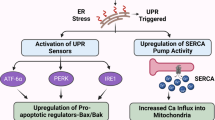
Abstract
BCR–ABL-targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) constitute the cornerstone of treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia. Although these agents are normally safe and effective, they can cause side effects that lead to intolerance and necessitate switching to an alternative treatment. In this review, we describe side effects that occur during treatment with imatinib, nilotinib or dasatinib—the currently approved TKI treatments for chronic myeloid leukemia—including class effects and key differences in safety profiles. We also describe how common side effects can be effectively managed and offer a working definition of intolerance that may be useful to clinicians when they consider switching between TKIs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A, Baccarani M . Chronic myeloid leukemia. Lancet 2007; 370: 342–350.
Johnson JR, Bross P, Cohen M, Rothmann M, Chen G, Zajicek A et al. Approval summary: imatinib mesylate capsules for treatment of adult patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 1972–1979.
Deininger M, O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Goldman JM, Hochhaus A, Hughes TP et al. International randomized study of interferon vs STI571 (IRIS) 8-year follow up: sustained survival and low risk for progression or events in patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP) treated with imatinib. Blood 2009; 114 (Suppl): (abstract 1126).
Hochhaus A, O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford S, Foroni L et al. Six-year follow-up of patients for the first-line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1054–1061.
Jabbour E, Kantarjian HM, Jones D, Shan J, O’Brien S, Reddy N et al. Imatinib mesylate dose escalation is associated with durable responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia after cytogenetic failure on standard-dose imatinib therapy. Blood 2009; 113: 2154–2160.
Kantarjian HM, Larson RA, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Mone M, Rudoltz M et al. Efficacy of imatinib dose escalation in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. Cancer 2009; 115: 551–560.
Rea D, Etienne G, Corm S, Cony-Makhoul P, Gardembas M, Legros L et al. Imatinib dose escalation for chronic phase-chronic myelogenous leukaemia patients in primary suboptimal response to imatinib 400 mg daily standard therapy. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1193–1196.
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 6041–6051.
de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, Milojkovic D, Reid AG, Bua M et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 3358–3363.
Steegmann JL, Michallet M, Morra E, Marin D, Ossenkippele GJ, Verhoef G et al. Imatinib use in chronic phase CML in clinical practice: the UNIC study. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26, (abstract 7077).
O’Hare T, Walters DK, Stoffregen EP, Jia T, Manley PW, Mestan J et al. In vitro activity of Bcr-Abl inhibitors AMN107 and BMS-354825 against clinically relevant imatinib-resistant Abl kinase domain mutants. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 4500–4505.
Weisberg E, Manley PW, Breitenstein W, Brüggen J, Cowan-Jacob SW, Ray A et al. Characterization of AMN107, a selective inhibitor of native and mutant Bcr-Abl. Cancer Cell 2005; 7: 129–141.
Hazarika M, Jiang X, Liu Q, Lee SL, Ramchandani R, Garnett C et al. Tasigna for chronic and accelerated phase Philadelphia chromosome—positive chronic myelogenous leukemia resistant to or intolerant of imatinib. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 5325–5331.
Lombardo LJ, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Barrish JC, Behnia K et al. Discovery of N-(2-chloro-6-methyl-phenyl)-2-(6-(4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-piperazin-1-yl)-2-methylpyrimidin-4-ylamino)thiazole-5-carboxamide (BMS-354825), a dual Src/Abl kinase inhibitor with potent antitumor activity in preclinical assays. J Med Chem 2004; 47: 6658–6661.
Shah NP, Tran C, Lee FY, Chen P, Norris D, Sawyers CL . Overriding imatinib resistance with a novel ABL kinase inhibitor. Science 2004; 305: 399–401.
Lee FY, Lombardo L, Camuso A, Castaneda S, Fager K, Flefleh C et al. BMS-354825 potently inhibits multiple selected oncogenic tyrosine kinases and possesses broad-spectrum antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 2005; 46: 159 (abstract 675).
Nam S, Kim D, Cheng JQ, Zhang S, Lee JH, Buettner R et al. Action of the Src family kinase inhibitor, dasatinib (BMS-354825), on human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9185–9189.
Schittenhelm MM, Shiraga S, Schroeder A, Corbin AS, Griffith D, Lee FY et al. Dasatinib (BMS-354825), a dual SRC/ABL kinase inhibitor, inhibits the kinase activity of wild-type, juxtamembrane, and activation loop mutant KIT isoforms associated with human malignancies. Cancer Res 2006; 66: 473–481.
