Abstract
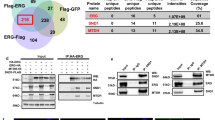
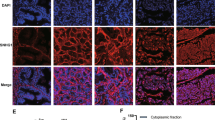
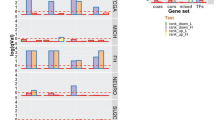
Annexin-A7 (ANXA7) tumor suppressor role has been shown in various tumors, and ANXA7 expression has been particularly lost in androgen-resistant prostate cancers. In this study, we studied ANXA7 regulation in normal prostate versus androgen-sensitive and -resistant prostate cancer cells. Deletion mapping analysis showed lowest ANXA7-promoter activities in androgen-sensitive LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Genomatix analysis of ANXA7 promoter identified a cluster of steroid nuclear hormone receptor elements, including V$GREF (V$GRE.02/ARE.02). Gelshift analysis clearly indicated distinct nuclear protein occupancy at this ANXA7-promoter site (−1086/−890) in prostate cancer (LNCaP, DU145, and PC3) versus normal prostate (PrEC) cells. In matrix-assisted laser desorption time-of-flight mass spectrometry-based search for ANXA7 nuclear regulators, we identified several heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) (A1, A2/B1 and K) attached to the steroid-associated ANXA7-promoter site in the androgen-resistant PC3 prostate cancer cells with high ANXA7 gene copy number, but not in PrEC. The hnPNP role in ANXA7 regulation (that was validated by hnRNPA2/B1 antibody interference) resulted in multiple ANXA7 cDNA and protein products in PC3, but not in PrEC. Ingenuity pathways analysis showed plausible molecular paths between ANXA7 and the hnRNP-associated network in prostate cancer progression. Thus, a multi-hnRNP complex can be responsible for aberrant ANXA7 transcription and splicing, thereby affecting ANXA7 expression pattern and tumor suppressor function in prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANXA7:
-
Annexin A7
- AR:
-
androgen receptor
- GR:
-
glucocorticoid receptor
- hnRNP:
-
heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein
- IPA:
-
ingenuity pathways analysis
- MALDI-TOF MS:
-
matrix-assisted laser desorption time-of-flight mass spectrometry
References
Adachi K, Tanaka T, Saito H, Oka T . (1999). Hormonal induction of mouse selenocysteine transfer ribonucleic acid (tRNA) gene transcription-activating factor and its functional importance in the selenocysteine tRNA gene transcription in mouse mammary gland. Endocrinology 140: 618–623.
Auboeuf D, Honig A, Berget SM, O′Malley BW . (2002). Coordinate regulation of transcription and splicing by steroid receptor coregulators. Science 298: 416–419.
Barboro P, Repaci E, Rubagotti A, Salvi S, Boccardo S, Spina B et al. (2009). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K: altered pattern of expression associated with diagnosis and prognosis of prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 100: 1608–1616.
Burd CG, Swanson MS, Görlach M, Dreyfuss G . (1989). Primary structures of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2, B1, and C2 proteins: a diversity of RNA binding proteins is generated by small peptide inserts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 9788–9792.
Caron D, Winstall E, Inaguma Y, Michaud S, Lettre F, Bourassa S et al. (2008). Proteomic characterization of mouse cytosolic and membrane prostate fractions: high levels of free SUMO peptides are androgen-regulated. J Proteome Res 7: 4492–4499.
Carpenter B, MacKay C, Alnabulsi A, MacKay M, Telfer C, Melvin WT et al. (2006). The roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in tumour development and progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1765: 85–100.
Chen H, Stuart W, Hu B, Nguyen L, Huang G, Clemens TL et al. (2005). Creation of estrogen resistance in vivo by transgenic overexpression of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-related estrogen response element binding protein. Endocrinology 146: 4266–4273.
Chen S, Wang J, Yu G, Liu W, Pearce D . (1997). Androgen and glucocorticoid receptor heterodimer formation. A possible mechanism for mutual inhibition of transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 272: 14087–14092.
Chen TC, Schwartz GG, Burnstein KL, Lokeshwar BL, Holick MF . (2000). The in vitro evaluation of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 19-nor-1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 as therapeutic agents for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 6: 901–908.
Cooper TA, Wan L, Dreyfuss G . (2009). RNA and disease. Cell 136: 777–793.
Courchet J, Buchet-Poyau K, Potemski A, Brès A, Jariel-Encontre I, Billaud M . (2008). Interaction with 14-3-3 adaptors regulates the sorting of hMex-3B RNA-binding protein to distinct classes of RNA granules. J Biol Chem 283: 32131–32142.
Dobi A, Debnam W, Dalgard C, Owusu A, von Agoston D . (2002). Mammalian expression cloning of nucleic acid binding proteins by agarose thin-layer gelshift clone selection. Biotechniques 33: 868–872.
