Abstract
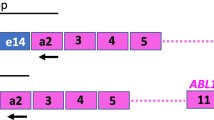
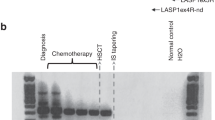
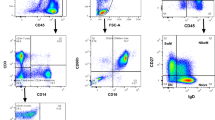
The degree of tumor load reduction after therapy is an important prognostic factor for patients with CML. Conventional metaphase analysis has been considered to be the ‘gold standard’ for evaluating patient response to treatment but this technique normally requires bone marrow aspiration and is therefore invasive. The frequency of cytogenetic analyses can be considerably reduced if patients are also monitored by molecular methods, which can be performed on peripheral blood specimens. Of the various techniques available, most attention has been paid to RT-PCR for BCR-ABL mRNA since this is by far the most sensitive. Simple, non-quantitative RT-PCR analysis gives only limited information on patients after treatment. Quantitative RT-PCR assays have been developed to monitor the kinetics of residual BCR-ABL transcripts over time. Variables in the quantitative PCR assay may be controlled for by quantification of transcripts of a normal gene (eg ABL or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, G6PD) as an internal standard. After allogeneic stem cell transplantation, most patients become RT-PCR negative, often after a period of low level positivity that may persist for several months. Those patients destined to relapse are characterized by the reappearance and/or rising levels of BCR-ABL transcripts. In contrast, for patients treated with interferon-α (IFN) residual disease is rarely, if ever, eliminated. The actual level of minimal residual disease in complete cytogenetic responders to IFN correlates with the probability of relapse. New quantitative real time procedures promise to simplify the protocols that are currently in use, but standardization and the introduction of rigorous, internationally accepted controls are required to enable RT-PCR to become a robust and routine basis for therapeutic decisions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nowell PC, Hungerford DA . A minute chromosome in human chronic granulocytic leukemia Science 1960 132: 1497–1501
Rowley JD . A new consistent chromosome abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia detected by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining Nature 1973 243: 290–293
Sawyers CL . Chronic myeloid leukemia New Engl J Med 1999 340: 1330–1340
Groffen J, Stephenson JR, Heisterkamp N, de Klein A, Bartram CR, Grosveld G . Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a limited region, bcr, on chromosome 22 Cell 1984 36: 93–99
Stam K, Heisterkamp N, Grosveld G, de Klein A, Verma RS, Coleman M, Dosik H, Groffen J . Evidence of a new chimeric bcr/c-abl mRNA in patients with chronic myelocytic leukemia and the Philadelphia chromosome New Engl J Med 1985 313: 1429–1433
Melo JV, Gordon DE, Cross NCP, Goldman JM . The ABL-BCR fusion gene is expressed in chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1993 81: 158–165
Thijsen SFT, Schuurhuis GJ, van Oostveen JW, Ossenkoppele GJ . Chronic myeloid leukemia from basics to bedside Leukemia 1999 13: 1646–1674
Hehlmann R, Heimpel H . Current aspects of drug therapy in Philadelphia-positive CML: Correlation of tumor burden with survival Leuk Lymphoma 1996 22: (Suppl. 1) 161–167
Hook EB . Exclusion of chromosomal mosaicism: tables of 90%, 95%, and 99% confidence limits and comments on use Am J Hum Genet 1977 29: 94–97
Cortes J, Talpaz M, O'Brien S, Rios MB, Majlis A, Keating M, Freireich EJ, Kantarjian H . Suppression on cytogenetic clonal evolution with interferon alfa therapy in patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 3279–3285
Kantarjian HM, Dixon D, Keating MJ, Talpaz M, Walters RS, McCredie KB, Freireich EJ . Characteristics of accelerated disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia Cancer 1988 61: 1441–1446
Tkachuk DC, Westbrook CA, Andreeff M, Donlon TA, Cleary ML, Suryanarayan K, Homge M, Redner A, Gray J, Pinkel D . Detection of bcr-abl fusion in chronic myelogeneous leukemia by in situ hybridization Science 1990 250: 559–562
