Featured
-
-
Article |
 Healable and conductive sulfur iodide for solid-state Li–S batteries
Healable and conductive sulfur iodide for solid-state Li–S batteries
A conductive, low-melting-point and healable sulfur iodide material aids the practical realization of solid-state Li–S batteries, which have high theoretical energy densities and show potential in next-generation battery chemistry.
- Jianbin Zhou
- , Manas Likhit Holekevi Chandrappa
- & Ping Liu
-
Article |
 Ligand-channel-enabled ultrafast Li-ion conduction
Ligand-channel-enabled ultrafast Li-ion conduction
An electrolyte design using small-sized fluoroacetonitrile solvents to form a ligand channel produces lithium-ion batteries simultaneously achieving high energy density, fast charging and wide operating temperature range, desirable features for batteries working in extreme conditions.
- Di Lu
- , Ruhong Li
- & Xiulin Fan
-
Article |
 A rechargeable calcium–oxygen battery that operates at room temperature
A rechargeable calcium–oxygen battery that operates at room temperature
A Ca–O2 battery that relies on a highly reversible two-electron redox to form chemically reactive calcium peroxide as the discharge product is reported to be stable in air and rechargeable for 700 cycles at room temperature.
- Lei Ye
- , Meng Liao
- & Huisheng Peng
-
Article |
 Recovery of isolated lithium through discharged state calendar ageing
Recovery of isolated lithium through discharged state calendar ageing
Calendar ageing of lithium metal batteries in the discharged state improves capacity retention through isolated lithium recovery, which is in contrast with the capacity degradation observed during charged state calendar ageing.
- Wenbo Zhang
- , Philaphon Sayavong
- & Yi Cui
-
Article |
 Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
Establishing reaction networks in the 16-electron sulfur reduction reaction
We investigate the mechanism underlying the sulfur reduction reaction that plays a central role in high-capacity lithium sulfur batteries, highlighting the electrocatalytic approach as a promising strategy for tackling the fundamental challenges associated with these batteries.
- Rongli Liu
- , Ziyang Wei
- & Xiangfeng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access The persistence of memory in ionic conduction probed by nonlinear optics
The persistence of memory in ionic conduction probed by nonlinear optics
Single-cycle terahertz pumps are used to impulsively trigger ionic hopping in battery solid electrolytes, probing ion transport at its fastest limit and demonstrating the connection between activated transport and the thermodynamics of information.
- Andrey D. Poletayev
- , Matthias C. Hoffmann
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article |
 Interface design for all-solid-state lithium batteries
Interface design for all-solid-state lithium batteries
The inclusion of a Mg–Bi-based interlayer between the lithium metal and solid electrolyte and a F-rich interlayer on the cathode improves the stability and performance of solid-state lithium-metal batteries.
- Hongli Wan
- , Zeyi Wang
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Article |
 Visualizing interfacial collective reaction behaviour of Li–S batteries
Visualizing interfacial collective reaction behaviour of Li–S batteries
In situ liquid-cell electrochemical transmission electron microscopy allows the direct visualization of the transformation of lithium polysulfides over electrode surfaces at the atomic scale, leading to a new energy-storage mechanism in lithium–sulfur batteries.
- Shiyuan Zhou
- , Jie Shi
- & Hong-Gang Liao
-
Article |
 Ultrafast deposition of faceted lithium polyhedra by outpacing SEI formation
Ultrafast deposition of faceted lithium polyhedra by outpacing SEI formation
We report the discovery of lithium metal’s intrinsic growth morphology, a rhombic dodecahedron, and leverage these rhombic dodecahedra as nucleation seeds for improved battery performance.
- Xintong Yuan
- , Bo Liu
- & Yuzhang Li
-
Article |
 Dendrite initiation and propagation in lithium metal solid-state batteries
Dendrite initiation and propagation in lithium metal solid-state batteries
Analysis of dendrite initiation, owing to filling of pores with lithium by means of microcracks, and propagation, caused by wedge opening, shows that there are two separate processes during dendrite failure of lithium metal solid-state batteries.
