Abstract
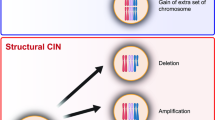
Chromosomal INstability (CIN), a hallmark of cancer, refers to cells with an increased rate of gain or loss of whole chromosomes or chromosome parts. CIN is linked to the progression of tumors with poor clinical outcomes such as drug resistance. CIN can give tumors the diversity to resist therapy, but it comes at the cost of significant stress to tumor cells. To tolerate this, cancer cells must modify their energy use to provide adaptation against genetic changes as well as to promote their survival and growth. In this study, we have demonstrated that CIN induction causes sensitivity to metabolic stress. We show that mild metabolic disruption that does not affect normal cells, can lead to high levels of oxidative stress and subsequent cell death in CIN cells because they are already managing elevated stress levels. Altered metabolism is a differential characteristic of cancer cells, so our identification of key regulators that can exploit these changes to cause cell death may provide cancer-specific potential drug targets, especially for advanced cancers that exhibit CIN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mertens F, Mandahl N, Mitelman F, Heim S . Cytogenetic analysis in the examination of solid tumors in children. Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1994; 11: 361–377.
Weaver BA, Cleveland DW . Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol 2006; 18: 658–667.
Thompson SL, Compton DA . Examining the link between chromosomal instability and aneuploidy in human cells. J Cell Biol 2008; 180: 665–672.
Weaver B, Cleveland DW . Aneuploidy: instigator and inhibitor of tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 2007; 67: 10103–10105.
Sotillo R, Schvartzman JM, Socci ND, Benezra R . Mad2-induced chromosome instability leads to lung tumour relapse after oncogene withdrawal. Nature 2010; 464: 436–440.
Wassmann K, Benezra R . Mitotic checkpoints: from yeast to cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2001; 11: 83–90.
Baker DJ, Jin F, Jeganathan KB, van Deursen JM . Whole chromosome instability caused by Bub1 insufficiency drives tumorigenesis through tumor suppressor gene loss of heterozygosity. Cancer Cell 2009; 16: 475–486.
Swanton C, Nicke B, Schuett M, Eklund AC, Ng C, Li Q et al. Chromosomal instability determines taxane response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2009; 106: 8671–8676.
Carter SL, Eklund AC, Kohane IS, Harris LN, Szallasi Z . A signature of chromosomal instability inferred from gene expression profiles predicts clinical outcome in multiple human cancers. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1043–1048.
Shaukat Z, Wong HW, Nicolson S, Saint RB, Gregory SL . A screen for selective killing of cells with chromosomal instability induced by a spindle checkpoint defect. PLoS ONE 2012; 7: e47447.
Buffin E, Emre D, Karess RE . Flies without a spindle checkpoint. Nat Cell Biol 2007; 9: 565–572.
Warburg O . On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956; 123: 309–314.
Yun J, Rago C, Cheong I, Pagliarini R, Angenendt P, Rajagopalan H et al. Glucose deprivation contributes to the development of KRAS pathway mutations in tumor cells. Science 2009; 325: 1555–1559.
Yuneva M, Zamboni N, Oefner P, Sachidanandam R, Lazebnik Y . Deficiency in glutamine but not glucose induces MYC-dependent apoptosis in human cells. J Cell Biol 2007; 178: 93–105.
Puzio-Kuter AM . The role of p53 in metabolic regulation. Genes Cancer 2011; 2: 385–391.
Pfau SJ, Amon A . Chromosomal instability and aneuploidy in cancer: from yeast to man. EMBO Rep 2012; 13: 515–527.
Clem B, Telang S, Clem A, Yalcin A, Meier J, Simmons A et al. Small-molecule inhibition of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase activity suppresses glycolytic flux and tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther 2008; 7: 110–120.
Le A, Cooper CR, Gouw AM, Dinavahi R, Maitra A, Deck LM et al. Inhibition of lactate dehydrogenase A induces oxidative stress and inhibits tumor progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 2037–2042.
Michelakis ED, Sutendra G, Dromparis P, Webster L, Haromy A, Niven E et al. Metabolic modulation of glioblastoma with dichloroacetate. Sci Transl Med 2010; 2: 31ra34.
Kaplan O, Navon G, Lyon RC, Faustino PJ, Straka EJ, Cohen JS . Effects of 2-deoxyglucose on drug-sensitive and drug-resistant human breast cancer cells: toxicity and magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of metabolism. Cancer Res 1990; 50: 544–551.
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM et al. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2009; 27: 3297–3302.
Gross S, Cairns RA, Minden MD, Driggers EM, Bittinger MA, Jang HG et al. Cancer-associated metabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate accumulates in acute myelogenous leukemia with isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations. J Exp Med 2010; 207: 339–344.