Nacheva E, Holloway T, Brown K, Bloxham D, Green AR . Philadelphia-negative chronic myeloid leukaemia: detection by FISH of BCR-ABL fusion gene localized either to chromosome 9 or chromosome 22 Br J Haematol 1994 87: 409–412
Hochhaus A, Reiter A, Skladny H, Melo JV, Sick C, Berger U, Guo JQ, Arlinghaus RB, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . A novel BCR-ABL fusion gene (e6a2) in a patient with Philadelphia chromosome negative chronic myelogenous leukemia Blood 1996 88: 2236–2240
Melo JV . The diversity of BCR-ABL fusion proteins and their relationship to leukemia phenotype Blood 1996 88: 2375–2384
Weber-Matthiesen K, Winkemann M, Müller-Hermelink A, Schlegelberger B, Grote W . Simultaneous fluorescence immunophenotyping and interphase cytogenetics: a contribution to characterization of tumor cells J Histochem Cytochem 1992 40: 171–175
Haferlach T, Winkemann M, Nickenig C, Meeder M, Ramm-Petersen L, Schoch R, Nickelsen M, Weber-Matthiesen K, Schlegelberger B, Schoch C, Gassmann W, Löffler H . Which compartments are involved in Philadelphia-chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia? An answer at the single cell level by combining May-Grünwald-Giemsa staining and fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques Br J Haematol 1997 97: 99–106
Bentz M, Cabot G, Moos M, Speicher MR, Ganser A, Lichter P, Döhner H . Detection of chimeric BCR-ABL genes on bone marrow samples and blood smears in chronic myeloid and acute lymphoblastic leukemia by in situ hybridization Blood 1994 83: 1922–1928
Garcia-Isidoro M, Tabernero MD, Garcia JL, Najera ML, Hernandez JM, Wiegant J, Raap A, San Miguel J, Orfao A . Detection of the Mbcr/abl translocation in chronic myeloid leukemia by fluorescence in situ hybridization: comparison with conventional cytogenetics and implications for minimal residual disease detection Hum Pathol 1997 28: 154–159
Cuneo A, Bigoni R, Emmanuel B, Smit E, Rigolin GM, Roberti MG, Bardi MG, Piva N, Scapoli G, Castoldi G, Van den Berghe H, Hagemeijer A . Fluorescence in situ hybridization for the detection and monitoring of the Ph-positive clone in chronic myelogenous leukemia: comparison with metaphase banding analysis Leukemia 1998 12: 1718–1723
Yanagi M, Shinjo K, Takeshita A, Tobita T, Yano K, Kobayashi M, Terasaki H, Naoe T, Ohnishi K, Ohno R . Simple and reliably sensitive diagnosis and monitoring of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells in chronic myeloid leukemia by interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization of peripheral blood cells Leukemia 1999 13: 542–552
Chase A, Grand F, Zhang JG, Blackett N, Goldman J, Gordon M . Factors influencing the false positive and negative rates of BCR-ABL fluorescence in-situ hybridization Genes Chromosom Cancer 1997 18: 246–253
Cox Froncillo MC, Cantonetti M, Masi M, Lentini R, Giudiceandrea P, Maffei L, Tribalto M, Amadori S, Papa G . Cytogenetic analysis is non-informative for assessing the remission rate in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients on interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) therapy Cancer Genet Cytogenet 1995 84: 15–18
Mühlmann J, Thaler J, Hilbe W, Bechter O, Erdel M, Utermann G, Duba HC . Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) on peripheral blood smears for monitoring Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) during interferon treatment: a new strategy for remission asssessment Genes Chromosom Cancer 1998 21: 90–100
Cox Froncillo MC, Maffei L, Cantonetti M, Del Poeta G, Lentini R, Bruno A, Masi M, Tribalto M, Amadori S . FISH analysis for CML monitoring? Ann Hematol 1996 73: 113–119
Tchirkov A, Giollant M, Tavernier F, Briancon G, Tournilhac O, Kwiatkowski F, Philippe P, Choufi B, Demeocq F, Travade P, Malet P . Interphase cytogenetics and competitive RT-PCR for residual disease monitoring in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia during interferon-α therapy Br J Haematol 1998 101: 552–557
Verfaillie C, Bhatia R, Miller W, Mortari F, Roy V, Burger S, McCullough J, Stieglbauer K, Dewald G, Heimfeld S, Miller JS, McGlave P . BCR/ABL-negative primitive progenitors suitable for transplantation can be selected from the marrow of most early-chronic phase but not accelerated-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia patients Blood 1996 87: 4770–4779
