Abstract
The physiological response to individual and combined stressors of elevated temperature and pCO2 were measured over a 24-day period in four Pacific corals and their respective symbionts (Acropora millepora/Symbiodinium C21a, Pocillopora damicornis/Symbiodinium C1c-d-t, Montipora monasteriata/Symbiodinium C15 and Turbinaria reniformis/Symbiodinium trenchii). Multivariate analyses indicated that elevated temperature played a greater role in altering physiological response, with the greatest degree of change occurring within M. monasteriata and T. reniformis. Algal cellular volume, protein and lipid content all increased for M. monasteriata. Likewise, S. trenchii volume and protein content in T. reniformis also increased with temperature. Despite decreases in maximal photochemical efficiency, few changes in biochemical composition (i.e. lipids, proteins and carbohydrates) or cellular volume occurred at high temperature in the two thermally sensitive symbionts C21a and C1c-d-t. Intracellular carbonic anhydrase transcript abundance increased with temperature in A. millepora but not in P. damicornis, possibly reflecting differences in host mitigated carbon supply during thermal stress. Importantly, our results show that the host and symbiont response to climate change differs considerably across species and that greater physiological plasticity in response to elevated temperature may be an important strategy distinguishing thermally tolerant vs. thermally sensitive species.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Coral reefs represent one of the most biologically rich ecosystems on the planet. The importance of scleractinian corals to continual reef accretion has placed much attention on understanding how they will respond to future climate conditions, including elevated seawater temperature and ocean acidification. Water temperatures of just a few degrees above the summer maximum average can lead to large-scale coral bleaching events1, which are often characterized by the expulsion of symbiotic dinoflagellates (Symbiodinium spp.). Such bleaching events can result in high coral mortality and a significant loss in coral cover1.
Photoinactivation and damage to the photosystem II (PSII) reaction center is often a first sign of temperature stress within thermally susceptible Symbiodinium2,3. Photoinactivation can result in reduced photosynthetic rates and elevated reactive oxygen species, further damaging the symbiont and coral4,5,6. This stress can change the energetic/metabolic demands of the symbiont, reducing the amount of photosynthate translocated to the host. In turn, host catabolic pathways are utilized to supply additional energy to compensate for the loss of translocated carbon and/or to keep pace with greater metabolic demand from high temperature stress, leading to a decline in one or more of the host’s energy reserves of proteins, carbohydrates and lipids (defined hereafter as the biochemical composition)7,8,9. However, other mechanisms such as enhanced heterotrophy can compensate for reduced photosynthate translocation and maintain biochemical composition8,10,11. Similar to other marine phytoplankton, symbiont biochemical composition may also change in response to temperature stress12,13. Thus, due to variation in host and symbiont thermal tolerance, the overall thermal response of the holobiont (i.e. the host + the symbiont) can vary widely across different corals.
Ocean acidification (abbreviated OA hereafter), which describes the decrease in seawater pH resulting from increasing atmospheric CO2 partial pressure (pCO2) levels and subsequent dissolution and acid production, has the potential to affect many aspects of coral physiology. Several studies have noted reduced coral calcification at high pCO2 (e.g.,11,14,15). However, some corals show no decline or a delayed decline in calcification well below the current aragonite saturation state, suggesting the response to high pCO2 is highly species specific (e.g.,11,14,16). Compared to calcification studies, less attention has been placed on other aspects of holobiont physiology, including primary productivity and biochemical composition. As CO2(aq) concentrations increase with OA, symbiont productivity could increase due to a release from carbon limitation17. Greater net productivity with elevated CO2 was reported for symbiotic sea anemones in laboratory experiments and near natural CO2 seeps18,19. Highly variable, CO2 driven changes in respiration and productivity may result in significant changes to host and symbiont metabolism and are likely to affect the overall health and resilience of the coral as these organisms cope with additional environmental stressors.
High CO2 conditions enhanced productivity for some cultured Symbiodinium, but not others20 and this variability may be linked with differences in carbon acquisition as well as the preference in dissolved inorganic carbon (CO2 vs. HCO3-) among algal species21. In addition, increased respiration rates, along with changes in the transcriptional response of genes involved with metabolic pathways and cellular structure, were noted in scleractinians in response to OA22,23. Specifically, genes associated with energy production and ion transport were up-regulated under acidification conditions24, suggesting changes in the biochemical composition of the symbiosis.