Duncan R, Carpenter B, Main LC, Telfer C, Murray GI . (2008). Characterisation and protein expression profiling of annexins in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 98: 426–433.
Eggert H, Schulz M, Fackelmayer FO, Renkawitz R, Eggert M . (2001). Effects of the heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (hnRNP U/SAF-A) on glucocorticoid-dependent transcription in vivo. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 78: 59–65.
Enge M, Bao W, Hedström E, Jackson SP, Moumen A, Selivanova G . (2009). MDM2-dependent downregulation of p21 and hnRNP K provides a switch between apoptosis and growth arrest induced by pharmacologically activated p53. Cancer Cell 15: 171–183.
Graveley BR . (2009). Alternative splicing: regulation without regulators. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16: 13–15.
He Y, Brown MA, Rothnagel JA, Saunders NA, Smith R . (2005). Roles of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins A and B in cell proliferation. J Cell Sci 118: 3173–3183.
Heemers HV, Verhoeven G, Swinnen JV . (2006). Androgen activation of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein pathway: current insights. Mol Endocrinol 20: 2265–2277.
Hellwinkel OJ, Rogmann JP, Asong LE, Luebke AM, Eichelberg C, Ahyai S et al. (2008). A comprehensive analysis of transcript signatures of the phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/protein kinase B signal-transduction pathway in prostate cancer. BJU Int 101: 1454–1460.
Hilbe W, Dirnhofer S, Greil R, Woll E . (2004). Biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer prevention. Eur J Cancer Prev 13: 425–436.
Juven-Gershon T, Hsu JY, Theisen JW, Kadonaga JT . (2008). The RNA polymerase II core promoter—the gateway to transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20: 253–259.
Kang HS, Angers M, Beak JY, Wu X, Gimble JM, Wada T et al. (2007). Gene expression profiling reveals a regulatory role for ROR alpha and ROR gamma in phase I and phase II metabolism. Physiol Genomics 31: 281–294.
Karagianni N, Tsawdaroglou N . (1994). The c-fos serum response element (SRE) confers negative response to glucocorticoids. Oncogene 9: 2327–2334.
Kim TH, Barrera LO, Zheng M, Qu C, Singer MA, Richmond TA et al. (2005). High-resolution map of active promoters in the human genome. Nature 436: 876–880.
Kimura E, Abe K, Suzuki K, Sorimachi H . (2003). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K interacts with and is proteolyzed by calpain in vivo. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67: 1786–1796.
Lee BJ, Cansizoglu AE, Süel KE, Louis TH, Zhang Z, Chook YM . (2006). Rules for nuclear localization sequence recognition by karyopherin beta 2. Cell 126: 543–558.
Li T, Evdokimov E, Shen RF, Chao CC, Tekle E, Wang T et al. (2004). Sumoylation of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins, zinc finger proteins, and nuclear pore complex proteins: a proteomic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101: 8551–8556.
Magendzo K, Shirvan A, Cultraro C, Srivastava M, Pollard HB, Burns AL . (1991). Alternative splicing of human synexin mRNA in brain, cardiac, and skeletal muscle alters the unique N-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 266: 3228–3232.
Mikula M, Dzwonek A, Karczmarski J, Rubel T, Dadlez M, Wyrwicz LS et al. (2006). Landscape of the hnRNP K protein-protein interactome. Proteomics 6: 2395–2406.
Mukhopadhyay NK, Kim J, Cinar B, Ramachandran A, Hager MH, Di Vizio D et al. (2009). Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K is a novel regulator of androgen receptor translation. Cancer Res 69: 2210–2218.
Myslinski E, Gérard MA, Krol A, Carbon P . (2006). A genome scale location analysis of human Staf/ZNF143-binding sites suggests a widespread role for human Staf/ZNF143 in mammalian promoters. J Biol Chem 281: 39953–39962.
Nakielny S, Dreyfuss G . (1999). Transport of proteins and RNAs in and out of the nucleus. Cell 99: 677–690.
Patry C, Bouchard L, Labrecque P, Gendron D, Lemieux B, Toutant J et al. (2003). Small interfering RNA-mediated reduction in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoparticule A1/A2 proteins induces apoptosis in human cancer cells but not in normal mortal cell lines. Cancer Res 63: 7679–7688.
Pollard HB, Caohuy H, Minton AP, Srivastava M . (1998). Synexin (annexin VII) hypothesis for Ca2+/GTP-regulated exocytosis. Adv Pharmacol 42: 81–87.
Reed R, Hurt E . (2002). A conserved mRNA export machinery coupled to pre-mRNA splicing. Cell 108: 523–531.
Rizzo G, Fiorucci S . (2006). PPARs and other nuclear receptors in inflammation. Curr Opin Pharmacol 6: 421–427.
