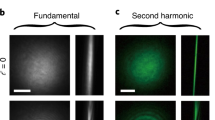
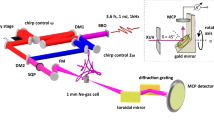
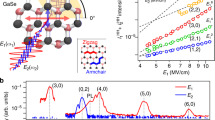
Abstract
The roles of energy, momentum and orbital angular momentum conservation in high-harmonic generation were studied in the past. Here, we explore the role of spin angular momentum in high-harmonic generation by experimentally generating high harmonics of bichromatic elliptically polarized pump beams that interact with isotropic media. We explain qualitatively many observed intricate selection rules with a model that includes spin conservation in the conversion of many pump photons into a single photon. However, we also observe unequivocal deviations from this model, indicating that emission of an elliptically polarized high-energy photon is accompanied by an additional excitation (radiative or electronic). The presented results are also important for applications, because our system exhibits full control over the polarization of the harmonics, from circular through elliptical to linear polarization, without compromising the efficiency of the process. This work paves the way for a broad range of applications with high-harmonic generation, including ultrafast circular dichroism of molecules and magnetic materials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goulielmakis, E. et al. Real-time observation of valence electron motion. Nature 466, 739–744 (2010).
Baker, S. et al. Probing proton dynamics in molecules on an attosecond time scale. Science 312, 424–427 (2006).
Li, W. et al. Time-resolved dynamics in N2O4 probed using high harmonic generation. Science 322, 1207–1211 (2008).
Wörner, H. J., Bertrand, J. B., Kartashov, D. V., Corkum, P. B. & Villeneuve, D. M. Following a chemical reaction using high-harmonic interferometry. Nature 466, 604–607 (2010).
Cavalieri, A. L. et al. Attosecond spectroscopy in condensed matter. Nature 449, 1029–1032 (2007).
Mathias. S. et al. Probing the timescale of the exchange interaction in a ferromagnetic alloy. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 109, 4792–4797 (2012).
Salières, P. et al. Frequency-domain interferometry in the XUV with high-order harmonics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 83, 5483–5486 (1999).
Seaberg, M. D. et al. Ultrahigh 22 nm resolution coherent diffractive imaging using a desktop 13 nm high harmonic source. Opt. Express 19, 22470–22479 (2011).
Siemens, M. E. et al. Quasi-ballistic thermal transport from nanoscale interfaces observed using ultrafast coherent soft X-ray beams. Nature Mater. 9, 26–30 (2010).
Corkum, P. B. Plasma perspective on strong field multiphoton ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1994–1997 (1993).
Boyd, R. W. Nonlinear Optics 3rd edn (Academic, 2008).
Bloembergen, N. Conservation laws in nonlinear optics. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 70, 1429–1436 (1980).
Eden, J. G. High-order harmonic generation and other intense optical field–matter interactions: review of recent experimental and theoretical advances. Prog. Quantum Electron. 28, 197–246 (2004).
Perry, M. D. & Crane, J. K. High-order harmonic emission from mixed fields. Phys. Rev. A. 48, R4051–R4054 (1993).
Bertrand, J. B. et al. Ultrahigh-order wave mixing in noncollinear high harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 106, 023001 (2011).
Gariepy G. et al. Conservation of Orbital Angular Momentum in High-Harmonic Generation. MSc thesis, Univ. Ottawa (2013).
Lewenstein, M., Balcou, Ph., Ivanov, M. Yu., L'Huillier, A. & Corkum, P. B. Theory of high-harmonic generation by low-frequency laser fields. Phys. Rev. A 49, 2117–2132 (1994).
Weihe, F. A. et al. Polarization of high-intensity high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. A 51, R3433–R3436 (1995).
Strelkov, V. V., Gonoskov, A. A., Gonoskov, I. A. & Ryabikin, M. Yu. Origin for ellipticity of high-order harmonics generated in atomic gases and the sublaser-cycle evolution of harmonic polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 043902 (2011).
Antoine, P., Carré, B., L'Huiller, A. & Lewenstein, M. Polarization of high-order harmonics. Phys. Rev. A 55, 1314–1324 (1997).
Zhou, X. et al. Elliptically polarized high-order harmonic emission from molecules in linearly polarized laser fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 073902 (2009).
Mairesse, Y. et al. High harmonic spectroscopy of multichannel dynamics in strong-field ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 213601 (2010).
Dietrich, P., Burnett, N. H., Ivanov, M. & Corkum, P. B. High-harmonic generation and correlated two-electron multiphoton ionization with elliptically polarized light. Phys. Rev. A 50, R3585 (1994).
Vodungbo, B. et al. Polarization control of high order harmonics in the EUV photon energy range. Opt. Express 19, 4346–4356 (2011).
Alon, O. E., Averbukh, V. & Moiseyev, N. Selection rules for the high harmonic generation spectra. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 3743–3746 (1998).
Husakou, A., Kelkensberg, F., Herrmann, J. & Vrakking, M. J. J. Polarization gating and circularly-polarized high harmonic generation using plasmonic enhancement in metal nanostructures. Opt. Express 19, 25346–25354 (2011).
