex molecules offers an avenue for developing new therapeutics and biological probes. Here, a catalyst is described that forms a covalent bond to the substrate before selectively functionalizing a proximal functional group. Cis-1,2-diols are targeted allowing for the derivatization of the axial hydroxyls of monosaccharides in the presence of unprotected equatorial hydroxyls.
- Xixi Sun
- , Hyelee Lee
- & Kian L. Tan
-
Article |
 A simple and accessible synthetic lectin for glucose recognition and sensing
A simple and accessible synthetic lectin for glucose recognition and sensing
Selective carbohydrate binding is a difficult task, usually accomplished by proteins (lectins) or complex synthetic analogues. It has now been achieved by a remarkably simple compound, accessible in just five steps from commercially available materials. This new receptor is highly selective for all-equatorial carbohydrates, and may be used to sense glucose through changes in anthracene fluorescence.
- Chenfeng Ke
- , Harry Destecroix
- & Anthony P. Davis
-
Research Highlights |
 Ordering from nature's catalogue
Ordering from nature's catalogue
Mechanistic analysis and reaction optimization provides access to a variety of useful chemical building blocks from biogenic feedstocks.
- Stephen Davey

 Synthesis of a glycan hairpin
Synthesis of a glycan hairpin