Abstract
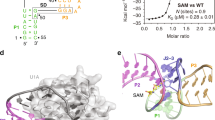
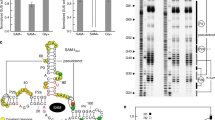
Coenzyme B12 has a key role in various enzymatic reactions and controls expression of bacterial genes through riboswitches. Here we report the crystal structure of the Symbiobacterium thermophilum B12 riboswitch bound to its ligand adenosylcobalamin. The riboswitch forms a unique junctional structure with a large ligand-binding pocket tailored for specific recognition of the adenosyl moiety and flanked by structural elements that stabilize the regulatory region and enable control of gene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Lundrigan, M.D., Koster, W. & Kadner, R.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 1479–1483 (1991).
Nou, X. & Kadner, R.J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 7190–7195 (2000).
Ravnum, S. & Andersson, D.I. Mol. Microbiol. 39, 1585–1594 (2001).
Mironov, A.S. et al. Cell 111, 747–756 (2002).
Nahvi, A. et al. Chem. Biol. 9, 1043 (2002).
Winkler, W., Nahvi, A. & Breaker, R.R. Nature 419, 952–956 (2002).
Nahvi, A., Barrick, J.E. & Breaker, R.R. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 143–150 (2004).
Rodionov, D.A., Vitreschak, A.G., Mironov, A.A. & Gelfand, M.S. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41148–41159 (2003).
Jaeger, L., Verzemnieks, E.J. & Geary, C. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 215–230 (2009).
Serganov, A., Huang, L. & Patel, D.J. Nature 458, 233–237 (2009).
Serganov, A., Huang, L. & Patel, D.J. Nature 455, 1263–1267 (2008).
Gallo, S., Oberhuber, M., Sigel, R.K. & Krautler, B. ChemBioChem 9, 1408–1414 (2008).
Sussman, D., Nix, J.C. & Wilson, C. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 53–57 (2000).
Borovok, I., Gorovitz, B., Schreiber, R., Aharonowitz, Y. & Cohen, G. J. Bacteriol. 188, 2512–2520 (2006).
Warner, D.F., Savvi, S., Mizrahi, V. & Dawes, S.S. J. Bacteriol. 189, 3655–3659 (2007).
Loh, E. et al. Cell 139, 770–779 (2009).
Serganov, A. et al. Eur. J. Biochem. 246, 291–300 (1997).
Pikovskaya, O., Serganov, A.A., Polonskaia, A., Serganov, A. & Patel, D.J. Methods Mol. Biol. 540, 115–128 (2009).
Adams, P.D. et al. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 213–221 (2010).
Emsley, P., Lohkamp, B., William, G., Scott, W.G. & Cowtan, K. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 486–501 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We thank personnel of beamlines X25 and X4C at the Brookhaven National Laboratory funded by the US Department of Energy, O. Ouerfelli (Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center) for the synthesis of iridium hexamine and E. Wasmuth for initial input into the project. A.S. was supported by funds from the New York University School of Medicine.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.P. crystallized the AdoCbl riboswitch, A.S. determined the crystal structure. A.P. and A.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–5 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 5382 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peselis, A., Serganov, A. Structural insights into ligand binding and gene expression control by an adenosylcobalamin riboswitch. Nat Struct Mol Biol 19, 1182–1184 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2405
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2405
This article is cited by
-
Recognition of the bacterial alarmone ZMP through long-distance association of two RNA subdomains
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2015)
-
Structural basis for gene regulation by a B12-dependent photoreceptor
Nature (2015)
-
The photochemical mechanism of a B12-dependent photoreceptor protein
Nature Communications (2015)
-
A critical base pair in k-turns that confers folding characteristics and correlates with biological function
Nature Communications (2014)