- Ziyang Ning
- , Guanchen Li
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Article |
 Mapping internal temperatures during high-rate battery applications
Mapping internal temperatures during high-rate battery applications
The state of charge, mechanical strain and temperature within lithium-ion 18650 cells operated at high rates are characterized and operando temperature rise is observed to be due to heat accumulation, strongly influenced by cell design and charging protocol.
- T. M. M. Heenan
- , I. Mombrini
- & P. R. Shearing
-
Article |
 A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor compatible with lithium metal
A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor compatible with lithium metal
A LaCl3-based lithium superionic conductor is developed that has excellent interfacial compatibility with lithium metal electrodes, with its optimized Li0.388Ta0.238La0.475Cl3 electrolyte exhibiting good Li+ conductivity and low activation energy.
- Yi-Chen Yin
- , Jing-Tian Yang
- & Hong-Bin Yao
-
Article |
 Electrolyte design for Li-ion batteries under extreme operating conditions
Electrolyte design for Li-ion batteries under extreme operating conditions
An electrolyte design strategy based on a group of soft solvents is used to achieve lithium-ion batteries that operate safely under extreme conditions without lithium plating and with the capability of fast charging.
- Jijian Xu
- , Jiaxun Zhang
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Article |
 Strain-retardant coherent perovskite phase stabilized Ni-rich cathode
Strain-retardant coherent perovskite phase stabilized Ni-rich cathode
The introduction of a coherent perovskite phase into the layered structure of a lithium-ion battery reduces lattice strain and stress to produce a robust crystal structure.
- Liguang Wang
- , Tongchao Liu
- & Jun Lu
-
Article |
 Fast charging of energy-dense lithium-ion batteries
Fast charging of energy-dense lithium-ion batteries
A new approach to charging energy-dense electric vehicle batteries, using temperature modulation with a dual-salt electrolyte, promises a range in excess of 500,000 miles using only rapid (under 12 minute) charges.
- Chao-Yang Wang
- , Teng Liu
- & Brian D. McCarthy
-
Article |
 Compositionally complex doping for zero-strain zero-cobalt layered cathodes
Compositionally complex doping for zero-strain zero-cobalt layered cathodes
A compositionally complex (high-entropy) doping strategy is proposed to fabricate zero-strain high-Ni and Co-free layered cathodes with superior structural and mechanical stabilities and long cycle life.
- Rui Zhang
- , Chunyang Wang
- & Huolin L. Xin
-
Article |
 Fast-charging aluminium–chalcogen batteries resistant to dendritic shorting
Fast-charging aluminium–chalcogen batteries resistant to dendritic shorting
An aluminium–chalcogen battery operating with a molten-salt electrolyte composed of NaCl–KCl–AlCl3 is presented, which allows rapid charging at up to 200C for hundreds of cycles, and is scalable, fire-resistant and low cost.
- Quanquan Pang
- , Jiashen Meng
- & Donald R. Sadoway
-
Article |
 Origin of structural degradation in Li-rich layered oxide cathode
Origin of structural degradation in Li-rich layered oxide cathode
Diffractive imaging of an important class of battery electrodes during cycling shows that lattice strain is a crucial yet overlooked factor that contributes to voltage fade over time.
- Tongchao Liu
- , Jiajie Liu
- & Khalil Amine
-
Perspective |
 The challenges and opportunities of battery-powered flight
The challenges and opportunities of battery-powered flight
The economic, technical, environmental and safety requirements of battery-powered aircraft are considered, and promising technologies and future prospects for battery innovation are discussed.
- Venkatasubramanian Viswanathan
- , Alan H. Epstein
- & Michael Winter
-
Article |
 Elastomeric electrolytes for high-energy solid-state lithium batteries
Elastomeric electrolytes for high-energy solid-state lithium batteries
An elastomeric solid-state electrolyte shows desirable mechanical properties and high electrochemical stability, and is used to demonstrate a high-energy solid-state lithium battery at ambient temperature.