Research to date has largely focused on the physiological changes and metabolic pathways most important towards understanding the coral response to climate change. However, because most studies have focused on just a few model scleractinian species25,26,27,28,29, less is known about the potential for physiological diversity within each unique host/symbiont combination. Whether or not the physiological responses to both elevated temperature and pCO2 that have been described11,30,31 accurately depict the range of coral responses within the entire Scleractinian taxa remains to be seen.
Here, we utilized a combination of physiological and transcriptional approaches to characterize both the host and symbiont response to elevated temperature and pCO2. Through the comparative analysis of multiple physiological variables within the host and symbiont, the unique response to temperature and pCO2 within each species was characterized. This approach highlights the diversity of physiological responses within scleractinian corals and how each host/symbiont system responds uniquely to a changing environment anticipated under future climate change conditions.
Results
Symbiont Identification
Continual specificity between hosts and symbionts was noted for the duration of the experiment, with Symbiodinium C21a in A. millepora, C1c-d-t in P. damicornis, C15 in M. monasteriata and S. trenchii (formerly called D1a) in T. reniformis. No other symbiont fingerprints were detected.
Multivariate Analyses (ANOSIM and SIMPER)
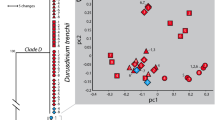
The greatest separation between low and high temperature treatments was found within M. monasteriata, followed by T. reniformis and then A. millepora (Table. 1). Although separation between temperature treatments was also significant for P. damicornis, the correlation was very low (r < 0.2), suggesting only a minimal thermal effect within this species. The relative contribution of the measured variables to the overall dissimilarity between low and high temperature differed among species, with host lipid and protein and LEDR contributing 36% in A. millepora whereas symbiont lipids and LEDR contributed the most (30%) in M. monasteriata. Lastly, temperature induced changes in T. reniformis were mostly explained through changes in symbiont protein and lipid content, as well as LEDR, accounting for 43% of the dissimilarity (Section S9). Significant CO2 effects were only observed for A. millepora and T. reniformis (Table 1). However, correlation values for CO2 in both A. millepora and T. reniformis were very low and therefore were not followed by SIMPER analysis. Figure 1 provides an overview of the above trends. (Fig. 1).
Non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) plot displaying similarities within temperature treatments for the four coral species.
Black = A. millepora, green = P. damicornis, red = M. monsateriata and blue = T. reniformis. Closed circles represent low temperature treatments and open circles represent high temperature treatments. Ellipses represent a 99% confidence bubble around the mean for low temperature (closed ellipse) and high temperature (open ellipse) treatments. Because the ANOSIM analysis found CO2 to be insignificant or explain only minimal separation across fragments, only temperature differences are depicted in this figure.
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Elevated temperature significantly reduced maximum PSII photosynthetic efficiency (Fv/Fm) in both C21a in A. millepora and C1c-d-t in P. damicornis (Fig. 2a,b) (Supplemental Section S3). Significant interactive effects were observed for C15 in M. monasteriata, as Fv/Fm decreased with temperature only within the ambient pCO2 treatment (Fig. 2c) (Table S3). The control treatment was also significantly higher than medium pCO2 treatments and the high temperature, high pCO2 treatment as well. Fv/Fm did not change for S. trenchii in T. reniformis (Fig. 2d). There was no change in the photosynthesis to respiration ratios (P:R) across treatments for any coral species (Fig. 3a–d) (Section S4). For A. millepora, a significant interactive effect was observed for light enhanced dark respiration (LEDR). However, pair-wise comparisons revealed significant differences only between the high temperature, medium pCO2 treatment and the ambient temperature, high pCO2 treatment (Fig. 3e). For P. damicornis, significant interactive effects were also observed, as LEDR increased with temperature but was significant only within the low and high pCO2 treatments (Fig. 3f). Elevated temperature also significantly increased LEDR in M. monasteriata and T. reniformis (Fig. 3g,h).
Average (±1SE) maximum photosynthetic efficiency of PSII (Fv/Fm) in Acropora millepora (a), Pocillopora damicornis (b), Montipora monasteriata (c) and Turbinaria reniformis (d) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
Average (±1SE) photosynthesis to respiration (P:R) and light enhanced dark respiration (LEDR) of Acropora millepora (a,e), Pocillopora damicornis (b,f), Montipora monasteriata (c,g) and Turbinaria reniformis (d,h) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
Patterns of Symbiont Soluble Proteins, Carbohydrates, Lipids and Cell Volume
Symbiont protein concentration differed with CO2 for all three clade C symbionts (Fig. 4a–c), significantly increasing between ambient and medium pCO2 treatments in C15 and decreasing between medium and high pCO2 treatments in C21a (Section S5). An interactive effect was noted for C1c-d-t, as protein content was significantly elevated within the high temperature, medium CO2 treatment as compared to the ambient temperature, low CO2 treatment. Notably, protein concentration increased significantly in S. trenchii under elevated temperature by an average of 297% (Fig. 4d) whereas a smaller (25%) increase was noted for Symbiodinium C15 (Section S5).