Mahon FX, Hayette S, Lagarde V, Belloc F, Turcq B, Nicolini F et al. Evidence that resistance to nilotinib may be due to BCR-ABL, Pgp, or Src kinase overexpression. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 9809–9816.
Redaelli S, Piazza R, Rostagno R, Magistroni V, Perini P, Marega M et al. Activity of bosutinib, dasatinib, and nilotinib against 18 imatinib-resistant BCR/ABL mutants. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 469–471.
Brave M, Goodman V, Kaminskas E, Farrell A, Timmer W, Pope S et al. Sprycel for chronic myeloid leukemia and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia resistant to or intolerant of imatinib mesylate. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 352–359.
Kantarjian HM, Giles F, Gatterman N, Bhalla K, Alimena G, Palandri F et al. Nilotinib (formerly AMN107), a highly selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor, is effective in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase following imatinib resistance and intolerance. Blood 2007; 110: 3540–3546.
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Deininger M, Apperley JF, Lipton JH, Goldberg SL et al. Dasatinib induces durable cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1200–1206.
le Coutre PD, Giles F, Hochhaus A, Apperley JF, Ossenkoppele G, Haque A et al. Nilotinib in chronic myeloid leukemia patients in accelerated phase (CML-AP) with imatinib (IM) resistance or intolerance: Longer follow-up results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27, (abstract 7057).
Saglio G, Kantarjian HM, Hochhaus A, Goh YT, Masszi T, Pasquini R et al. Dasatinib 140 mg once daily (QD) demonstrates equivalent efficacy and improved safety compared with 70 mg twice daily (BID) in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in blast phase (CML-BP): 2-year data from CA180-035. Blood 2008; 112, (abstract 3226).
Kantarjian H, Cortes J, Kim DW, Dorlhiac-Llacer P, Pasquini R, DiPersio J et al. Phase 3 study of dasatinib 140 mg once daily versus 70 mg twice daily in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase resistant or intolerant to imatinib: 15-month median follow-up. Blood 2009; 113: 6322–6329.
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes J, Shah S, Ayala M et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 2260–2270.
Saglio G, Kim DW, Issaragrisil S, le Coutre P, Etienne G, Lobo C et al. Nilotinib versus imatinib for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2010; 362: 2251–2259.
Shah NP, Kim DW, Kantarjian H, Rousselot P, Llacer PE, Enrico A et al. Potent, transient inhibition of BCR-ABL with dasatinib 100 mg daily achieves rapid and durable cytogenetic responses and high transformation-free survival rates in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance, suboptimal response or intolerance to imatinib. Haematologica 2010; 95: 232–240.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N et al. IRIS Investigators. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–2417.
Deininger MWN, O’Brien SG, Ford JM, Druker BJ . Practical management of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia receiving imatinib. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1637–1647.
Cortes JE, Baccarani M, Guilhot F, Druker BJ, Branford F, Kim DW et al. Phase III, randomized, open-label study of daily imatinib mesylate 400 mg versus 800 mg in patients with newly diagnosed, previously untreated chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase using molecular end points: tyrosine kinase inhibitor optimization and selectivity study. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 424–430.
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Apperley J, Crawley C, Ruutu T, Corradini P et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia in Europe 2006: transplant activity, long-term data and current results. An analysis by the Chronic Leukemia Working Party of the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT). Haematologica 2006; 91: 513–521.
O’Brien SG, Guilhot F, Larson RA, Gathmann I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F et al. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 348: 994–1004.
Kantarjian HM, Giles FJ, Bhalla KN, Pinilla-Ibarz J, Larson RA, Gattermann N et al. Update on imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia patients in chronic phase (CML-CP) on nilotinib therapy at 24 months: clinical response, safety, and long-term outcomes. Blood 2009; 114, (abstract 1129).
Shah NP, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Réa D, Dorlhiac-Llacer E, Milone JH et al. Intermittent target inhibition with dasatinib (100 mg once daily) preserves efficacy and improves tolerability in imatinib-resistant and –intolerant chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2008; 226: 3204–3212.
Cortes JE, Jones D, O’Brien S, Jabbour E, Konopleva M, Ferrajoli A et al. Nilotinib as front-line treatment for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in early chronic phase. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 392–397.
