Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Solution structures of multiple G-quadruplex complexes induced by a platinum(II)-based tripod reveal dynamic binding
Solution structures of multiple G-quadruplex complexes induced by a platinum(II)-based tripod reveal dynamic binding
DNA G-quadruplexes occur in oncologically relevant regions, thus are interesting targets for cancer research and treatment. Here, the authors solved the 1:1 and 4:2 (ligand/DNA) NMR structures of human telomeric DNA in complex with platinum(II)-tripod ligand and show that the binding is dynamic.
- Wenting Liu
- , Yi-Fang Zhong
- & Zong-Wan Mao
-
Article
| Open Access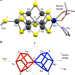 N2 activation on a molybdenum–titanium–sulfur cluster
N2 activation on a molybdenum–titanium–sulfur cluster
Nitrogenase—whose cofactor consists of a metal–sulfur cluster—catalyzes the production of NH3 from N2, but designing metal–sulfur complexes capable of promoting this conversion remains challenging. Here, the authors report on the activation of N2 by a metal–sulfur cluster containing [Mo3S4Ti] cubes, demonstrating NH3 and N2H4 production.
- Yasuhiro Ohki
- , Keisuke Uchida
- & Takehiro Ohta
-
Article
| Open Access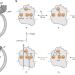 Control of transmembrane charge transfer in cytochrome c oxidase by the membrane potential
Control of transmembrane charge transfer in cytochrome c oxidase by the membrane potential
Cytochrome c oxidase (CytcO) is the last enzyme of the electron transport chain, but how the electrochemical membrane potential affects CytcO is unclear. Here the authors show that proton uptake to the catalytic site of CytcO and presumably proton translocation was impaired by the potential, but electron transfer was not affected.
- Markus L. Björck
- & Peter Brzezinski
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the coordination and function of Fe4S4 modules in nitrogenase assembly protein NifB
Probing the coordination and function of Fe4S4 modules in nitrogenase assembly protein NifB
NifB is a key enzyme in the biosynthesis pathway of the nitrogenase FeMo cofactor. Here, the authors investigate the maturation of its iron-sulfur clusters by EPR and biochemical analyses, showing how individual precursor clusters participate in the formation of the final iron-sulfur cluster.
- Lee A. Rettberg
- , Jarett Wilcoxen
- & Yilin Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Fine control of metal concentrations is necessary for cells to discern zinc from cobalt
Fine control of metal concentrations is necessary for cells to discern zinc from cobalt
Bacteria possess transcription factors whose DNA-binding activity is altered upon binding to specific metals, but the binding of metals is not specific in vitro. Here, Osman et al. show that tight regulation of buffered intracellular metal concentrations is a prerequisite for metal specificity.
- Deenah Osman
- , Andrew W. Foster
- & Nigel J. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticle formation by a multimeric multicopper oxidase Mnx
Biogenic manganese oxide nanoparticle formation by a multimeric multicopper oxidase Mnx
Significant challenges exist for structural characterization of enzymes responsible for biomineralization. Here the authors show that native mass spectrometry and high resolution electron microscopy can define the subunit topology and copper binding of a manganese oxidizing complex, and describe early stage formation of its mineral products
- Christine A. Romano
- , Mowei Zhou
- & Bradley M. Tebo
-
Article
| Open Access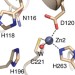 A general reaction mechanism for carbapenem hydrolysis by mononuclear and binuclear metallo-β-lactamases
A general reaction mechanism for carbapenem hydrolysis by mononuclear and binuclear metallo-β-lactamases
Carbapenem-resistant bacteria pose a major health threat by expressing metallo-β-lactamases (MβLs), enzymes able to hydrolyse these life-saving drugs. Here the authors use biophysical and computational methods and show that different MβLs share the same reaction mechanism, suggesting new strategies for drug design.
- María-Natalia Lisa
- , Antonela R. Palacios
- & Alejandro J. Vila
-
Article
| Open Access Rationally designed mineralization for selective recovery of the rare earth elements
Rationally designed mineralization for selective recovery of the rare earth elements
Lanthanide elements are difficult to separate from aqueous solution with low energy input. Here, the authors design a peptide that recognizes and drives the precipitation of an insoluble lanthanide complex under physiological conditions, introducing a biomineralization-based approach for rare earth recovery.