Average (±1SE) total (μg cell−1) protein, carbohydrates and lipid content and cell volume for symbiont type C21a-A. millepora (a,e,i,m), C1-P. damicornis (b,f,j,n), C15-M. monasteriata (c,g,k,o) and S. trenchii-T. reniformis (d,h,l,p) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
While there were no changes in carbohydrates for C1c-d-t and C15 symbionts, an interactive effect was observed for C21a, as carbohydrates decreased between ambient and medium pCO2 only within the ambient temperature treatments (Fig. 4e–g). Overall carbohydrates in S. trenchii dropped significantly with elevated temperature (Fig. 4d) (Section S5).
Lipid concentrations did not change significantly in Symbiodinium C21a or C1c-d-t (Fig. 4I,j). However, an interactive effect was observed for symbiont C15 (), as lipid concentrations increased with temperature but only within the low and high pCO2 treatments (Fig. 4k). For S. trenchii, lipid concentration declined with both temperature and pCO2 with the high pCO2 treatments significantly lower than the low and medium pCO2 treatments (Fig. 4l).
Cell volume of the C21a symbiont within the medium pCO2 treatments was significantly elevated over both ambient and high pCO2 treatments (Fig. 4m). No significant changes in volume were detected for the C1c-d-t symbiont (Fig. 4n). Cell volume increased significantly with temperature for both C15 (and S. trenchii (Fig. 4o,p). For S. trenchii, cell volume also varied with pCO2, as cells within the medium pCO2 treatment were significantly smaller than those within the low and high pCO2 treatments (Section S5).
Patterns of Host Soluble Protein, Carbohydrate and Lipid Content
Host protein concentrations declined with temperature in A. millepora and M. monasteriata. In contrast, host protein generally increased with temperature in T. reniformis (Fig. 5a,c,d; Section S6). In addition, A. millepora protein content was significantly lower within the medium pCO2 treatments as compared to both low and high pCO2 treatments. Host protein content decreased with increasing pCO2 for P. damicornis and medium and high pCO2 treatments were significantly lower than ambient pCO2 (Fig. 5b).
Average (±1SE) total (μg cm2) animal protein, carbohydrates and lipid from the host corals Acropora millepora (a,e,i), Pocillopora damicornis (b,f,j), Montipora monasteriata (c,g,k) and Turbinaria reniformis (d,h,l) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
A. millepora carbohydrates did not change (Fig. 5e). However, P. damicornis carbohydrates decreased with elevated pCO2 (Fig. 5f), while carbohydrates decreased with temperature in M. monasteriata (Fig. 5g). A significant interactive effect was observed for T. reniformis, however post hoc analyses found no significant differences among any of the pCO2 treatments (Fig. 5e) (Section S6).
A. millepora lipids decreased significantly as temperature and pCO2 increased (Fig. 5i). Lipid content did not change significantly in P. damicornis (Fig. 5j). Significant interactive effects were observed for M. monasteriata, as lipid content was significantly higher within the control temperature and CO2 treatment as compared to all other treatments (Fig. 5k). For T. reniformis, lipid content was significantly higher in the high pCO2 treatments as compared to the medium and low pCO2 treatments (Fig. 5l) (Section S6).
Gene Expression Patterns in Hosts and Symbionts:
Intracellular carbonic anhydrase transcript abundance was significantly up-regulated at high temperature in A. millepora (Fig 6a; Section S7). In contrast, no significant differences were observed for P. damicornis (Fig 6b) or for extracellular carbonic anhydrase and Calcium-ATPase in either species (Fig. 6c–f) (Section S7). There was a significant interaction for GAPDH in A. millepora and transcript abundance was significantly higher within both the low and high pCO2 treatments when compared to the medium pCO2 treatment, but only within the ambient temperature treatments (Fig. 6g). An interactive effect was also observed for HSP90 where transcript abundance was significantly higher within the high pCO2 treatment compared to the medium pCO2, but only within the ambient temperature treatments (Fig. 6i) (Section S7). There was no change in the GAPDH transcript abundance for P. damicornis (Fig. 6h). However there was a significant increase in HSP90 transcript abundance with temperature (Fig. 6j).
