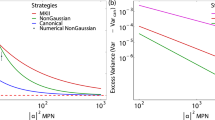
Abstract
Optical phase estimation is a vital measurement strategy that is used to perform accurate measurements of various physical quantities including length, velocity and displacements1,2. The precision of such measurements can be greatly enhanced by the use of entangled or squeezed states of light as demonstrated in a variety of different optical systems3,4,5,6,7,8. Most of these accounts, however, deal with the measurement of a very small shift of an already known phase, which is in stark contrast to ab initio phase estimation where the initial phase is unknown9,10,11,12. Here, we report on the realization of a quantum-enhanced and fully deterministic ab initio phase estimation protocol based on real-time feedback control. Using robust squeezed states of light combined with a real-time Bayesian adaptive estimation algorithm, we demonstrate deterministic phase estimation with a precision beyond the quantum shot noise limit. The demonstrated protocol opens up new opportunities for quantum microscopy, quantum metrology and quantum information processing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caves, C. M. Quantum mechanical noise in an interferometer. Phys. Rev. D 23, 1693–1708 (1981).
Giovannetti, V., Lloyd, S. & Maccone, L. Advances in quantum metrology. Nature Photon. 5, 222–229 (2011).
Nagata, T., Okamoto, R., O'Brien, J., Sasaki, K. & Takeuchi, S. Beating the standard quantum limit with four-entangled photons. Science 316, 726 (2007).
Banaszek, K., Demkowicz-Dobrzanski, R. & Walmsley, I. A. Quantum states made to measure. Nature Photon. 3, 673–676 (2009).
Kacprowicz, M., Demkowicz-Dobrzanski, R., Wasilewski, W., Banaszek, K. & Walmsley, I. A. Experimental quantum-enhanced estimation of a lossy phase shift. Nature Photon. 4, 357–360 (2010).
The LIGO Scientific Collaboration. tA gravitational wave observatory operating beyond the quantum shot-noise limit. Nature Phys. 7, 962–965 (2011).
Yonezawa, H. et al. Quantum-enhanced optical phase tracking. Science 337, 1514–1517 (2012).
Hoff, U. B. et al. Quantum-enhanced micromechanical displacement sensitivity. Opt. Lett. 38, 1413–1415 (2012).
Wiseman, H. M. Adaptive phase measurement of optical modes: going beyond the marginal Q distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 75, 4587–4590 (1995).
Berry, D. W. & Wiseman, H. M. Adaptive phase measurements for narrowband squeezed beams. Phys. Rev. A 73, 063824 (2006).
Kolodynski, J. & Demkowicz-Dobrzanski, R. Phase estimation without a priori phase knowledge in the presence of loss. Phys. Rev. A 82, 053804 (2010).
Xiang, G. Y., Higgins, B. L., Berry, D. W., Wiseman, H. M. & Pryde, G. J. Entanglement-enhanced measurement of a completely unknown optical phase. Nature Photon. 5, 43–47 (2010).
Barnett, S. M. & Pegg, D. T. Phase in quantum optics. J. Phys. A 19, 3849–3862 (1986).
Hradil, Z. & Rehacek, J. Quantum interference and Fisher information. Phys. Lett. A 334, 267–272 (2005).
Escher, B. M., de Matos Filho, R. L. & Davidovich, L. General framework for estimating the ultimate precision limit in noisy quantum-enhanced metrology. Nature Phys. 7, 406–411 (2011).
Cramer, H. Mathematical Methods of Statistics (Princeton Univ. Press, 1946).
Braunstein, S. L. & Caves, C. M. Statistical distance and the geometry of quantum states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 3439–3443 (1994).
D'Ariano, G. M., Paris, M. G. A. & Seno, R. Feedback-assisted homodyne detection of phase shifts. Phys. Rev. A 54, 4495–4504 (1996).
Armen, M. A., Au, J. K., Stockton, J. K., Doherty, A. C. & Mabuchi, H. Adaptive homodyne measurement of optical phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 89, 133602 (2002).
Wheatley, T. A. et al. Adaptive optical phase estimation using time-symmetric quantum smoothing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 093601 (2010).
Weedbrook, C. et al. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 84, 621–669 (2012).
Monras, A. Optimal phase measurements with pure Gaussian states. Phys. Rev. A 73, 033821 (2006).
Olivares, S. & Paris, M. G. A. Bayesian estimation in homodyne interferometry. J. Phys. B 42, 055506 (2009).
Barndorff-Nielsen, O. E. & Gill, R. D. Fisher information in quantum statistics. J. Phys. A 33, 4481–4490 (2000).
Aspachs, M., Calsamiglia, J., Munoz-Tapia, R. & Bagan, E. Phase estimation for thermal Gaussian states. Phys. Rev. A 79, 033834 (2009).
Berni, A. Quantum Metrology With Squeezed Light. Master's thesis (Università degli Studi di Milano, 2011).
Eberle, T., Händchen, V. & Schnabel, R. Stable control of 10 dB two-mode squeezed vacuum states of light. Opt. Express 21, 11546–11553 (2013).
Carlton, P. M. et al. Fast live simultaneous multiwavelength four-dimensional optical microscopy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 16016–16022 (2010).
Pototschnig, M. et al. Controlling the phase of a light beam with a single molecule. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 063001 (2011).
Genoni, M. G. et al. Optimal estimation of joint parameters in phase space. Phys. Rev. A 87, 012107 (2013).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the Danish Agency for Science, Technology and Innovation (Sapere Aude grant from FTP: 10-081599) and the Lundbeck Foundation. T.G. was supported by the HC Ørsted Postdoc programme. The authors would like to thank Roman Schnabel from the Albert Einstein Institute in Hannover for the support in using the squeezing source.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.A.B. and T.G. performed the main experiment and analysed the data. A.A.B., T.G. and B.M.N. developed the feedback protocol. T.G. and V.H. built the squeezed light source. A.A.B., T.G., M.G.A.P. and U.L.A. discussed the results. A.A.B and U.L.A wrote the paper with support from T.G. and M.G.A.P. U.L.A. conceived and supervised the project.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 1742 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berni, A., Gehring, T., Nielsen, B. et al. Ab initio quantum-enhanced optical phase estimation using real-time feedback control. Nature Photon 9, 577–581 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.139
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.139
This article is cited by
-
Weak signal extraction in non-stationary channel with weak measurement
Communications Physics (2023)
-
Experimental metrology beyond the standard quantum limit for a wide resources range
npj Quantum Information (2023)
-
Enhancing the precision limits of interferometric satellite geodesy missions
npj Microgravity (2022)
-
Determination of the asymptotic limits of adaptive photon counting measurements for coherent-state optical phase estimation
npj Quantum Information (2022)
-
A machine learning approach to Bayesian parameter estimation
npj Quantum Information (2021)