Rosti G, Castagnetti F, Palandri F, Poerio A, Soverini S, Breccia M et al. Efficacy and safety of nilotinib 800 mg daily in early chronic phase Ph+ chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase II trial at 2 years. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28, (abstract 6515).
Cortes JE, Jones D, O’Brien S, Jabbour E, Ravandi F, Koller C et al. Results of dasatinib therapy in patients with early chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2010; 28: 398–404.
Rosti G, Hochhaus A, le Coutre P, Baccarani M, Bhalla K, Ossenkoppele G et al. Nilotinib is associated with minimal cross intolerance to imatinib in patients with imatinib-intolerant Philadelphia-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in either chronic phase or accelerated phase. Haematologica 2007; 92 (Suppl 1): 319–320, (abstract 0860).
Khoury HJ, Goldberg SL, Mauro MJ, Stone RM, Matloub Y, Chen T et al. Dasatinib lack of intolerance to imatinib in patients (pts) with chronic myelogenous leukemia chronic phase (CML-CP) intolerant: a retrospective analysis of safety. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26, (abstract 7015).
National Cancer Institute (NCI). Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) v.4. Accessed February 2010. Available at http://evs.nci.nih.gov/ftp1/CTCAE/About.html.
Rosti G, Palandri F, Castagnetti F, Breccia M, Levato L, Gugliotta G et al. Nilotinib for the frontline treatment of Ph(+) chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 4933–4938.
Henkes M, van der Kuip H, Aulitzky WE . Therapeutic options for chronic myeloid leukemia: focus on imatinib (Glivec®, Gleevec™). Therapeut Clin Risk Manag 2008; 4: 163–187.
Sawyers CL, Hochhaus A, Feldman E, Goldman JM, Miller CB, Ottmann OG et al. Imatinib induces hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in myeloid blast crisis: results of a phase II study. Blood 2002; 99: 3530–3539.
Talpaz M, Silver RT, Druker BJ, Goldman JM, Gambacorti-Passerini C, Guilhot F et al. Imatinib induces durable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with accelerated phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results of a phase 2 study. Blood 2002; 99: 1928–1937.
Giles FJ, Larson RA, Kantarjian HM, le Coutre P, Palandri F, Haque A et al. Nilotinib in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia in blast crisis (CML-BC) who are resistant or intolerant to imatinib. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26, (abstract 7017).
Quintás-Cardama A, Han X, Kantarjian H, Cortes J . Tyrosine kinase inhibitor-induced platelet dysfunction in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009; 114: 261–263.
Gratacap MP, Martin V, Valéra MC, Allart S, Garcia C, Sié P et al. The new tyrosine-kinase inhibitor and anticancer drug dasatinib reversibly affects platelet activation in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2009; 114: 1884–1892.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Gleevec® (imatinib mesylate) Prescribing Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: East Hanover, NJ, 2009
Yu EY, Wilding G, Posadas E, Gross M, Culine S, Massard C et al. Phase II study of dasatinib in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2009; 15: 7421–7428.
Galinsky I, Buchanan S . Practical management of dasatinib for maximum patient benefit. Clin J Oncol Nurs 2009; 13: 329–335.
Quintás-Cardama A, De Souza Santos FP, Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, Faderl S, Awais A et al. Dynamics and management of cytopenias associated with dasatinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase after imatinib failure. Cancer 2009; 115: 3935–3943.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN). Clinical practice guidelines in oncology Chronic myelogenous leukemia. v2 2010, Accessed February 2010. Available at http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/cml.pdf.
Porkka K, Khoury HJ, Paquette RL, Matloub Y, Sinha R, Cortes JE . Dasatinib 100 mg once daily minimizes the occurrence of pleural effusion in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase and efficacy is unaffected in patients who develop pleural effusion. Cancer 2010; 116: 377–386.
Kelly K, Swords R, Mahalingam D, Padmanabhan S, Giles FJ . Serosal inflammation (pleural and pericardial effusions) related to tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Target Oncol 2009; 4: 99–105.
Bergeron A, Réa D, Levy V, Picard C, Meignin V, Tamburini J et al. Lung abnormalities after dasatinib treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia: a case series. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2007; 176: 814–818.