- Takaaki Hatanaka
- , Akimasa Matsugami
- & Nobuhiro Ishida
-
Article
| Open Access ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
ISCA1 is essential for mitochondrial Fe4S4 biogenesis in vivo
The mitochondrial proteins ISCA1 and ISCA2 form a complex that is involved in the biogenesis of Fe–S clusters. Here the authors report that ISCA1 and ISCA2 interact differently with proteins of the Fe–S machinery and that under certain conditions, ISCA2 seems dispensable for Fe–S biogenesis.
- Lena Kristina Beilschmidt
- , Sandrine Ollagnier de Choudens
- & Alain Martelli
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the NO sensor NsrR reveal how its iron-sulfur cluster modulates DNA binding
Crystal structures of the NO sensor NsrR reveal how its iron-sulfur cluster modulates DNA binding
NsrR is a bacterial transcriptional regulator that acts as a nitric oxide (NO) sensor. Here, the authors present the crystal structure of NsrR, which reveals an unusual Fe-S cluster coordination and explains how NO exposure leads to the degradation of the cluster.
- Anne Volbeda
- , Erin L. Dodd
- & Juan C. Fontecilla-Camps
-
Article
| Open Access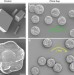 Chiral acidic amino acids induce chiral hierarchical structure in calcium carbonate
Chiral acidic amino acids induce chiral hierarchical structure in calcium carbonate
Chiral structures are formed in numerous processes including biomineralization of calcium carbonate. Here, the authors demonstrate that the chiral, hierarchically-organized architecture of the calcium carbonate mineral, vaterite, can be controlled simply by the addition of chiral acidic amino acids.
- Wenge Jiang
- , Michael S. Pacella
- & Marc D. McKee
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesis and reactivity of a mononuclear non-haem cobalt(IV)-oxo complex
Synthesis and reactivity of a mononuclear non-haem cobalt(IV)-oxo complex
Terminal CoIV-oxo species are key intermediates in various cobalt-mediated oxidation reactions, but little is known about their chemical properties. Here the authors generate and isolate a mononuclear non-haem CoIV-O complex and analyse its structure and reactivity towards a range of catalytic transformations.
- Bin Wang
- , Yong-Min Lee
- & Wonwoo Nam
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Observation of gold sub-nanocluster nucleation within a crystalline protein cage
Proteins can template the synthesis of inorganic nanoparticles, but the formation mechanisms remain vague. Here, the authors directly observe, through a sequence of X-ray crystal structures, the stages of gold sub-nanocluster growth within the confined environment of a ferritin cage.
- Basudev Maity
- , Satoshi Abe
- & Takafumi Ueno
-
Article
| Open Access A natural light-driven inward proton pump
A natural light-driven inward proton pump
Proton pumps that are driven by light to pump protons out of the cell are involved in the conversion of sunlight into proton motive force; pumps to drive protons in the other direction have been engineered. Here, the authors report the identification and characterisation of a naturally occurring inward-driven protein pump.
- Keiichi Inoue
- , Shota Ito
- & Hideki Kandori
-
Article
| Open Access Sulfheme formation during homocysteine S-oxygenation by catalase in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases
Sulfheme formation during homocysteine S-oxygenation by catalase in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases
High levels of homocysteine in cells are linked to pathological states. Here, the authors report that homocysteine inactivates catalase by modifying the heme group, impairing cellular redox homeostasis, and show that this modification occurs in cancer cells and in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease.
- Dominique Padovani
- , Assia Hessani
- & Isabelle Artaud
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structure of bacterial haem importer complex in the inward-facing conformation
Crystal structure of bacterial haem importer complex in the inward-facing conformation
Pathogenic bacteria acquire iron from heme cofactors imported by ABC heme transporters. Here the authors present crystal structures of Burkholderia cenocepaciaheme importer BhuUV with and without the heme-binding protein BhuT, gathering mechanistic insight into the catalytic cycle of heme import.
- Youichi Naoe
- , Nozomi Nakamura
- & Hiroshi Sugimoto
-
Article
| Open Access Neutralizing blood-borne polyphosphate in vivo provides safe thromboprotection
Neutralizing blood-borne polyphosphate in vivo provides safe thromboprotection
The inorganic procoagulant polymer polyphosphate participates in thrombosis via factor XII. Here the authors use recombinant probes that specifically bind or degrade circulating polyphosphate to protect mice in arterial and venous thrombosis models without an increased bleeding risk, the primary complication of all currently used anticoagulants.