- Michael J. Lee
- , Junghun Han
- & Seung Woo Lee
-
Article |
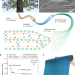 Copper-coordinated cellulose ion conductors for solid-state batteries
Copper-coordinated cellulose ion conductors for solid-state batteries
By coordinating copper ions with the oxygen-containing groups of cellulose nanofibrils, the molecular spacing in the nanofibrils is increased, allowing fast transport of lithium ions and offering hopes for solid-state batteries.
- Chunpeng Yang
- , Qisheng Wu
- & Liangbing Hu
-
Article |
 Scalable production of high-performing woven lithium-ion fibre batteries
Scalable production of high-performing woven lithium-ion fibre batteries
Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries produced in the form of metre-long fibres can be woven into sturdy, washable textiles on an industrial loom and used to power other fabric-based electronic components.
- Jiqing He
- , Chenhao Lu
- & Huisheng Peng
-
Article |
 Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries
Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries
Rechargeable Na/Cl2 and Li/Cl2 batteries are produced with a microporous carbon positive electrode, aluminium chloride in thionyl chloride as the electrolyte, and either sodium or lithium as the negative electrode.
- Guanzhou Zhu
- , Xin Tian
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Article |
 Operando optical tracking of single-particle ion dynamics in batteries
Operando optical tracking of single-particle ion dynamics in batteries
The dynamics of ions within a working lithium-ion battery are examined using optical interferometric scattering microscopy, which allows ion transport to be related to phase transitions and microstructural features.
- Alice J. Merryweather
- , Christoph Schnedermann
- & Akshay Rao
-
Article |
 Tomographic reconstruction of oxygen orbitals in lithium-rich battery materials
Tomographic reconstruction of oxygen orbitals in lithium-rich battery materials
High-energy X-ray Compton measurements and first-principles modelling reveal how the electronic orbital responsible for the reversible anionic redox activity can be imaged and visualized, and its character and symmetry determined.
- Hasnain Hafiz
- , Kosuke Suzuki
- & Venkatasubramanian Viswanathan
-
Article |
 A dynamic stability design strategy for lithium metal solid state batteries
A dynamic stability design strategy for lithium metal solid state batteries
A multi-layered electrolyte, in which a less stable electrolyte is sandwiched between two electrolyte layers that are more stable, can inhibit the growth of lithium dendrites in highly pressurized solid-state lithium metal batteries.
- Luhan Ye
- & Xin Li
-
Article |
 Polypeptide organic radical batteries
Polypeptide organic radical batteries
An environmentally friendly, all-organic radical battery is demonstrated, in which redox-active polypeptides perform as both cathode and anode materials, with a metal-free organic electrolyte.
- Tan P. Nguyen
- , Alexandra D. Easley
- & Karen L. Wooley
-
Article |
 A highly stable and flexible zeolite electrolyte solid-state Li–air battery
A highly stable and flexible zeolite electrolyte solid-state Li–air battery
Flexible, stable and energy-dense solid-state Li–air batteries are realised using ultrathin, chemically inert ion-conductive zeolite membranes as a solid electrolyte.
- Xiwen Chi
- , Malin Li
- & Jihong Yu
-
Article |
 Diversity-oriented synthesis of polymer membranes with ion solvation cages
Diversity-oriented synthesis of polymer membranes with ion solvation cages
A diversity-oriented synthesis approach that yields a library of architecturally broad microporous polymers is used to develop structurally diverse polymer membranes with ion specificity and to screen their properties.
- Miranda J. Baran
- , Mark E. Carrington
- & Brett A. Helms
-
Article |
 A disordered rock salt anode for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries
A disordered rock salt anode for fast-charging lithium-ion batteries
A vanadium-based lithium-rich disordered rock salt oxide is shown to work as a low-potential anode with rapid intercalation kinetics for lithium-ion batteries.
- Haodong Liu
- , Zhuoying Zhu
- & Ping Liu
-
Article |
 In situ NMR metrology reveals reaction mechanisms in redox flow batteries
In situ NMR metrology reveals reaction mechanisms in redox flow batteries
Real-time nuclear magnetic resonance studies of electrolyte decomposition and self-discharge in redox flow batteries provide insights into the underlying mechanisms of the reactions, such as radical formation and electron transfer.