Rozanov DV, Savinov AY, Williams R, Liu K, Golubkov VS, Krajewski S et al. (2008). Molecular signature of MT1-MMP: transactivation of the downstream universal gene network in cancer. Cancer Res 68: 4086–4096.
Sakaguchi M, Murata H, Sonegawa H, Sakaguchi Y, Futami J, Kitazoe M et al. (2007). Truncation of annexin A1 is a regulatory lever for linking epidermal growth factor signaling with cytosolic phospholipase A2 in normal and malignant squamous epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 282: 35679–35686.
Shi L, Ko S, Kim S, Echchgadda I, Oh TS, Song CS et al. (2008). Loss of androgen receptor in aging and oxidative stress through Myb protooncoprotein-regulated reciprocal chromatin dynamics of p53 and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase PARP-1. J Biol Chem 283: 36474–36485.
Shi Y, Manley JL . (2007). A complex signaling pathway regulates SRp38 phosphorylation and pre-mRNA splicing in response to heat shock. Mol Cell 28: 79–90.
Shirvan A, Srivastava M, Wang MG, Cultraro C, Magendzo K, McBride OW et al. (1994). Divergent structure of the human synexin (annexin VII) gene and assignment to chromosome 10. Biochemistry 33: 6888–6901.
Srivastava M, Atwater I, Glasman M, Leighton X, Goping G, Caohuy H et al. (1999). Defects in inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor expression, Ca(2+) signaling, and insulin secretion in the anx7(+/−) knockout mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 13783–13788.
Srivastava M, Montagna C, Leighton X, Glasman M, Naga S, Eidelman O et al. (2003). Haploinsufficiency of Anx7 tumor suppressor gene and consequent genomic instability promotes tumorigenesis in the Anx7(+/−) mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 14287–14292.
Srivastava M, Pollard HB . (2000). Low in vivo levels of human anx7 (annexin VII) gene expression are due to endogenous inhibitory promoter sequences. Cell Biol Int 24: 475–481.
Srivastava M, Torosyan Y, Raffeld M, Eidelman O, Pollard HB, Bubendorf L . (2007). ANXA7 expression represents hormone-relevant tumor suppression in different cancers. Int J Cancer 121: 2628–2636.
Tokusumi Y, Ma Y, Song X, Jacobson RH, Takada S . (2007). The new core promoter element XCPE1 (X Core Promoter Element 1) directs activator-, mediator-, and TATA-binding protein-dependent but TFIID-independent RNA polymerase II transcription from TATA-less promoters. Mol Cell Biol 27: 1844–1858.
Torosyan Y, Dobi A, Naga S, Mezhevaya K, Glasman M, Norris C et al. (2006). Distinct effects of annexin A7 and p53 on arachidonate lipoxygenation in prostate cancer cells involve 5-lipoxygenase transcription. Cancer Res 66: 9609–9616.
Torosyan Y, Simakova O, Naga S, Mezhevaya K, Leighton X, Diaz J et al. (2009). Annexin-A7 protects normal prostate cells and induces distinct patterns of RB-associated cytotoxicity in androgen-sensitive and -resistant prostate cancer cells. Int J Cancer 125: 2528–2539.
Wolf M, Mousses S, Hautaniemi S, Karhu R, Huusko P, Allinen M et al. (2004). High-resolution analysis of gene copy number alterations in human prostate cancer using CGH on cDNA microarrays: impact of copy number on gene expression. Neoplasia 6: 240–247.
Yemelyanov A, Czwornog J, Chebotaev D, Karseladze A, Kulevitch E, Yang X et al. (2007). Tumor suppressor activity of glucocorticoid receptor in the prostate. Oncogene 26: 1885–1896.
Zheng Z, Cai C, Omwancha J, Chen SY, Baslan T, Shemshedini L . (2006). SUMO-3 enhances androgen receptor transcriptional activity through a sumoylation-independent mechanism in prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 281: 4002–4012.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Gideon Dreyfuss (University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine) for providing hnRNPA2/B1 antibody. This work was supported by grants funded by the US Department of Defense (DoD).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torosyan, Y., Dobi, A., Glasman, M. et al. Role of multi-hnRNP nuclear complex in regulation of tumor suppressor ANXA7 in prostate cancer cells. Oncogene 29, 2457–2466 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The TLR/MyD88 signalling cascade in inflammation and gastric cancer: the immune regulatory network of Helicobacter pylori
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A/B: an emerging group of cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets
Cell Death Discovery (2022)
-
HnRNPA2 is a novel histone acetyltransferase that mediates mitochondrial stress-induced nuclear gene expression
Cell Discovery (2016)
-
Influence of annexin A7 on insulin sensitivity of cellular glucose uptake
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2015)
-
Measuring gene similarity by means of the classification distance
Knowledge and Information Systems (2011)