- Linda Labberton
- , Ellinor Kenne
- & Thomas Renné
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights of ZIP4 extracellular domain critical for optimal zinc transport
Structural insights of ZIP4 extracellular domain critical for optimal zinc transport
Mutations in the extracellular domain of zinc transporter ZIP4 result in a lethal disorder. Here, the authors report the first crystal structure of ZIP4 extracellular domain, unveiling its unprecedented dimerization and two structural independent subdomains that have crucial roles in zinc transport.
- Tuo Zhang
- , Dexin Sui
- & Jian Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for Mep2 ammonium transceptor activation by phosphorylation
Structural basis for Mep2 ammonium transceptor activation by phosphorylation
Mep2 proteins are tightly regulated fungal ammonium transporters. Here, the authors report the crystal structures of closed states of Mep2 proteins and propose a model for their regulation by comparing them with the open ammonium transporters of bacteria.
- Bert van den Berg
- , Anupama Chembath
- & Julian C. Rutherford
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale assembly processes revealed in the nacroprismatic transition zone of Pinna nobilis mollusc shells
Nanoscale assembly processes revealed in the nacroprismatic transition zone of Pinna nobilis mollusc shells
The study of biomineralization processes in molluscs can help to understand the properties of the final composites. Here, Hovden et al. have studied the early stages of nacre formation using high resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy, giving new insight into nacre formation.
- Robert Hovden
- , Stephan E. Wolf
- & Lara A. Estroff
-
Article
| Open Access Sequential substitution of K+ bound to Na+,K+-ATPase visualized by X-ray crystallography
Sequential substitution of K+ bound to Na+,K+-ATPase visualized by X-ray crystallography
The Na+,K+-ATPase moves three Na+ ions out of the cell and transfers two K+ ions in the opposite direction. Here the authors use X-ray crystallography to look at the substitution of two bound K+with those in the medium and show that it occurs sequentially through a narrow gate.
- Haruo Ogawa
- , Flemming Cornelius
- & Chikashi Toyoshima
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a dirhodium artificial metalloenzyme for selective olefin cyclopropanation
Engineering a dirhodium artificial metalloenzyme for selective olefin cyclopropanation
Artificial metalloenzymes (ArMs) have the potential to improve transition metal reactivity in complex media. Here, the authors link a dirhodium catalyst to a prolyl oligopeptidase to create an ArM that catalyzes enantioselective olefin cyclopropanation in aqueous solution.
- Poonam Srivastava
- , Hao Yang
- & Jared C. Lewis
-
Article
| Open Access Force-induced chemical reactions on the metal centre in a single metalloprotein molecule
Force-induced chemical reactions on the metal centre in a single metalloprotein molecule
The investigation of the chemical reactivity of metal centres in metalloproteins in aqueous solution is challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate the use of single molecule force spectroscopy to study the chemical reactivity of the iron-sulfur centre in rubredoxin in aqueous solution.
- Peng Zheng
- , Guilherme M. Arantes
- & Hongbin Li
-
Article
| Open Access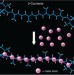 Multinuclear metal-binding ability of a carotene
Multinuclear metal-binding ability of a carotene
Carotenes are naturally abundant, widely studied unsaturated hydrocarbon pigments but their metal-binding ability has been virtually unexplored. Here, the authors demonstrate that they can be used to reversibly assemble and align homo- and hetero-metallic decanuclear chain complexes.
- Shinnosuke Horiuchi
- , Yuki Tachibana
- & Tetsuro Murahashi
-
Article |
 Edge dislocation slows down oxide ion diffusion in doped CeO2 by segregation of charged defects
Edge dislocation slows down oxide ion diffusion in doped CeO2 by segregation of charged defects
Electrochemical devices based on oxide materials, such as batteries or fuel cells, rely on the transport of ions through the crystal lattice. Here, the authors model ion diffusion through CeO2and observe that edge dislocations slow down ion diffusion, contrary to similar processes in metals.
- Lixin Sun
- , Dario Marrocchelli
- & Bilge Yildiz
-
Article |
 Identity of a Plasmodium lactate/H+ symporter structurally unrelated to human transporters
Identity of a Plasmodium lactate/H+ symporter structurally unrelated to human transporters
Malaria parasites generate metabolic energy through anaerobic glycolysis, yielding lactate and protons that are then secreted out of the parasite cell by an unknown transporter. Here, the authors identify and characterize a lactate/proton transporter that may be carrying out such function in Plasmodium.