- Evan Wenbo Zhao
- , Tao Liu
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Article |
 Closed-loop optimization of fast-charging protocols for batteries with machine learning
Closed-loop optimization of fast-charging protocols for batteries with machine learning
A closed-loop machine learning methodology of optimizing fast-charging protocols for lithium-ion batteries can identify high-lifetime charging protocols accurately and efficiently, considerably reducing the experimental time compared to simpler approaches.
- Peter M. Attia
- , Aditya Grover
- & William C. Chueh
-
Article |
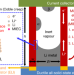 Li metal deposition and stripping in a solid-state battery via Coble creep
Li metal deposition and stripping in a solid-state battery via Coble creep
By containing lithium metal within oriented tubes of a mixed ionic-electronic conductor, a 3D anode for lithium metal batteries is produced that overcomes chemomechanical stability issues at the electrolyte interface.
- Yuming Chen
- , Ziqiang Wang
- & Ju Li
-
Article |
 Superstructure control of first-cycle voltage hysteresis in oxygen-redox cathodes
Superstructure control of first-cycle voltage hysteresis in oxygen-redox cathodes
In oxygen-redox intercalation cathodes, voltage hysteresis can be avoided by forming cathode materials with a ‘ribbon’ superstructure in the transition metal layers that suppresses transition metal migration.
- Robert A. House
- , Urmimala Maitra
- & Peter G. Bruce
-
Review Article |
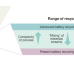 Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles
Recycling lithium-ion batteries from electric vehicles
Processes for dismantling and recycling lithium-ion battery packs from scrap electric vehicles are outlined.
- Gavin Harper
- , Roberto Sommerville
- & Paul Anderson
-
Letter |
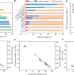 Quantifying inactive lithium in lithium metal batteries
Quantifying inactive lithium in lithium metal batteries
Titration gas chromatography is developed as an analytical method of distinguishing between lithium metal and lithium compounds within a cycled battery and assessing the amount of unreacted metallic lithium available.
- Chengcheng Fang
- , Jinxing Li
- & Ying Shirley Meng
-
Article |
 Electrolytic vascular systems for energy-dense robots
Electrolytic vascular systems for energy-dense robots
An energy-dense hydraulic fluid is used to construct a synthetic circulatory system in a lionfish-like soft robot, enabling untethered movement for up to 36 hours.
- Cameron A. Aubin
- , Snehashis Choudhury
- & Robert F. Shepherd
-
Letter |
 Aqueous Li-ion battery enabled by halogen conversion–intercalation chemistry in graphite
Aqueous Li-ion battery enabled by halogen conversion–intercalation chemistry in graphite
Composite cathodes created by anionic redox reactions of bromine and chlorine intercalated into graphite, combined with water-in-salt electrolyte and graphite anodes, provide aqueous lithium-ion batteries with improved energy density.
- Chongyin Yang
- , Ji Chen
- & Chunsheng Wang
-
Letter |
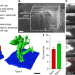 Cryo-STEM mapping of solid–liquid interfaces and dendrites in lithium-metal batteries
Cryo-STEM mapping of solid–liquid interfaces and dendrites in lithium-metal batteries
Direct observation of the anode–electrolyte interface in a lithium-metal battery, without removing the liquid electrolyte, reveals two types of dendrites, one of which may contribute disproportionately to capacity fade.
- Michael J. Zachman
- , Zhengyuan Tu
- & Lena F. Kourkoutis
-
Article |
 Niobium tungsten oxides for high-rate lithium-ion energy storage
Niobium tungsten oxides for high-rate lithium-ion energy storage
Micrometre-sized particles of two niobium tungsten oxides have high volumetric capacities and rate performances, enabled by very high lithium-ion diffusion coefficients.
- Kent J. Griffith
- , Kamila M. Wiaderek
- & Clare P. Grey
-
Letter |
 Heterointerface effects in the electrointercalation of van der Waals heterostructures
Heterointerface effects in the electrointercalation of van der Waals heterostructures
The electrointercalation of lithium into van der Waals heterostructures of graphene, hexagonal boron nitride and molybdenum dichalcogenides is studied at the level of individual atomic interfaces.