Holen K, Saltz LB, Hollywood E, Burk K, Hanauske A-R . The pharmacokinetics, toxicities, and biologic effects of FK866, a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide biosynthesis inhibitor. Invest New Drugs 2008; 26: 45–51.
Schläfli P, Borter E, Spielmann P, Wenger RH . The PAS-domain kinase PASKIN: a new sensor in energy homeostasis. Cell Mol Life Sci 2009; 66: 876–883.
Hao H-X, Rutter J . The role of PAS kinase in regulating energy metabolism. IUBMB Life 2008; 60: 204–209.
O’Keefe L V, Colella A, Dayan S, Chen Q, Choo A, Jacob R et al. Drosophila orthologue of WWOX, the chromosomal fragile site FRA16D tumour suppressor gene, functions in aerobic metabolism and regulates reactive oxygen species. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: 497–509.
Stanton RC . Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, NADPH, and cell survival. IUBMB Life 2012; 64: 362–369.
Wong HW-S, Shaukat Z, Wang J, Saint R, Gregory SL . JNK signaling is needed to tolerate chromosomal instability. Cell Cycle 2013; 13: 1–10.
Iijima K, Zhao L, Shenton C, Iijima-Ando K . Regulation of energy stores and feeding by neuronal and peripheral CREB activity in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2009; 4: e8498.
Hao H-X, Cardon CM, Swiatek W, Cooksey RC, Smith TL, Wilde J et al. PAS kinase is required for normal cellular energy balance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 15466–15471.
Hockenbery DM . Targeting mitochondria for cancer therapy. Environ Mol Mutagen 2010; 51: 476–489.
Gogvadze V, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B . Mitochondria in cancer cells: what is so special about them? Trends Cell Biol 2008; 18: 165–173.
Terhzaz S, Cabrero P, Chintapalli VR, Davies SA, Dow JT . Mislocalization of mitochondria and compromised renal function and oxidative stress resistance in Drosophila SesB mutants. Physiol Genomics 2010; 41: 33–41.
Radyuk SN, Rebrin I, Klichko VI, Sohal BH, Michalak K, Benes J et al. Mitochondrial peroxiredoxins are critical for the maintenance of redox state and the survival of adult Drosophila. Free Radic Biol Med 2010; 49: 1892–1902.
Sheltzer JM, Torres EM, Dunham MJ, Amon A . Transcriptional consequences of aneuploidy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2012; 109: 12644–12649.
Coe JP, Rahman I, Sphyris N, Clarke AR, Harrison DJ . Glutathione and p53 independently mediate responses against oxidative stress in ES cells. Free Radic Biol Med 2002; 32: 187–196.
Wu D, Cederbaum AI . Oxidative stress mediated toxicity exerted by ethanol-inducible CYP2E1. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005; 207 (2 Suppl): 70–76.
Owusu-Ansah E, Banerjee U . Reactive oxygen species prime Drosophila haematopoietic progenitors for differentiation. Nature 2009; 461: 537–541.
Miwa S, St-Pierre J, Partridge L, Brand MD . Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by Drosophila mitochondria. Free Radic Biol Med 2003; 35: 938–948.
Oromendia AB, Dodgson SE, Amon A . Aneuploidy causes proteotoxic stress in yeast. Genes Dev 2012; 26: 2696–2708.
Liu J, Wang X, Shigenaga MK, Yeo HC, Mori A, Ames BN . Immobilization stress causes oxidative damage to lipid, protein, and DNA in the brain of rats. FASEB J 1996; 10: 1532–1538.
Tanaka T, Halicka HD, Huang X, Traganos F, Darzynkiewicz Z . Constitutive histone H2AX phosphorylation and ATM activation, the reporters of DNA damage by endogenous oxidants. Cell Cycle 2008; 5: 1940–1945.
Janssen A, van der Burg M, Szuhai K, Kops GJ, Medema RH . Chromosome segregation errors as a cause of DNA damage and structural chromosome aberrations. Science 2011; 333: 1895–1898.
Crasta K, Ganem NJ, Dagher R, Lantermann AB, Ivanova EV, Pan Y et al. DNA breaks and chromosome pulverization from errors in mitosis. Nature 2012; 482: 53–58.
Kasai H, Nishimura S . Hydroxylation of deoxyguanosine at the C-8 position by ascorbic acid and other reducing agents. Nucleic Acids Res 1984; 12: 2137–2145.
Kops GJPL, Weaver B, Cleveland DW . On the road to cancer: aneuploidy and the mitotic checkpoint. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 773–785.
