Abstract
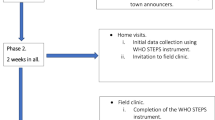
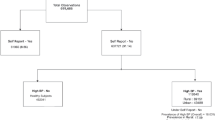
Hypertension is an important public health problem in India. To determine its prevalence, awareness, treatment and control among women, we performed a nationwide study. Population-based studies among women aged 35–70 years were performed in four urban and five rural locations. Stratified sampling was performed and we enrolled 4608 (rural 2604 and urban 2004) of the targeted 8000 (57%). Demographic details, medical history, diet, physical activity, anthropometry and blood pressure (BP) were recorded. Descriptive statistics are reported. Logistic regression was performed to determine the association of hypertension and its awareness, treatment and control with socioeconomic factors. Age-adjusted prevalence of hypertension (known or BP⩾140/⩾90 mm Hg) was observed in 1672 women (39.2%) (rural 746, 31.5%; urban 926, 48.2%). Significant determinants of hypertension were urban location, greater literacy, high dietary fat, low fibre intake, obesity and truncal obesity (P<0.01). Hypertension awareness was noted in 727 women (42.8%), more in urban (529, 56.8%) than in rural (198, 24.6%). Of these, 38.6% of the women were on treatment (urban 35.7, rural 46.5) and of those treated, controlled blood pressure (<140 and <90 mm Hg) was observed in 21.5% (urban 28.3 vs 10.2). Among hypertensive subjects, treatment was noted in 18.3% (rural 13.1, urban 22.5) and control in 3.9% (rural 1.3, urban 5.9). A significant determinant of low awareness, treatment and control was rural location (multivariate-adjusted P<0.05). There is a high prevalence of hypertension in middle-aged Asian Indian women. Very low awareness, treatment and control status are observed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand SS, Yusuf S . Stemming the global tsunami of cardiovascular disease. Lancet 2011; 377: 529–532.
Murray CJL, Lopez AD . Mortality by cause for eight regions of the world: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 1997; 349: 1269–1276.
Fuster V, Kelly BB, Board for Global Health.. Promoting Cardiovascular Health in Developing World: A Critical Challenge to Achieve Global Health. Institute of Medicine: Washington, 2010. Available at: http://www.iom.edu/Reports/2010/Promoting-Cardiovascular-Health-in-the-Developing-World-A-Critical-Challenge-to-Achieve-Global-Health.aspx (accessed 12 September 2010).
Patel V, Chatterjee S, Chisholm D, Ebrahim S, Gopalakrishna G, Mathers C et al. Chronic diseases and injuries in India. Lancet 2011; 377: 413–428.
Gupta R . Trends in hypertension epidemiology in India. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18: 73–78.
van den Hoogen PCW, Feskens EJM, Nagelkere NJD, Menotti A, Nissinen A, Kromhout D, for the Seven Countries Study Research Group. The relation between blood pressure and mortality due to coronary heart disease among men in different parts of the world. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 1–8.
Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002; 360: 1903–1913.
Pednekar MS, Gupta R, Gupta PC . Association of blood pressure and cardiovascular mortality in India: Mumbai Cohort Study. Am J Hypertens 2009; 22: 1076–1084.
Sauvaget C, Ramadas K, Thomas G, Thara S, Sanakaranarayan R . Prognosis criteria of casual systolic and diastolic blood pressure values in a prospective study in India. J Epid Comm Health 2010; 64: 366–372.
Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lin JK, Singh GM, Paciorek CJ, Cowan MJ, et al., Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors for Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Pressure). National, regional and global trends in systolic blood pressure since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 786 country-years and 5.4 million participants. Lancet 2011; 377: 568–577.
Kaplan NM, Opie LH . Controversies in hypertension. Lancet 2006; 367: 168–176.
Egan BM, Zhao Y, Axon RN . US trends in prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension, 1988–2008. JAMA 2010; 303: 2043–2050.
Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, Giampoli S, Hense HW, Joffres M et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada and the United States. JAMA 2003; 289: 2363–2369.