- D. Kwabena Bediako
- , Mehdi Rezaee
- & Philip Kim
-
Article |
 Reversible Mn2+/Mn4+ double redox in lithium-excess cathode materials
Reversible Mn2+/Mn4+ double redox in lithium-excess cathode materials
Lithium-rich cathode materials in which manganese undergoes double redox could point the way for lithium-ion batteries to meet the capacity and energy density needs of portable electronics and electric vehicles.
- Jinhyuk Lee
- , Daniil A. Kitchaev
- & Gerbrand Ceder
-
Letter |
 A lithium–oxygen battery with a long cycle life in an air-like atmosphere
A lithium–oxygen battery with a long cycle life in an air-like atmosphere
A lithium–oxygen battery, comprising a lithium carbonate-based protected anode, a molybdenum disulfide cathode and an ionic liquid/dimethyl sulfoxide electrolyte, operates in a simulated air atmosphere with a long cycle life of up to 700 cycles.
- Mohammad Asadi
- , Baharak Sayahpour
- & Amin Salehi-Khojin
-
Letter |
 Lithium-ion battery structure that self-heats at low temperatures
Lithium-ion battery structure that self-heats at low temperatures
Here we report a lithium-ion all-climate battery that very efficiently heats itself up in extremely cold environments by diverting current through a strip of metal foil to generate heat of resistance and then reverts to normal high-power operation.
- Chao-Yang Wang
- , Guangsheng Zhang
- & Yongjun Leng
-
Letter |
 A lithium–oxygen battery based on lithium superoxide
A lithium–oxygen battery based on lithium superoxide
Lithium–oxygen batteries allow oxygen to be reduced at the battery’s cathode when a current is drawn; in present-day batteries, this results in formation of Li2O2, but it is now shown that another high energy density material, namely LiO2, with better electronic conduction can be used instead as the discharge product, if the electrode is decorated with iridium nanoparticles.
- Jun Lu
- , Yun Jung Lee
- & Khalil Amine
-
Letter |
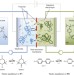 An aqueous, polymer-based redox-flow battery using non-corrosive, safe, and low-cost materials
An aqueous, polymer-based redox-flow battery using non-corrosive, safe, and low-cost materials
An affordable, safe, and scalable battery system is presented, which uses organic polymers as the charge-storage material in combination with inexpensive dialysis membranes and an aqueous sodium chloride solution as the electrolyte.
- Tobias Janoschka
- , Norbert Martin
- & Ulrich S. Schubert
-
Letter |
 An ultrafast rechargeable aluminium-ion battery
An ultrafast rechargeable aluminium-ion battery
An aluminium-ion battery is reported that can charge within one minute, and offers improved cycle life compared to previous devices; it operates through the electrochemical deposition and dissolution of aluminium at the anode, and the intercalation/de-intercalation of chloroaluminate anions into a novel graphitic-foam cathode.
- Meng-Chang Lin
- , Ming Gong
- & Hongjie Dai
-
Letter |
 Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance
Conductive two-dimensional titanium carbide ‘clay’ with high volumetric capacitance
Two-dimensional titanium carbide has been produced by etching out aluminium in a lithium fluoride and hydrochloric acid mixture; it is hydrophilic and mouldable like clay and has excellent volumetric capacitance and cyclability, properties that are desirable for portable electronics.
- Michael Ghidiu
- , Maria R. Lukatskaya
- & Michel W. Barsoum
-
Letter |
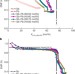 Lithium–antimony–lead liquid metal battery for grid-level energy storage
Lithium–antimony–lead liquid metal battery for grid-level energy storage
All-liquid batteries comprising a lithium negative electrode and an antimony–lead positive electrode have a higher current density and a longer cycle life than conventional batteries, can be more easily used to make large-scale storage systems, and so potentially present a low-cost means of grid-level energy storage.
- Kangli Wang
- , Kai Jiang
- & Donald R. Sadoway

 Chemical short-range disorder in lithium oxide cathodes
Chemical short-range disorder in lithium oxide cathodes