DeBerardinis RJ, Lum JJ, Hatzivassiliou G, Thompson CB . The biology of cancer: metabolic reprogramming fuels cell growth and proliferation. Cell Metab 2008; 7: 11–20.
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC, Thompson CB . Understanding the Warburg effect: the metabolic requirements of cell proliferation. Science 2009; 324: 1029–1033.
Li M, Fang X, Baker DJ, Guo L, Gao X, Wei Z et al. The ATM-p53 pathway suppresses aneuploidy-induced tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 14188–14193.
Torres EM, Sokolsky T, Tucker CM, Chan LY, Boselli M, Dunham MJ et al. Effects of aneuploidy on cellular physiology and cell division in haploid yeast. Science 2007; 317: 916–924.
Williams B, Prabhu V, Hunter K . Aneuploidy affects proliferation and spontaneous immortalization in mammalian cells. Science 2008; 322: 703–709.
Wang J, Yuan W, Chen Z, Wu S, Chen J, Ge J et al. Overexpression of G6PD is associated with poor clinical outcome in gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 2012; 33: 95–101.
Kuo W, Lin J, Tang TK . Human glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) gene transforms NIH 3T3 cells and induces tumors in nude mice. Int J Cancer 2000; 85: 857–864.
Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhu Y, Qin S . Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a biomarker and potential therapeutic target for cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 2014; 14: 280–289.
Howes RE, Piel FB, Patil AP, Nyangiri OA, Gething PW, Dewi M et al. G6PD deficiency prevalence and estimates of affected populations in malaria endemic countries: a geostatistical model-based map. PLoS Med 2012; 9: e1001339.
Manganelli G, Masullo U, Passarelli S, Filosa S . Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: disadvantages and possible benefits. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets 2013; 13: 73–82.
Zhang J . Suppression of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene expression by reduced endogenous glutathione level. Biochim Biophys Acta 2007; 1772: 1175–1181.
Cairns R, Harris IS, Mak TW . Regulation of cancer cell metabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 2011; 11: 85–95.
Ren J-G, Seth P, Everett P, Clish CB, Sukhatme VP . Induction of erythroid differentiation in human erythroleukemia cells by depletion of malic enzyme 2. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e12520.
Beumer KJ, Trautman JK, Bozas A, Liu J-L, Rutter J, Gall JG et al. Efficient gene targeting in Drosophila by direct embryo injection with zinc-finger nucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 19821–19826.
Reuter S, Gupta SC, Chaturvedi MM, Aggarwal BB . Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: how are they linked? Free Radic Biol Med 2010; 49: 1603–1616.
Bauer G . Tumor cell-protective catalase as a novel target for rational therapeutic approaches based on specific intercellular ROS signaling. Anticancer Res 2012; 32: 2599–2634.
Sajesh B V, Bailey M, Lichtensztejn Z, Hieter P, McManus KJ . Synthetic lethal targeting of superoxide dismutase 1 selectively kills RAD54B-deficient colorectal cancer cells. Genetics 2013; 195: 757–767.
Cheung-Ong K, Giaever G, Nislow C . DNA-damaging agents in cancer chemotherapy: serendipity and chemical biology. Chem Biol 2013; 20: 648–659.
Smart DK, Ortiz KL, Mattson D, Bradbury CM, Bisht KS, Sieck LK et al. Thioredoxin reductase as a potential molecular target for anticancer agents that induce oxidative stress. Cancer Res 2004; 64: 6716–6724.
Ozben T . Oxidative stress and apoptosis: impact on cancer therapy. J Pharm Sci 2007; 96: 2181–2196.
Fang J, Nakamura H, Iyer AK . Tumor-targeted induction of oxystress for cancer therapy. J Drug Target 2007; 15: 475–486.
Sotgia F, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lisanti MP . Cancer metabolism: new validated targets for drug discovery. Oncotarget 2013; 4: 1309–1316.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaukat, Z., Liu, D., Choo, A. et al. Chromosomal instability causes sensitivity to metabolic stress. Oncogene 34, 4044–4055 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.344
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.344
This article is cited by
-
Aneuploidy is Linked to Neurological Phenotypes Through Oxidative Stress
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2024)
-
Mitochondrial RNA methyltransferase TRMT61B is a new, potential biomarker and therapeutic target for highly aneuploid cancers
Cell Death & Differentiation (2023)
-
The role of canonical and non-canonical Hedgehog signaling in tumor progression in a mouse model of small cell lung cancer
Oncogene (2017)
-
Autophagy suppresses Ras-driven epithelial tumourigenesis by limiting the accumulation of reactive oxygen species
Oncogene (2017)
-
Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase Maintains Glycolysis-driven Growth in Drosophila Tumors
Scientific Reports (2017)