Average (±1SE) relative expression of genes in A. millepora and P. damincornis encoding intercellular carbonic anhydrase (a,b), extracellular carbonic anhydrase (c,d), calcium ATP ion channel (e,f), glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (g,h) and heat shock protein 90 (i,j) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
There was no significant difference in glutamine synthetase gene expression for the C21a symbiont, whereas transcript abundance decreased with elevated temperature for C1c-d-t (Fig. 7a,b). High pCO2 exposure led to a significant up-regulation in symbiont C21a α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase transcript abundance (Fig. 7c). Elevated temperature also increased C21a α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase transcript abundance. However this thermal increase was principally driven by the increase observed under medium pCO2 (Fig. 7c). There was a significant interactive effect for α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (Section S8) in Symbiodinium C1c-d-t in P. damicornis, as transcript abundance increased significantly with temperature but only within the high pCO2 treatment (Fig. 7d). For the C21a symbiont, malonyl Co-A acyl transferase increased with pCO2 and both medium and high pCO2 treatments were significantly elevated over low pCO2 (Fig. 7e). Elevated temperature also significantly increased malonyl Co-A acyl transferase in this symbiont, yet again, this was principally driven by the increase observed under medium pCO2 (Fig. 7e). Malonyl Co-A acyl transferase expression did not change in the C1 symbiont (Fig. 7f, Section S8).
Average (±1SE) relative expression of genes within Symbiodinium C21a and C1c-d-t encoding glutamine synthetase (a,b), α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (c,d), malonyl Co-A acyl transferase (e,f) at three pCO2 levels and 26.5 °C (light bars) or 31.5 °C (dark bars).
For each pane, the designations ‘temp’, ‘pCO2’ and ‘int’ indicate significant temperature, pCO2 or interactive effects (two-way ANOVA). If a pCO2 effect was observed, the letters indicate significant differences between pCO2 groups (n = 6). If an interactive effect was observed, the letters above each bar indicate significant differences among the 6 treatments.
Discussion
The consequence of both host and alga in forming a physiologically unique symbiosis is becoming increasingly clear as we gain a better understanding of the extensive genetic and physiological diversity that exists for both partners. Multivariate analyses utilized here show clear separation among coral species and a more definitive thermal response as compared with pCO2. Importantly, the largest thermal separation occurred within species hosting the more historically thermally tolerant symbiont types: Symbiodinium C15 (M. monasteriata) and S. trenchii (T. reniformis)7,32 indicating larger physiological changes in response to elevated temperature. Assessing thermal sensitivity in corals has largely relied on stability of physiological measurements such as cellular density, chlorophyll and Fv/Fm at elevated temperatures to define thermal tolerance3. However, by incorporating a broad range of both host and symbiont physiological variables into our analyses, we show that physiological plasticity may be an important thermal stress mechanism, enabling high temperature tolerance in certain host-symbiont combinations. Additionally, because the direction of thermal separation within M, monasteriata and T. reniformis differed (Fig 1), the specific holobiont response to high temperature also differed between species. By comparing changes observed in the physiological variables measured, we can better understand the unique physiological responses to both temperature and pCO2 found within each species.
With respect to elevated temperature, there were significant changes in cell volume and biochemical composition in Symbiodinium C15 and S. trenchii (Fig. 3), whereas there were no changes for the more thermally sensitive symbionts C21a and C1c-d-t. In agreement, heat-induced reductions in PSII efficiency were more pronounced in symbionts C21a and C1c-d-t as compared to C15 and S. trenchii and are likely due to an initial increase in photo-stress within the photosynthetic apparatus. While the photochemical response of S. trenchii noted here is consistent with thermal tolerance, there was a significant reduction in Fv/Fm under elevated temperature and ambient pCO2 in the C15 symbiont. Additionally, reductions in Fv/Fm in the C15 symbiont were also observed with increasing pCO2. This contrasts with Wall et al. (2013) where there was no change in maximal PSII efficiency in Seriatopora caliendrum due to elevated pCO2 exposure33. It is also likely that the photochemical responses noted here were influenced by relatively low light levels (275 μmol quanta m−2 s−1), as previous work has highlighted the importance of light intensity in the physiological response to elevated temperature34 and pCO235.