Kirk JA, Reems JA, Roecklein BA, Van Devanter DR, Bryant EM, Radich J, Edmands S, Lee A, Torok Storb B . Benign marrow progenitors are enriched in the CD34+/HLA-DRlo population but not in the CD34+/CD38lo population in chronic myeloid leukemia: an analysis using interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization Blood 1995 86: 737–743
Sinclair PB, Green AR, Grace C, Nacheva EP . Improved sensitivity of BCR-ABL detection: a triple-probe three-color fluorescence in situ hybridization system Blood 1997 90: 1395–1402
Buno I, Wyatt WA, Zinsmeister AR, Dietz-Band J, Silver RT, Dewald GW . A special fluorescent in situ hybridization technique to study peripheral blood and assess the effectiveness of interferon therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1998 92: 2315–2321
Dewald GW, Wyatt WA, Juneau AL, Carlson RO, Zinsmeister AR, Jalal SM, Spurbeck JL, Silver RT . Highly sensitive fluorescence in situ hybridization method to detect double BCR/ABL fusion and monitor response to therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1998 91: 3357–3365
Grand F, Kulkarni S, Chase A, Goldman JM, Gordon MY, Cross NCP . Frequent deletion of hSNF5/INI1, a component of the SWI/SNF complex, during progression of chronic myeloid leukemia Cancer Res 1999 59: 3870–3874
El Rifai W, Ruutu T, Vettentanta K, Temtamy S, Knuutila S . Minimal residual disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia: a metaphase-FISH study Br J Haematol 1996 92: 365–369
Seong DC, Kantarjian HM, Ro JY, Talpaz M, Xu J, Robinson JR, Deisseroth AB, Champlin RE, Siciliano MJ . Hypermetaphase fluorescence in situ hybridization for quantitative monitoring of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia during treatment Blood 1995 86: 2343–2349
Seong D, Giralt S, Fischer H, Hayes K, Glassman A, Arlinghaus R, Xu J, Kantarjian H, Siciliano M, Champlin R . Usefulness of detection of minimal residual disease by ‘hypermetaphase’ fluorescent in situ hybridization after allogeneic BMT for chronic myelogenous leukemia Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 19: 565–570
Reiter A, Skladny H, Hochhaus A, Seifarth W, Heimpel H, Bartram CR, Cross NCP, Hehlmann R . Molecular response of CML patients treated with interferon-α monitored by quantitative Southern blot analysis Br J Haematol 1997 97: 86–93
Fishleder AJ, Shadrach B, Tuttle C . bcr rearrangement: potential false positive secondary to an EcoRI restriction fragment length polymorphism Leukemia 1989 3: 746–748
Grossman A, Mathew A, O'Connell MP, Tiso P, Distenfeld A, Benn P . Multiple restriction enzyme digests are required to rule out polymorphism in the molecular diagnosis of chronic myeloid leukemia Leukemia 1990 4: 63–64
Popenoe DW, Schaefer Rego K, Mears JG, Bank A, Leibowitz D . Frequent and extensive deletion during the 9,22 translocation in CML Blood 1986 68: 1123–1128
Bartram CR, Bross Bach U, Schmidt H, Waller HD . Philadelphia-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia with breakpoint 5′ of the breakpoint cluster region but within the bcr gene Blut 1987 55: 505–511
Saglio G, Guerrasio A, Rosso C, Zaccaria A, Tassinari A, Serra A, Rege Cambrin G, Mazza U, Gavosto F . New type of Bcr/Abl junction in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia Blood 1990 76: 1819–1824
Stock W, Westbrook CA, Peterson B, Arthur DC, Szatrowski TP, Silver RT, Sher DA, Wu D, LeBeau MM, Schiffer CA, Bloomfield CD . Value of molecular monitoring during treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia: a Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study J Clin Oncol 1997 15: 26–36
Verschraegen CF, Talpaz M, Hirsch Ginsberg CF, Pherwani R, Rios MB, Stass SA, Kantarjian HM . Quantification of the breakpoint cluster region rearrangement for clinical monitoring in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1995 85: 2705–2710
Steegmann JL, Requena MJ, Casado LF, Pico M, Panarrubia MJ, Ferro MT, Resino M, Fernandez-Ranada JM . Southern technique and cytogenetics are complementary and must be used together in the evaluation of Ph1, M-BCR positive chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) patients treated with alpha interferon (IFN-ALPHA) Am J Hematol 1996 53: 169–174