Whelton PK, He J, Muntner P . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in North America, North Africa and Asia. J Human Hypertens 2004; 18: 545–551.
Cífková R, Skodová Z, Bruthans J, Holub J, Adámková V, Jozífová M et al. Longitudinal trends in cardiovascular mortality and blood pressure levels, prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in the Czech population from 1985 to 2007/2008. J Hypertens 2010; 28: 2196–2203.
Kastarinen M, Antikainen R, Peltonen M, Laatikainen T, Barengo NC, Jula A et al. Prevalence, awareness and treatment of hypertension in Finland during 1982–2007. J Hypertens 2009; 27: 1552–1559.
Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Whelton PK, He J . Worldwide prevalence of hypertension: a systematic review. J Hypertens 2004; 22: 11–19.
Chadha SL, Radhakrishnan S, Ramachandran K, Kaul U, Gopinath N . Prevalence, awareness and treatment status of hypertension in urban population of Delhi. Indian J Med Res 1990; 92: 233–240.
Thakur K, Malhotra P, Walia I, Kumar R . Health awareness and treatment compliance of high blood pressure among women in a peri-urban colony of Chandigarh, India. J Indian Med Assoc 1999; 97: 217–219.
Kalavathy MC, Thankappan KR, Sarma PS, Vasan RS . Prevalence, awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in an elderly community-based sample in Kerala, India. Natl Med J India 2000; 13: 9–15.
Bharucha NE, Kuruvilla T . Hypertension in the Parsi community of Bombay: a study on prevalence, awareness and compliance to treatment. BMC Public Health 2003; 3: 1.
Zachariah MG, Thankappan KR, Alex SC, Sarma PS, Vasan RS . Prevalence, correlates, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in a middle-aged urban population in Kerala. Indian Heart J 2003; 55: 245–251.
Chaturvedi S, Pant M, Neelam, Yadav G . Hypertension in Delhi: prevalence, awareness, treatment and control. Trop Doct 2007; 37: 142–145.
Mohan V, Deepa M, Farooq S, Datta M, Deepa R . Prevalence, awareness and control of hypertension in Chennai-The Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES-52). J Assoc Physicians India 2007; 55: 326–332.
Thankappan KR, Sivasankaran S, Sarma PS, Mini G, Khader SA, Padmanabhan P et al. Prevalence-correlates-awareness-treatment and control of hypertension in Kumarakom, Kerala: baseline results of a community-based intervention program. Indian Heart J 2006; 58: 28–33.
Vimala A, Ranji SA, Jyosna MT, Chandran V, Mathews SR, Pappachan JM . The prevalence, risk factors and awareness of hypertension in an urban population of Kerala (South India). Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl 2009; 20: 685–689.
Jonas JB, Nangia V, Matin A, Joshi PP, Ughade SN . Prevalence, awareness, control, and associations of arterial hypertension in a rural central India population: the Central India Eye and Medical Study. Am J Hypertens 2010; 23: 347–350.
By Y, Mr NG, Ag U . Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural areas of Davanagere. Indian J Community Med 2010; 35: 138–141.
Bhardwaj R, Kandori A, Marwah R, Vaidya P, Singh B, Dhiman P et al. Prevalence, awareness and control of hypertension in rural communities of Himachal Pradesh. J Assoc Physicians India 2010; 58: 423–424.
Pandey RM, Gupta R, Misra A, Misra P, Singh V, Agrawal A et al. Determinants of urban-rural differences in cardiovascular risk factors in middle-aged women in India: a cross-sectional study. Int J Cardiol 2011 (doi:10.1016/j.icard.2011.06.008).
World Health Organization. Diet, nutrition and the prevention of chronic diseases. Report of a Joint WHO/FAO expert consultation. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2003.
Luepkar RV, Evans A, McKeigue P, Reddy KS. . Cardiovascular survey methods, 3rd edn. World Health Organization: Geneva, 2003.