Yuan, K.-J. & Bandrauk, A. D. Generation of circularly polarized attosecond pulses by intense ultrashort laser pulses from extended asymmetric molecular ions. Phys. Rev. A 84, 023410 (2011).
Fleischer, A. et al. Generation of high-order harmonics with controllable elliptical polarization. Opt. Lett. 38, 223–225 (2013).
Ruiz, C., Hoffmann, D. J., Torres, R., Chipperfield, L. E. & Marangos, J. P. Control of the polarization of attosecond pulses using a two-color field. New J. Phys. 11, 113045 (2009).
Long, S., Becker, W. & McIver, J. K. Model calculations of polarization-dependent two-color high-harmonic generation. Phys. Rev. A 52, 2262–2278 (1995).
Eichmann, H. et al. Polarization-dependent high-order two-color mixing. Phys. Rev. A 51, R3414 (1995).
Kfir, O. et al. Generation of phase-matched circularly-polarized extreme ultraviolet high harmonics for magnetic circular dichroism spectroscopy. http://arxiv.org/abs/1401.4101(2014).
Boeglin, C. et al. Distinguishing the ultrafast dynamics of spin and orbital moments in solids. Nature 465, 458–461 (2010).
Jahnke, T. et al. Circular dichroism in k-shell ionization from fixed-in-space CO and N2 molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 073002 (2002).
Wang, Y. & Gedik, N. Circular dichroism in angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy of topological insulators. Phys. Status Solidi 7, 64–71 (2013).
Eckle, P. et al. Attosecond ionization and tunneling delay time measurements in helium. Science 322, 1525–1529 (2008).
Fleischer, A. et al. Probing angular correlations in sequential double ionization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 107, 113003 (2011).
Hernández-García, C. et al. Zeptosecond high harmonic keV X-ray waveforms driven by midinfrared laser pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 111, 033002 (2013).
Milošević, D. B. & Becker, W. Attosecond pulse trains with unusual nonlinear polarization. Phys. Rev. A 62, 011403(R) 10.1103/PhysRevA.62.011403(2000).
Milošević, D. B. & Sandner, W. Extreme-ultraviolet harmonic generation near 13 nm with a two-color elliptically polarized laser field. Opt. Lett. 25, 1532–1534 (2000).
Lamberti, C. et al. Oxide/metal interface distance and epitaxial strain in the NiO/Ag(001) system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 91, 046101 (2003).
Vondungbo, B. et al. Laser-induced ultrafast demagnetization in the presence of a nanoscale magnetic domain network. Nature Commun. 3, 999 (2012).
Cinchetti, M. et al. Spin-flip processes and ultrafast magnetization dynamics in Co: unifying the microscopic and macroscopic view of femtosecond magnetism. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 177201 (2006).
Stamm, C. et al. Femtosecond modification of electron localization and transfer of angular momentum in nickel. Nature Mater. 6, 740–743 (2007).
Smirnova, O. et al. Attosecond circular dichroism spectroscopy of polyatomic molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 063601 (2009).
McFarland, B. K., Farrell, J. P., Bucksbaum, P. H. & Gühr, M. High harmonic generation from multiple orbitals in N2 . Science 322, 1232–1235 (2008).
Xie, X. et al. Internal momentum state mapping using high harmonic radiation. Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 033901 (2008).
Barth, I., Manz, J., Shigeta, Y. & Yagi, K. Unidirectional electronic ring current driven by a few cycle circularly polarized laser pulse: quantum model simulations for Mg-porphyrin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 128, 7043–7049 (2006).
Kaminski, A. et al. Spontaneous breaking of time-reversal symmetry in the pseudogap state of a high-Tc superconductor. Nature 416, 610–613 (2002).
Gao, J., Shen, F. & Eden, J. G. Quantum electrodynamic treatment of harmonic generation in intense optical fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 1833–1836 (1998).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank T. Yasniger, S. Avikzar, A. Anashkin and D. Cohen from the Technion for technical assistance. This work was support by ICore—the Israeli Excellence Center ‘Circle of Light’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.F. and O.C. conceived the idea. A.F., O.K. and P.S. carried out experiments. A.F. and T.D. carried out the numerical analysis. All authors contributed to the analysis, interpretation and writing of the manuscript. O.C. supervised the project.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2572 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fleischer, A., Kfir, O., Diskin, T. et al. Spin angular momentum and tunable polarization in high-harmonic generation. Nature Photon 8, 543–549 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.108
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.108
This article is cited by
-
Topological high-harmonic spectroscopy
Communications Physics (2024)
-
Enabling elliptically polarized high harmonic generation with short cross polarized laser pulses
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Attosecond circular-dichroism chronoscopy of electron vortices
Nature Physics (2022)
-
Amplification of elliptically polarized sub-femtosecond pulses in neon-like X-ray laser modulated by an IR field
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Progress on table-top isolated attosecond light sources
Nature Photonics (2022)