Yoffe G, Blick M, Kantarjian H, Spitzer G, Gutterman J, Talpaz M . Molecular analysis of interferon-induced suppression of Philadelphia chromosome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia Blood 1987 69: 961–963
Guo JQ, Lian JY, Xian YM, Lee MS, Deisseroth AB, Stass SA, Champlin RE, Talpaz M, Wang JY, Arlinghaus RB . BCR-ABL protein expression in peripheral blood cells of chronic myelogenous leukemia patients undergoing therapy Blood 1994 83: 3629–3637
Guo JQ, Lian J, Glassman A, Talpaz M, Kantarjian H, Deisseroth AB, Arlinghaus RB . Comparison of bcr-abl protein expression and Philadelphia chromosome analyses in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients Am J Clin Pathol 1996 106: 442–448
Morgan GJ, Hughes T, Janssen JW, Gow J, Guo AP, Goldman JM, Wiedemann LM, Bartram CR . Polymerase chain reaction for detection of residual leukaemia Lancet 1989 1: 928–929
Hughes T, Martiat P, Morgan G, Sawyers C, Witte ON, Goldman JM . Significance of residual leukaemia transcripts after bone marrow transplant for CML Lancet 1990 335: 50
Hughes T, Janssen JWG, Morgan G, Martiat P, Saglio G, Pignon JM, Pignatti FP, Mills K, Keating A, Gluckman E, Bartram CR, Goldman JM . False-positive results with PCR to detect leukaemia-specific transcript Lancet 1990 335: 1037–1038
Hughes T, Goldman JM . Improved results with PCR for chronic myeloid leukaemia Lancet 1990 336: 812
Cross NCP, Feng L, Chase A, Bungey J, Hughes TP, Goldman JM . Competitive polymerase chain reaction to estimate the number of BCR-ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia patients after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1993 82: 1929–1936
Lion T, Henn T, Gaiger A, Kalhs P, Gadner H . Early detection of relapse after bone marrow transplantation in patients with chronic myelogenous leukaemia Lancet 1993 341: 275–276
Malinge MC, Mahon FX, Delfau MH, Daheron L, Kitzis A, Guilhot F, Tanzer J, Grandchamp B . Quantitative determination of the hybrid Bcr-Abl RNA in patients with chronic myelogenous leukaemia under interferon therapy Br J Haematol 1992 82: 701–707
Hochhaus A, Lin F, Reiter A, Skladny H, Mason PJ, van Rhee F, Shepherd PCA, Allan NC, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Quantification of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia patients on interferon-α therapy by competitive polymerase chain reaction Blood 1996 87: 1549–1555
Cross NCP, Melo JV, Feng L, Goldman JM . An optimized multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for detection of BCR-ABL fusion mRNAs in haematological disorders Leukemia 1994 8: 186–189
Melo JV, Myint H, Galton DA, Goldman JM . P190BCR-ABL chronic myeloid leukaemia: the missing link with chronic myelomonocytic leukaemia? Leukemia 1994 8: 208–211
Rubinstein R, Purves LR . A novel BCR-ABL rearrangement in a Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myelogenous leukaemia variant with thrombocythaemia Leukemia 1998 12: 230–232
Clarkson B, Strife A . Linkage of proliferative and maturational abnormalities in chronic myelogenous leukemia and relevance to treatment Leukemia 1993 7: 1683–1721
Morley A . Quantifying leukemia New Engl J Med 1998 339: 627–629
van Dongen JJM, MacIntyre EA, Gabert JA, Delabesse E ., Rossi V, Saglio G, Gotardi E, Rambaldi A, Dotti G, Giesinger F, Parreira A, Gameiro P, Gonzalez Diaz M, Malec M, Langerak AW, San Miguel JF, Biondi A. Standardized RT-PCR analysis of fusion gene transcripts from chromosome aberrations in acute leukemia for detection of minimal residual disease Leukemia 1999 12: 1901–1928
Cross NCP . Assessing residual leukaemia Baillières Clin Haematol 1997 10: 389–403
Cross NCP, Feng L, Zhang JG, Goldman JM . Competitive PCR to monitor residual disease after bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia. In: Borden EC, Goldman JM, Grignani F (eds) Molecular Diagnosis and Monitoring of Leukaemia and Lymphoma Ares-Serono Symposia Publications: Rome 1994 119–126
Potter MN, Cross NCP, van Dongen JJ, Saglio G, Oakhill A, Bartram CR, Goldman JM . Molecular evidence of minimal residual disease after treatment for leukaemia and lymphoma: an updated meeting report and review Leukemia 1993 7: 1302–1314
