Abstract
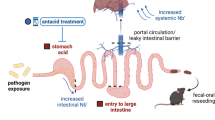
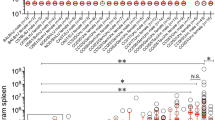
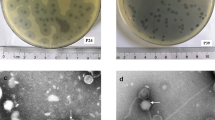
Infection of inbred mouse strains with Citrobacter rodentium represents an ideal model to reveal the genetic factors controlling host resistance to noninvasive enteric bacterial pathogens. We have chosen a positional cloning approach to identify putative gene(s) that control the known difference in survival between resistant C57BL/6J and susceptible C3H/HeJ and C3H/HeOuJ mice. Our work has identified one major locus within proximal chromosome 15 that is responsible for the marked susceptibility of both C3H strains, and we formally exclude Tlr4 from control of survival to this pathogen. We have named this new host resistance locus Cri1 (Citrobacter rodentium infection 1). The Cri1 genetic interval currently spans ∼16 Mb and it confers survival to the infection in a recessive manner. Transfer of the Cri1 locus from the surviving B6 mice into a congenic mouse with a C3Ou genetic background confirms its overall chromosomal localization and its highly significant effect on host survival. The C3Ou.B6-Cri1 mice thus produced have also enabled us to dissociate the control of mouse survival from the control of bacterial load early in the infection as well as from control of colonic hyperplasia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brennan PC, Fritz TE, Flynn RJ, Poole CM . Citrobacter Freundii associated with diarrhea in a laboratory mice. Lab Anim Care 1965; 15: 266–275.
Muto T, Nakagawa M, Isobe Y, Saito M, Nakano T . Infectious megaenteron of mice. I. Manifestation and pathological observation. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 1969; 22: 363–374.
Nakagawa M, Sakazaki R, Muto T, Saito M, Hagiwara T . Infectious megaenteron of mice. II. Detection of coliform organisms of an unusual biotype as the primary cause. Jpn J Med Sci Biol 1969; 22: 375–382.
Ediger RD, Kovatch RM, Rabstein MM . Colitis in mice with a high incidence of rectal prolapse. Lab Anim Sci 1974; 24: 488–494.
Barthold SW, Coleman GL, Bhatt PN, Osbaldiston GW, Jonas AM . The etiology of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab Anim Sci 1976; 26 (6 Part 1): 889–894.
Mundy R, MacDonald TT, Dougan G, Frankel G, Wiles S . Citrobacter rodentium of mice and man. Cell Microbiol 2005; 7: 1697–1706.
Deborah Chen H, Frankel G . Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: unravelling pathogenesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2005; 29: 83–98.
Nataro JP, Kaper JB . Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 1998; 11: 142–201.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2009). http://www.cdc.gov/nczved/divisions/dfbmd/diseases/enterohemorrhagic_ecoli/technical.html.
Manning SD, Motiwala AS, Springman AC, Qi W, Lacher DW, Ouellette LM et al. Variation in virulence among clades of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with disease outbreaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 4868–4873.
Serna AT, Boedeker EC . Pathogenesis and treatment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 2008; 24: 38–47.
Deng W, Li Y, Vallance BA, Finlay BB . Locus of enterocyte effacement from Citrobacter rodentium: sequence analysis and evidence for horizontal transfer among attaching and effacing pathogens. Infect Immun 2001; 69: 6323–6335.
Deng W, Puente JL, Gruenheid S, Li Y, Vallance BA, Vazquez A et al. Dissecting virulence: systematic and functional analyses of a pathogenicity island. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101: 3597–3602.
Fagundes Neto U, Ferreira Vde C, Patricio FR, Mostaco VL, Trabulsi LR . Protracted diarrhea: the importance of the enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) strains and Salmonella in its genesis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1989; 8: 207–211.
Fagundes-Neto U, Kallas MR, Patricio FR . Morphometric study of the small bowel mucosa in infants with diarrhea due to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Hepatogastroenterology 1997; 44: 1051–1056.
Karch H . The role of virulence factors in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC)--associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 2001; 27: 207–213.
Tacket CO, Sztein MB, Losonsky G, Abe A, Finlay BB, McNamara BP et al. Role of EspB in experimental human enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection. Infect Immun 2000; 68: 3689–3695.
Barthold SW, Osbaldiston GW, Jonas AM . Dietary, bacterial, and host genetic interactions in the pathogenesis of transmissible murine colonic hyperplasia. Lab Anim Sci 1977; 27: 938–945.