Misra A, Pandey RM, Devi JR, Sharma R, Vikram NK, Khanna N . High prevalence of diabetes, obesity and dyslipidemia in urban skum population in northern India. Int J Obesity 2001; 25: 1722–1729.
Bharathi AV, Sandhya N, Vaz M . The development and characteristics of a physical activity questionnaire for epidemiological studies in urban middle class Indians. Indian J Med Res 2000; 111: 95–102.
WHO Expert Consultation. Appropriate body mass index for Asian populations and its implications for policy and intervention strategies. Lancet 2004; 363: 157–163.
Deedwania PC, Gupta R . Hypertension in South Asians. In: Black HR, Elliott WJ (eds). Hypertension: A Companion Textbook to Braunwald's Heart Disease, 2nd edn. WB Saunders: New York, 2012.
Gupta PC, Gupta R, Pednekar M . Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure trends in 88 653 subjects in Mumbai, India. J Hum Hypertens 2004; 18: 907–910.
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr et al. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure; National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. The seventh report of the Joint National Committee On Prevention, Detection, Evaluation And Treatment Of High Blood Pressure: the JNC 7 report. JAMA 2003; 289: 2560–2572.
MacMahon S, Peto R, Cutler J, Collins R, Sorlie P, Neaton J et al. Blood pressure, stroke and coronary heart disease. Part I. Prolonged differences in blood pressure: prospective observational studies corrected for regression dilution bias. Lancet 1990; 335: 765–774.
Marmot M, Wilkinson RG. . Social Determinants of Health. Oxford University Press: Oxford, 1999.
Kinra S, Bowen LJ, Lyngdoh T, Prabhakaran D, Reddy KS, Ramakrishnan L et al. Sociodemographic patterning of non-communicable disease risk factors in rural India: a cross sectional study. BMJ 2010; 341: c4974.
Gupta R, Sharma AK . Prevalence of hypertension and sub-types in an Indian rural population. Clinical and electrocardiographic correlates. J Hum Hypertens 1994; 8: 823–829.
Vartiainen E, Laatikainen T, Peltonen M, Juolevi A, Mannisto S, Sundvall J et al. Thirty five year trends in cardiovascular risk factors in Finland. Int J Epidemiol 2010; 39: 504–518.
Hill MN, Miller NH, Degeest S, American Society of Hypertension Writing Group. Adherence and persistence with taking medicines to control high blood pressure. J Am Soc Hypertens 2011; 5: 56–63.
Morgado M, Rolo S, Macedo AF, Periera L, Castelo-Branco M . Predictors of uncontrolled hypertension and antihypertensive medical adherence. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 2010; 1: 196–202.
Joshi PP, Salkar RG, Heller RF . Determinants of poor blood pressure control in urban hypertensives of central India. J Hum Hypertens 1996; 10: 299–303.
Krousel-Wood MA, Muntner P, Islam T, Morisky DE, Webber LS . Barriers to and determinants of medication adherence in hypertension management. Med Clin North Am. 2009; 93: 753–769.
Reddy KS, Patel V, Jha P, Paul VK, Kumar AK, Dandona L . Towards achievement of universal health care in India by 2020; a call to action. Lancet 2011; 377: 760–768.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by ad-hoc research grants from the Science and Society Division, Department of Science and Technology, Government of India, New Delhi, to all the participating centres.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Pandey, R., Misra, A. et al. High prevalence and low awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Asian Indian women. J Hum Hypertens 26, 585–593 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2011.79
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2011.79
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Examining sex disparity in the association of waist circumference, waist-hip ratio and BMI with hypertension among older adults in India
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The roles of economic growth and health expenditure on CO2 emissions in selected Asian countries: a quantile regression model approach
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2021)
-
Emerging trends in hypertension epidemiology in India
Journal of Human Hypertension (2019)
-
Prevalence of and risk factors for hypertension in urban and rural India: the ICMR–INDIAB study
Journal of Human Hypertension (2015)
-
Trends of hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment and control in rural areas of northern China during 1991–2011
Journal of Human Hypertension (2014)