Reiter E, Greinix HT, Keil F, Brugger S, Rabitsch W, Schulenburg A, Mannhalter C, Schwarzinger I, Worel N, Volc-Platzer B, Fischer G, Dieckmann K, Hinterberger W, Schneider B, Haas OA, Geissler K, Kalhs P . Long-term follow-up of patients after related- and unrelated-donor bone marrow transplantation for chronic myelogenous leukemia Ann Hematol 1999 78: 507–513
Zhang JG, Lin F, Chase A, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Comparison of genomic DNA and cDNA for detection of residual disease after treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia with allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Blood 1996 87: 2588–2593
Hochhaus A, Lin F, Reiter A, Skladny H, van Rhee F, Shepherd PCA, Allan NC, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Variable numbers of BCR-ABL transcripts persist in CML patients whoachieve complete cytogenetic remission with interferon-α Br J Haematol 1995 91: 126–131
Biernaux C, Loos M, Sels A, Huez G, Stryckmans P . Detection of major bcr-abl gene expression at a very low level in blood cells of some healthy individuals Blood 1995 88: 3118–3122
Bose S, Deininger M, Gora-Tybor J, Goldman JM, Melo JV . The presence of typical and atypical BCR-ABL fusion genes in leukocytes of normal individuals: biological significance and implications for the assessment of minimal residual disease Blood 1998 92: 3362–3367
Melo JV . The molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukaemia Leukemia 1996 10: 751–756
Lion T, Izraeli S, Henn T, Gaiger A, Mor W, Gadner H . Monitoring of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia by quantitative polymerase chain reaction Leukemia 1992 6: 495–499
Thompson JD, Brodsky I, Yunis JJ . Molecular quantification of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1992 79: 1629–1635
Nagel S, Schmidt M, Thiede C, Huhn D, Neubauer A . Quantification of Bcr-Abl transcripts in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) using standardized, internally controlled, competitive differential PCR (CD-PCR) Nucleic Acids Res 1996 24: 4102–4103
Delage R, Soiffer RJ, Dear K, Ritz J . Clinical significance of bcr-abl gene rearrangement detected by polymerase chain reaction after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in chronic myelogenous leukemia Blood 1991 78: 2759–2767
Lin F, van Rhee F, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Kinetics of increasing BCR-ABL transcript numbers in chronic myeloid leukemia patients who relapse after bone marrow transplantation Blood 1996 87: 4473–4478
Lin F, Kirkland MA, van Rhee F, Chase A, Coulthard S, Bungey J, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . Molecular analysis of transient cytogenetic relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukaemia Bone Marrow Transplant 1996 18: 1147–1152
van Rhee F, Lin F, Cullis JO, Spencer A, Cross NCP, Chase A, Garicochea B, Bungey J, Barrett J, Goldman JM . Relapse of chronic myeloid leukemia after allogeneic bone marrow transplant: the case for giving donor leukocyte transfusions before the onset of hematologic relapse Blood 1994 83: 3377–3383
Raanani P, Dazzi F, Sohal J, Szydlo R, van Rhee F, Reiter A, Lin F, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . The rate and kinetics of molecular response to donor leucocyte transfusions in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients treated for relapse after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Br J Haematol 1997 99: 945–950
Corsetti MT, Lerma E, Dejana A, Basta P, Ferrara R, Benvenuto F, Vassallo F, Abate M, Piaggio G, Parodi C, Sessarego M, Pira GL, Manca F, Carella AM . Quantitative competitive reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction for BCR-ABL on Philadelphia-negative leukaphereses allows the selection of low-contaminated peripheral blood progenitor cells for autografting in chronic myelogenous leukemia Leukemia 1999 13: 999–1008
Hochhaus A, Reiter A, Saußele S, Reichert A, Emig M, Kaeda J, Schultheis B, Berger U, Shepherd PCA, Allan N, Hehlmann R, Goldman JM, Cross NCP, for the German CML Study Group and the UK MRC CML Study Group . Molecular heterogeneity in complete cytogenetic responders after interferon-α therapy for chronic myeloid leukaemia: low levels of minimal residual disease are associated with continuing remission Blood 2000 95: 62–66