- Binghua Wu
- , Janis Rambow
- & Eric Beitz
-
Article
| Open Access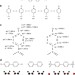 Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Porous coordination polymers with ubiquitous and biocompatible metals and a neutral bridging ligand
Inexpensive porous materials synthesized from Group II metals may be useful for industrial applications. Here, the authors demonstrate that neutral bridging ligands can be used for the synthesis of magnesium(II) and calcium(II) porous coordination polymers.
- Shin-ichiro Noro
- , Junya Mizutani
- & Takayoshi Nakamura
-
Article |
 Export of a single drug molecule in two transport cycles by a multidrug efflux pump
Export of a single drug molecule in two transport cycles by a multidrug efflux pump
Secondary multidrug transporters use ion concentration gradients to power the removal of drug molecules from cells. Here, Fluman et al. demonstrate that the bacterial transporter MdfA can catalyse the efflux of divalent cations in two consecutive transport cycles where each charged moiety is transported as if it were a separate substrate.
- Nir Fluman
- , Julia Adler
- & Eitan Bibi
-
Article |
 Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Physiological sodium concentrations enhance the iodide affinity of the Na+/I− symporter
Thyroid hormone synthesis requires import of iodide ions through the Na+/I− symporter, however its affinity for iodide is surprisingly low. Using a statistical thermodynamics approach, Nicola et al. show that sodium ion binding enhances iodide affinity, revealing a mechanism for iodide transport.
- Juan P. Nicola
- , Nancy Carrasco
- & L. Mario Amzel
-
Article |
 A light-driven sodium ion pump in marine bacteria
A light-driven sodium ion pump in marine bacteria
Light-driven proton-pumping rhodopsins are widely distributed in microorganisms and convert sunlight energy into proton gradients. Inoue et al. report the discovery of a light-driven sodium ion pump from marine bacteria.
- Keiichi Inoue
- , Hikaru Ono
- & Hideki Kandori
-
Article
| Open Access Prion protein facilitates uptake of zinc into neuronal cells
Prion protein facilitates uptake of zinc into neuronal cells
Prion proteins are implicated in a range of neurodegenerative diseases, which are, in part, due to a disruption of metal homeostasis. Wattet al.use selective antagonists to show that prion proteins mediate zinc uptake by interacting with GluA2-lacking, GluA1-containing AMPA receptors.
- Nicole T. Watt
- , David R. Taylor
- & Nigel M. Hooper
-
Article |
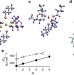 Transmembrane anion transport mediated by halogen-bond donors
Transmembrane anion transport mediated by halogen-bond donors
The transport of anions across bilayer membranes is achieved by ion channel proteins, but some small molecules are also able to mediate transmembrane movement of anions. In this study, the halogen bonding of small perfluorinated molecules is shown to allow the transmembrane movement of anions.
- Andreas Vargas Jentzsch
- , Daniel Emery
- & Stefan Matile
-
Article
| Open Access The dynamic relationships between the three events that release individual Na+ ions from the Na+/K+-ATPase
The dynamic relationships between the three events that release individual Na+ ions from the Na+/K+-ATPase
The Na+/K+-ATPase pump exports three Na+ ions for the exchange of two K+ ions, and three transient current components have been associated with Na+ binding and release. Now, these three components are found to be tightly correlated confirming that the binding and release of Na+ions is sequential.
- David C. Gadsby
- , Francisco Bezanilla
- & Miguel Holmgren
-
Article |
 A bacterial proteorhodopsin proton pump in marine eukaryotes
A bacterial proteorhodopsin proton pump in marine eukaryotes
Proteorhodopsin is used by prokaryotes to generate energy from light. In this study, the authors describe a prokaryote-to-eukaryote horizontal gene transfer of a bacterial proteorhodopsin gene to dinoflagellates, suggesting that these eukaryotes can also use proteorhodopsin to obtain light and produce energy.
- Claudio H. Slamovits
- , Noriko Okamoto
- & Patrick J. Keeling
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational rearrangement of gastric H+,K+-ATPase induced by an acid suppressant
Conformational rearrangement of gastric H+,K+-ATPase induced by an acid suppressant
The gastric proton pump, H+,K+-ATPase, contributes to stomach acidification and is a target of acid suppressants. Here, the three-dimensional structure of the pump is determined using electron crystallography, providing the first structural information about the binding of a new class of acid suppressants.
- Kazuhiro Abe
- , Kazutoshi Tani
- & Yoshinori Fujiyoshi

 Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria
Characterization of a long overlooked copper protein from methane- and ammonia-oxidizing bacteria