Quintás-Cardama A, Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, Borthakur G, Bruzzi J, Munden R et al. Pleural effusion in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia treated with dasatinib after imatinib failure. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3908–3914.
de Lavallade H, Punnialingam S, Milojkovic D, Bua M, Khorashad JS, Gabriel IH et al. Pleural effusions in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia treated with dasatinib may have an immune-mediated pathogenesis. Br J Haematol 2008; 141: 745–747.
Mustjoki S, Ekblom M, Arstila TP, Dybedal I, Epling-Burnette PK, Guilhot F et al. Clonal expansion of T/NK-cells during tyrosine kinase inhibitor dasatinib therapy. Leukemia 2009; 23: 1398–1405.
Rohon P, Porkka K, Mustjoki S . Differential effects of imatinib and dasatinib on immune effector cells in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Blood 2009; 114: 3285.
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. SPRYCEL® (dasatinib) Prescribing Information. Bristol-Myers: Princeton, NJ, 2009
Masiello D, Gorospe G, Yang A . The occurrence and management of pleural effusions associated with dasatinib treatment. J Hematol Oncol 2009; 2: 46.
LaRosée P, Leitner A, Martiat P, Klag T, Shazi S, Treschl A et al. Weekend drug holiday of dasatinib in CML patients not tolerating standard dosing regimens: reducing toxicity with maintained disease control. Blood 2009; 114, (abstract 1119).
Kerkelä R, Grazette L, Yacobi R . Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate. Nat Med 2006; 12: 908–916.
Xu Z, Cang S, Yang T, Delong L . Cardiotoxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myelogenous leukemia therapy. Hematol Rev 2009; 1: 17–21.
Atallah E, Durand J-B, Kantarjian H, Cortes J . Congestive heart failure is a rare event in patients receiving imatinib therapy. Blood 2007; 110: 1233–1237.
Hatfield A, Owen S, Pilot PR . In reply to ‘Cardiotoxicity of the cancer therapeutic agent imatinib mesylate’. Nat Med 2007; 13: 13.
Breccia M, Cannella L, Frustaci A, Stefanizzi C, Levi A, Alimena G et al. Cardiac events in imatinib mesylate-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients: A single institution experience. Leuk Res 2008; 32: 835–836.
Trent JC, Patel SS, Zhang J, Araujo DM, Plana JC, Lenihan DJ et al. Rare incidence of congestive heart failure in gastrointestinal stromal tumor and other sarcoma patients receiving imatinib mesylate. Cancer 2010; 116: 184–192.
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Tasigna® (nilotinib) Prescribing Information. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: East Hanover, NJ, 2009
Nicolini FE, Alimena G, Al-Ali HK, Turkina AT, Shen Z . Final safety analysis of 1793 CML patients from ENACT (Expanding Nilotinib Access in Clinical Trials) study in adult patients with imatinib-resistant or –intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 2009; 94 (Suppl 2): 255:0630.
Singer JB, Shou Y, Giles F, Kantarjian HM, Hsu Y, Robeva AS et al. UGT1A1 promoter polymorphism increases risk of nilotinib-induced hyperbilirubinemia. Leukaemia 2007; 21: 2311–2315.
Lin NU, Sarantopoulos S, Stone JR, Galinsky I, Stone RM, Deangelo DJ et al. Fatal hepatic necrosis following imatinib mesylate therapy. Blood 2003; 102: 3455–3456.
Cross TJS, Bagot C, Portmann B, Wendon J, Gillett D . Imatinib mesylate as a cause of acute liver failure. Am J Hematol 2006; 81: 189–192.
Ridruejo E, Cacchione R, Villamil AG, Marciano S, Gadano AC, Mando OG . Imatinib-induced fatal acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13: 6608–6611.
Thia TJK, Tan HH, Chuah THC, Chow WC, Lui HF . Imatinib mesylate-related fatal acute hepatic failure in a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia and chronic hepatitis B infection. Singapore Med J 2008; 49: e86–e89.
Ikuta K, Torimoto Y, Jimbo J, Inamura J, Shindo M, Sato K et al. Severe hepatic injury caused by imatinib mesylate administered for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia and the efficacy of prednisolone for its management. Int J Hematol 2005; 82: 343–346.
Yamazaki R, Okamoto S, Chen CK, Tada S, Saito H, Shibata R et al. Successful management of liver injury caused by imatinib mesylate in a patient with previously untreated chronic myelogenous leukemia in the chronic phase. Leuk Lymphoma 2006; 47: 1427–1430.