The contrasting trends in PSII photosynthetic efficiency, along with changes in algal density and size may point to important differences in response to high temperature between thermally tolerant vs. sensitive symbionts. We have previously shown that there was a significant drop in C15 density with elevated temperature (described in Schoepf et al. 2013) which may have increased the internal light field for the remaining symbionts36, resulting in a high-light acclimation phenotype. Previous studies have provided a clear link to internal light fields playing a substantial role to the bleaching response37 with high light intensity exacerbating thermal stress. It is interesting to note that increased cell volume is a common strategy for high light acclimation within many phytoplankton species38 and may also have played a similar function for the C15 symbiont. Despite thermal reductions in algal density only occurring under high pCO2 in T. reniformis, an increase in cell volume could still play a similar role in changing light fields for S. trenchii. While not reported here, pigment analysis from this study did result in a slight yet significant thermal rise in chlorophyll a cell−1 in T. reniformis (Pettay et al. in prep). An increase in cell volume would help offset potential increases in optical absorption cross section due to increases in chlorophyll density39. In addition, although thermally-induced changes in biochemical composition were observed for S. trenchii and C15, they differed with respect to which component (i.e., proteins or lipids) changed significantly (Fig 4), likely also influencing the direction of thermal change between the two species as observed in Figure 1. This may indicate differences in the biochemical pathways that correlate to specific changes in light absorption and thermal tolerance. Indeed, recent large-scale metatranscriptome analyses of phytoplankton across different ocean provinces have noted the incredible influence that temperature has over metabolic variability40. While protein cell−1 often rises with temperature in other phytoplankton41, shifting lipid composition has also been noted42.
Thicker coral tissue could provide greater symbiont photoprotection by changing the intensity and spectral properties of the internal light field43,44 and higher levels of energy reserves (the sum total of lipid, protein and carbohydrate) have been implicated in facilitating bleaching resistance in some Caribbean corals7, Hawaiian8 and Australian9 corals. Notably, coral tissue biomass was roughly 25% higher in T. reniformis as compared to the other three species11. In addition, host protein concentrations in T. reniformis were almost twice as high A. millepora and P. damicornis (Fig 5). At the same time, carbohydrate concentration in both M. monasteriata and T. reniformis were roughly 5–10 fold greater than either A. millepora or P. damicornis (Fig 5). This higher biomass may have contributed to providing the symbionts with additional photoprotection and a significant advantage within a high temperature and/or high CO2 environment.
Interestingly, host protein, lipid and carbohydrate concentrations within this study differ from Schoepf et al., (2013) where whole coral lipid concentrations for A. millepora declined at elevated temperature but only at the highest pCO2 level, whereas few physiological changes were observed within the other three species11. However, coral samples were sampled only from the growth tip of each coral species11. As skeletal porosity and thickness, along with symbiont cell density, photopigment concentrations and lipid concentrations may increase with distance from the growth tip45,46,47, it is likely that the biochemical composition of the symbiosis does as well. Therefore our approach here was to integrate these metrics over the whole coral fragment and quantify host and symbiont biochemical composition separately. As a result, the different trends in host soluble protein and carbohydrates between this study and Schoepf et al (2013) likely reflect spatial differences in physiological function and biochemical makeup between the growing tip (or edge) and the rest of the coral colony as a whole. Such spatial differences may be important in differentiating effects on short-term colony growth versus long-term colony maintenance and understanding if environmental stress differentially affects small coral recruits (which are likely most similar to coral tips) as compared to larger adult colonies.
The animal host fraction of A. millepora and M. monasteriata biochemical composition declined the most in response to elevated temperature (Fig 5), yet no thermally-induced differences were observed for Symbiodinium C21a, while C15 in M. monasteriata increased soluble protein and lipid concentrations with temperature (Fig 4). Increased symbiont lipid production, along with reductions in host energetic reserves in M. monasteriata, likely imposed substantial metabolic demand on the holobiont and may have contributed to the greater LEDR at high temperature. In contrast, few physiological changes were observed for P. damicornis, yet equally large increases in LEDR were noted, suggesting different oxygen consuming pathways are responsible for increased respiration in each species. In addition to thermal enhancement of respiration, divergent use of oxygen consuming pathways within the symbiont may play a role. Photorespiration, alternative oxidase and especially the Mehler ascorbate peroxidase cycle are all mechanisms possibly used for energy regulation in different phytoplankton, including Symbiodinium48,49. Likewise, several of these pathways have been implicated in different Symbiodinium subjected to high temperature2,50.