Vallance BA, Deng W, Jacobson K, Finlay BB . Host susceptibility to the attaching and effacing bacterial pathogen Citrobacter rodentium. Infect Immun 2003; 71: 3443–3453.
Khan MA, Ma C, Knodler LA, Valdez Y, Rosenberger CM, Deng W et al. Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to colitis development but not to host defense during Citrobacter rodentium infection in mice. Infect Immun 2006; 74: 2522–2536.
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998; 282: 2085–2088.
Qureshi ST, Lariviere L, Leveque G, Clermont S, Moore KJ, Gros P et al. Endotoxin-tolerant mice have mutations in Toll-like receptor 4 (Tlr4). J Exp Med 1999; 189: 615–625.
Borenshtein D, Nambiar PR, Groff EB, Fox JG, Schauer DB . Development of fatal colitis in FVB mice infected with Citrobacter rodentium. Infect Immun 2007; 75: 3271–3281.
Chen C-C, Louie S, McCormick B, Walker WA, Shi HN . Concurrent infection with an intestinal helminth parasite impairs host resistance to enteric Citrobacter rodentium and enhances Citrobacter-induced colitis in mice. Infect Immun 2005; 73: 5468–5481.
Borenshtein D, Fry R, Groff E, Nambiar P, Carey V, Fox J et al. Diarrhea as a cause of mortality in a mouse model of infectious colitis. Genome Biol 2008; 9: R122.
Borenshtein D, Schlieper KA, Rickman BH, Chapman JM, Schweinfest CW, Fox JG et al. Decreased expression of colonic Slc26a3 and carbonic anhydrase IV as a cause of fatal infectious diarrhea in mice. Infect Immun 2009; 77: 3639–3650.
Peterson EJ, Woods ML, Dmowski SA, Derimanov G, Jordan MS, Wu JN et al. Coupling of the TCR to integrin activation by SLAP-130/Fyb. Science 2001; 293: 2263–2265.
Peschon JJ, Morrissey PJ, Grabstein KH, Ramsdell FJ, Maraskovsky E, Gliniak BC et al. Early lymphocyte expansion is severely impaired in interleukin 7 receptor-deficient mice. J Exp Med 1994; 180: 1955–1960.
Maaser C, Housley MP, Iimura M, Smith JR, Vallance BA, Finlay BB et al. Clearance of Citrobacter rodentium requires B cells but not secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA) or IgM antibodies. Infect Immun 2004; 72: 3315–3324.
Bry L, Brenner MB . Critical role of T cell-dependent serum antibody, but not the gut-associated lymphoid tissue, for surviving acute mucosal infection with Citrobacter rodentium, an attaching and effacing pathogen. J Immunol 2004; 172: 433–441.
Wickham ME, Brown NF, Boyle EC, Coombes BK, Finlay BB . Virulence is positively selected by transmission success between mammalian hosts. Curr Biol 2007; 17: 783–788.
Petkov PM, Ding Y, Cassell MA, Zhang W, Wagner G, Sargent EE et al. An efficient SNP system for mouse genome scanning and elucidating strain relationships. Genome Res 2004; 14: 1806–1811.
LeBlanc PM, Yeretssian G, Rutherford N, Doiron K, Nadiri A, Zhu L et al. Caspase-12 modulates NOD signaling and regulates antimicrobial peptide production and mucosal immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2008; 3: 146–157.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a team grant from the Canadian Genetic Disease Network/Gene Cure Foundation (SG and DM) and a CIHR Operating Grant MOP89817 (SG). E Diez was the recipient of a Canadian Association of Gastroenterology/Canadian Institutes of Health Research-partnered (CAG-CIHR) postdoctoral fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diez, E., Zhu, L., Teatero, S. et al. Identification and characterization of Cri1, a locus controlling mortality during Citrobacter rodentium infection in mice. Genes Immun 12, 280–290 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.76
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2010.76
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Loss of disease tolerance during Citrobacter rodentium infection is associated with impaired epithelial differentiation and hyperactivation of T cell responses
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Enterobacteria and host resistance to infection
Mammalian Genome (2018)
-
Enterohepatic bacterial infections dysregulate the FGF15-FGFR4 endocrine axis
BMC Microbiology (2013)
-
R-Spondin 2 signalling mediates susceptibility to fatal infectious diarrhoea
Nature Communications (2013)
-
Citrobacter Infection and Wnt Signaling
Current Colorectal Cancer Reports (2012)