Kurzrock R, Estrov Z, Kantarjian H, Talpaz M . Conversion of interferon-induced, long-term cytogenetic remissions in chronic myelogenous leukemia to polymerase chain reaction negativity J Clin Oncol 1998 16: 1526–1531
Reiter A, Marley SB, Hochhaus A, Sohal J, Raanani P, Hehlmann R, Gordon MY, Goldman JM, Cross NCP . BCR-ABL positive progenitors in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in complete cytogenetic remission after treatment with interferon-α Br J Haematol 1998 102: 1271–1278.y
Mensink E, van de Locht A, Schattenberg A, Linders E, Schaap N, Guerts van Kessel A, de Witte T . Quantitation of minimal residual disease in Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using real-time quantitative RT-PCR Br J Haematol 1998 102: 768–774
Preudhomme C, Révillion F, Merlat A, Hornez L, Roumier C, Duflos-Grardel N, Jouet JP, Cosson A, Peyrat JP, Fenaux P . Detection of BCR-ABL transcripts in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) using a ‘real time’ quantitative RT-PCR assay Leukemia 1999 13: 957–964
Eder M, Battner K, Kafert S, Stucki A, Ganser A, Hertenstein B . Monitoring of BCR-ABL expression using real-time RT-PCR in CML after bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cell transplantation Leukemia 1999 13: 1383–1389
Branford S, Hughes TP, Rudzki Z . Monitoring chronic myeloid leukaemia therapy by real-time quantitative PCR in blood is a reliable alternative to bone marrow cytogenetics Br J Haematol 1999 107: 587–599
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ, Williams PM . Real time quantitative PCR Genome Res 1996 6: 986–994
Wittwer CT, Herrmann MG, Moss AA, Rasmussen RP . Continuous fluorescence monitoring of rapid cycle DNA amplification Biotechniques 1997 22: 130–138
Wittwer CT, Ririe KM, Andrew RV, David DA, Gundry RA, Balis UJ . The LightCycler: a microvolume multisample fluorimeter with rapid temperature control Biotechniques 1997 22: 176–181
Emig M, Saussele S, Wittor H, Weisser A, Reiter A, Willer A, Berger U, Hehlmann R, Cross NCP, Hochhaus A . Accurate and rapid analysis of residual disease in patients with CML using specific fluorescent hybridization probes for real time quantitative RT-PCR Leukemia 1999 13: 1825–1832
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Deutsche José-Carreras-Stiftung eV, the Leukaemia Research Fund (UK), the Tumorzentrum Heidelberg/Mannheim, and the Forschungsfonds der Fakultät für Klinische Medizin, Mannheim, Germany for financial support. The paper is based on a presentation at the ‘Workshop on Minimal residual disease’ at Reisensburg Castle/Ulm, Germany, funded by the Kind-Philipp-Foundation, October 24–26, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hochhaus, A., Weisser, A., Rosée, P. et al. Detection and quantification of residual disease in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 14, 998–1005 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401811
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2401811
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Measurable residual disease testing in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: hype, hope neither or both?
Leukemia (2021)
-
Consensus criteria for sensitive detection of minimal neuroblastoma cells in bone marrow, blood and stem cell preparations by immunocytology and QRT-PCR: recommendations by the International Neuroblastoma Risk Group Task Force
British Journal of Cancer (2009)
-
An “Age” Structured Model of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Organization with Application to Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2009)
-
Diagnostic algorithms, monitoring, prognostication, and therapy in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): a proposal of the Austrian CML platform
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift (2008)
-
Pathogenesis, treatment effects, and resistance dynamics in chronic myeloid leukemia - insights from mathematical model analyses
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2008)