Previous studies have reported a significant drop in coral carbonic anhydrase (CA) expression during acute heat51,52 and combined high temperature and pCO2 exposure53. In contrast, we note a temperature-driven increase for intracellular CA in A. millepora (Fig. 5a). If the intracellular carbonic anhydrase in A. millepora is heavily localized within the gastrodermal tissue layer, as in the coral Stylophora pistillata54, thermal up-regulation of this CA isoform could indicate enhanced host delivery of carbon to the symbiont. A. millepora also displayed a significant increase in net photosynthesis under high temperature (Pettay at al. in prep, data not shown) indicating a potential link between enhanced carbon delivery by the host and symbiont productivity. However, thermal reductions in Fv/Fm were also noted for A. millepora and further complicate the issue. The lack of change in CA expression in A. millepora with respect to pCO2 concentration is consistent with previous OA experiments with adult A. millepora colonies23.
Because both extracellular CA and CA-ATPase genes are thought to be involved in calcification27, it is of interest that no change in expression was noted for A. millepora despite pCO2 induced reductions in calcification11. In contrast, CA expression drops significantly under elevated CO2 in A. millepora planulae larvae undergoing initial stages of settlement and skeletal formation22, showing that the discrepancies between studies may be driven in part by different life stages tested. The complete lack of changes in either of the carbonic anhydrase or CA-ATPase genes tested within P. damicornis may indicate that carbon concentrating mechanisms may differ among species.
The increase in transcripts for heat shock protein 90 (HSP90) in A. millepora under high temperature and medium pCO2 agrees with previous studies, which documented up-regulation of heat-shock proteins as an important component of the thermal stress response55,56. However, for A. millepora, this increase in HSP90 transcript was not observed in the highest or lowest pCO2 treatment and may indicate a sensitivity in the host thermal response to pCO2. Significant thermal up-regulation of HSP90 transcripts were observed for P. damicornis, with the most pronounced increase occurring within the low pCO2 treatments (Fig 5j), again suggesting that the thermally induced increase in HSP90 may change with pCO2. As some heat shock proteins play a fundamental role in protein stabilization, the low pH associated with OA may also affect protein conformation, further complicating the HSP90 response under elevated temperature and high CO257. Lack of change in expression of GAPDH within either species is not surprising, as previous studies have suggested its relatively stable transcription rate can be utilized as a housekeeping gene for normalization of qPCR data58.
Studies of nuclear encoded gene expression in Symbiodinium typically note small to minimal changes, even when significant thermal and or light stress is applied59,60. This is likely a consequence of greater dependency on post-transcriptional regulation within dinoflagellates in general61,62. Nevertheless, our results demonstrate distinct expression patterns for two clade C symbionts in two different host species, thus illustrating the physiological diversity contained among different host/symbiont combinations. The symbiont genes studied here represent various metabolic pathways, including nitrogen metabolism (glutamine synthetase), the citric acid cycle (α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase) and fatty acid synthesis (malonyl Co-A acyl transferase). Interestingly, high temperature-induced down-regulation of glutamine synthetase (GSII) in Symbiodinium C1c-d-t is similar to the reduction in GSII transcripts within the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana and may indicate a reduction in nitrogen metabolism from nitrate63. Although minimal, the increase in α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase gene expression with increasing pCO2 in C21a correlated with the decline in carbohydrates, possibly indicating an increase in the citric acid cycle, which links amino acid synthesis and breakdown with sugar metabolism. While expression of malonly Co-A acyl transferase in Symbiodinium C21a increased, this may not suggest enhanced lipid synthesis at high pCO2, as there was little evidence for this based on cellular lipid content (Fig. 4i). However, it is possible that additional lipids synthesized by the symbiont were translocated to the host, where evidence of significant lipid catabolism in response to both temperature and pCO2 was noted.
Similarity analyses indicate that the physiological variables that explain the largest change in one species may be less important in explaining physiological change in another. For example, with respect to temperature, host parameters contributed the most to the physiological response of A. millepora, whereas symbiont metrics changed to a greater extent in T. reniformis. This highlights the uniqueness of each holobiont as host and symbiont tolerances to environmental stress may differ and greatly influence the resulting physiological responses. In addition, our results indicate that focusing on just a few key variables may not capture the full breadth of physiological change that may occur in response to thermal stress.