Al Sobhi E, Zahrani Z, Zevallos E, Zuraiki A . Imatinib-induced immune hepatitis: case report and literature review. Hematology 2007; 12: 49–53.
Berman E, Nicolaides M, Maki RG, Fleisher M, Chanel S, Scheu K et al. Altered bone and mineral metabolism in patients receiving imatinib mesylate. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: 2006–2013.
Joensuu H, Reichardt P . Imatinib and altered bone and mineral metabolism. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 628.
Owen S, Hatfield A, Letvak L . Imatinib and altered bone and mineral metabolism. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 627.
Fitter S, Dewar AL, Kostakis P, To LB, Hughes TP, Roberts MM et al. Long-term imatinib therapy promotes bone formation in CML patients. Blood 2008; 111: 2538–2547.
Khoury HJ, Guilhot F, Hughes TP, Kim DW, Cortes JE . Dasatinib treatment for Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias: practical considerations. Cancer 2009; 115: 1381–1394.
Osterberg L, Blaschke T . Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: 487–497.
Ingersoll KS, Cohen J . The impact of medication regimen factors on adherence to chronic treatment: a review of literature. J Behav Med 2008; 31: 213–224.
Tsang J, Rrudychev SL, Pescatore SL . Prescription compliance and persistency in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) and gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients (pts) on imatinib (IM). J Clin Oncol 2006; 24 (18S): (abstract 6119).
Sun SX, Fincher CL, Wang J, Lee KY, Buchner D . Real-world adherence rates of chronic myeloid leukemia patients to higher doses of imatinib. J Manag Care Pharm 2007; 13: 705 (abstract).
Darkow T, Henk HJ, Thomas SK, Feng W, Baladi JF, Goldberg GA et al. Treatment interruptions and non-adherence with imatinib and associated healthcare costs: a retrospective analysis among managed care patients with chronic myelogenous leukaemia. Pharmacoeconomics 2007; 25: 481–496.
Picard S, Titier K, Etienne G, Teilhet E, Ducint D, Bernard MA et al. Trough imatinib plasma levels are associated with both cytogenetic and molecular responses to standard-dose imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2007; 109: 3496–3499.
Larson RA, Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Riviere GJ, Krahnke T et al. Imatinib pharmacokinetics and its correlation with response and safety in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: a subanalysis of the IRIS study. Blood 2008; 111: 4022–4028.
Bazeos A, Khorashad J, Mahon FX, Eliasson LL, Milojkovic D, Bua M et al. Long term adherence to imatinib therapy is the critical factor for achieving molecular responses in chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Blood 2009; 114: 11–22, (abstract 3290).
Noens L, van Lierde MA, De Bock R, Verhoef G, Zachée P, Berneman Z et al. Prevalence, determinants, and outcomes of nonadherence to imatinib therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: the ADAGIO study. Blood 2009; 113: 5401–5411.
Haynes RB, Ackloo E, Sahota N, McDonald HP, Yao X . Interventions for enhancing medication adherence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2008, CD000011.
Acknowledgements
The authors take full responsibility for the content of this publication, and confirm that it reflects their viewpoint and medical expertise. They also wish to acknowledge StemScientific, funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb, for providing writing and editing support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Bristol-Myers Squibb did neither influence the content of the paper, nor did the authors receive financial compensation for authoring the paper. Dr Elias Jabbour is on the Speakers Bureau for Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis. Dr Andreas Hochhaus received Research Funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis. Dr Michael Deininger has served as a consultant for Bristol-Myers Squibb and Novartis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jabbour, E., Deininger, M. & Hochhaus, A. Management of adverse events associated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 25, 201–210 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.215
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2010.215
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Adverse effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer therapy: pathophysiology, mechanisms and clinical management
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
A Pilot Study on Probing of Imatinib Induced Platelet Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia-Chronic Phase and Absence of Associated Bleeding Manifestation: Trying to Solve an Enigma
Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion (2021)
-
Plasma concentrations of dasatinib have a clinical impact on the frequency of dasatinib dose reduction and interruption in chronic myeloid leukemia: an analysis of the DARIA 01 study
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2018)
-
Perioperativer Umgang mit antitumoralen Medikamenten
Der Chirurg (2018)
-
Changes in estimated glomerular filtration rate in chronic myeloid leukemia patients treated front line with available TKIs and correlation with cardiovascular events
Annals of Hematology (2018)