When directly comparing trends in each variable, substantial shifts in cell volume and biochemical composition within Symbiodinium C15 and S. trenchii point to potential strategies in thermal tolerance and acclimation not observed within C21a and C1c-d-t. With respect to elevated pCO2, increased expression of α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase correlated with declines in carbohydrate concentration for C21a and may reflect an increase in the citric acid cycle. In contrast, protein concentrations within the other two clade-C symbionts increased with pCO2 and reflect the physiological differences amongst symbiont types at the intra-cladal scale. Furthermore, differing thermal responses in biochemical composition within A. millepora and M. monasteriata belie similarities in respiration rates and suggest that reliance on a few physiological metrics may not fully characterize nuanced physiological differences in response to environmental change. Our results suggest that conclusions based on experimental work may only be applicable to the host/symbiont combination in question and care should be taken in attempting to apply “species-specific” responses towards a more general understanding of coral reef system-wide effects from climate change. Overall, elevated pCO2 induced very little change across all species, as compared to elevated temperature. However, these results are based on a relatively short-term exposure to OA as compared to what future reefs will endure. Therefore, further studies are required to better understand the extent of physiological change under long-term elevated pCO2.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Design
A detailed description of the experimental design is found in11. Briefly, six colonies of Acropora millepora, Pocillopora damicornis, Montipora monasteriata and Turbinaria reniformis were collected in northwest Fiji at a depth between 3–10 m, transported to a coral mariculture facility (Reef Systems Coral Farm, Ohio) and allowed to acclimate for two months prior to experimentation. Six fragments were removed from each parent colony species−1 and allowed to recover. Coral fragments were slowly acclimated (over a three weeks) to custom-made synthetic seawater closely resembling natural seawater chemistry (ESV Aquarium Products Inc.). There were 6 treatment systems, each consisting of six, 57 L aquaria connected to a central 905 L sump. One colony fragment species−1 was placed into each of the six replicate tanks in each system, with a separate colony fragment from each species in each replicate tank (i.e., four fragments per tank). Because replicate tanks were connected via a central sump per treatment, our design is technically a pseudo-replicate design64. However, controlling temperature, CO2, salinity and light intensity within individual replicate tanks is technically difficult and impractical for this type of study. Corals were maintained under a 9:15 hour light:dark cycle, providing light at 275 μmol quanta m−2 s−1 at the base of the filled aquaria. Each treatment ran for 24 days, with a 25% water change every three days. Salinity was maintained at 35 ppt through daily top-offs with RO filtered fresh water. Corals were fed Artemia nauplii every three days.
Treatments consisted of an ambient and high temperature treatment at three pCO2 conditions set to ambient (382 μatm), medium (607 μatm) and high CO2 (741 μatm). The pCO2 conditions reflect current (382 μatm) and elevated conditions expected by the mid (607 μatm) and late (741 μatm) 21st century65. Temperature within the high temperature treatments was slowly increased with titanium heaters from the ambient temperature of 26.5 °C to a maximum of 31.5 °C over the course of the experiment (see supplemental Figure 1 for temperature ramping profiles).
pH measurements were taken every 30 seconds (Thermos Scientific Orion Ross Ultra pH glass electrode) and were integrated into a pH stat system for precise control of air and CO2 gas input into each sump (KSgrowstat, University of Essex). For elevated pCO2 treatments, CO2 was increased by 100 μatm day−1 until the desired pCO2 was met. All pH electrodes were calibrated daily using three NBS standards (4.00, 7.00, 10.00) and independent measurements of pH with a dedicated Ross pH electrode and alkalinity with Gran titration were made using published protocols66. Total alkalinity, pH, salinity and temperature over the 24-day experiment were used to calculate carbonate system speciation using the CO2SYS program (Lewis & Wallace, 1998). The results are shown in supplementary table 1.
Symbiont Photophysiology
Daily dark acclimated maximum quantum yield of photosystem II (Fv/Fm) was measured one hour after the light period by pulse amplitude modulation fluorometry (Diving PAM, Waltz, Germany), by supplying a 600 ms pulse of saturating light to the surface of each coral fragment. On day 23, maximal photosynthetic rates and light acclimated dark respiration (RL) were measured for 6 fragments species−1 treatment−1 via respirometry with galvanic oxygen electrodes (Qubit systems) housed in clear acrylic chambers (350 mL). Chambers were temperature controlled to match experimental conditions and constantly stirred. Maximal photosynthesis was measured by providing illumination from a 24 LED array (Cree Cool White XP-G R5) set to 600 μmol quanta m−2 s−1. Pilot experiments at this light intensity showed no decrease in oxygen evolution (data not shown). Net maximal photosynthesis (Pmaxnet) was recorded for 15–20 minutes, followed by a 10-minute dark incubation to record the light enhanced dark respiration (RL) also known as the post-illumination respiration (referred to hereafter as the LEDR). The photosynthesis to respiration ratio was calculated as Pmaxgross/RL where Pmaxgross = (net photosynthesis + light enhanced dark respiration). Net photosynthesis (data not shown) and light enhanced dark respiration (RL) were normalized to total fragment surface area (cm2) (described below).
Host and Symbiont Physiology
At the end of the 24-day treatment, samples were frozen in liquid N2 and stored at −80 °C until further processing. All coral tissue was removed from each fragment using a water pick67. This is fundamentally different from our companion paper11 based on the same experiment, where only tissue from the branch tips or the leading edge of plating corals were analyzed (with the exception of cell density and chlorophyll content which were both integrated from the whole fragment). In contrast, this paper focuses on the physiological responses integrated over the entire fragment area. The resulting slurry was homogenized with a tissue tearer (Biospec products, Inc) and then centrifuged for 5 minutes (5,000 g) to separate the algal and coral fractions. Pelleted symbionts were resuspended in synthetic seawater and divided into 1 mL aliquots. One algal aliquot was preserved with 10 μL of 1% glutaraldehyde for cell enumeration and cell density and volume were recorded by light and fluorescence microscopy. Six independent replicate counts were performed for each algal sample on a hemocytometer. Samples were photographed using a Nikon microphot-FXA epifluorescent microscope (100x magnification) and analyzed using the software Image J (NIH) with the Analyze Particles function. Pixel size of each cell was converted to μm2 using a calibrated scale micrometer and then used to calculate cell diameter and volume based on calculations for a sphere. Surface area of T. reniformis and M. monasteriata was determined by the foil method68, while area for the branching A. millepora and P. damicornis was determined by the wax method69.
For soluble protein concentration of the host and symbiont, 1 mL samples were homogenized with a bead-beater (BioSpec) for 2 minutes and then analyzed using the BCA protein method (Thermo Scientific Pierce), with a bovine serum albumin standard70. For lipid extraction, host and symbiont portions were freeze-dried overnight and then extracted using a 2:1:0.8 chloroform:methanol:sodium chloride ratio71. Lipid quantification was carried out by a vanillin colorimetric assay using corn oil as standards72. For carbohydrate quantification, host and symbiont aliquots were homogenized with a bead-beater for 1.5 minutes and then extracted using a sulfuric acid/phenol, using glucose as standard73. Absorbance measurements for lipid, carbohydrate and protein assays were made at 540, 485 and 595 nm respectively using a FLUOstar Omega plate reader (BMG Labtech, Germany). Biochemical composition was normalized to coral surface area and algal cell number.
The genetic identity of the dominant algal symbiont of each coral fragment was determined through amplification of the internal transcribed spacer 2 region (ITS2) of the ribosomal array and subsequently analyzed by previously published protocols for denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) fingerprinting and cycle sequencing74. This method identifies the dominant (or co-dominant) sequence variants for the ribosomal genome of a particular symbiont lineage.
Targeted Host and Symbiont Gene Expression
Due to the greater availability of genomic data for the coral A. millepora and P. damicornis and their respective Symbiodinium, gene expression was examined only in these two species and their respective symbionts. Transcript abundance for host genes involved in several metabolic roles was investigated, including carbon acquisition (intra and extracellular carbonic anhydrase), calcium and ATP exchange (CA-ATPase), carbon metabolism (Glyceraldehyde 3-phophate dehydrogenase (GAPDH)) and thermal response (Heat Shock Protein 90 (HSP90)). For algal gene expression, transcript abundance was monitored in pathways related to carbon metabolism (α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase), nitrogen metabolism (glutamine synthetase) and fatty acid synthesis (malonyl Co-A acyl transferase)52.
For intra and extracellular carbonic anhydrases and Ca-ATPase, A. millepora and P. damicornis expressed sequence tags were searched using a conventional BLAST search within the National Center for Bioinformatics (NCBI) and PocilloporaBase (cnidarians.bu.edu/PocilloporaBase/cgi-bin/index.cgi) databases respectively. Databases were queried with well-characterized gene transcripts from Stylophora pistillata, intra and extracellular carbonic anhydrase (STPCA-2, EU532164.1 and STPCA EU159467.1 respectively) and CA-ATPase (AY360080.1)27,54,75. Databases were also searched using the sequences for GAPDH (EZ026309.1) and HSP90 (DY584045.1) from Acropora aspera52. The top blast hits were confirmed as homologous genes through phylogenetic analysis (Geneious, Biomaters Ltd). All coral genes were normalized to transcripts encoding ribosomal subunit protein 7 (rsp7) and Elongation factor 1 α (EF1α)58. Algal transcripts were normalized to the housekeeping genes encoding S-adenosyl methionine synthetase (SAM)59 and the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)52. Primers for qPCR were designed with Primer-Quest software (Integrated DNA Technologies) or from published studies52,58. Primer sets and efficiency scores for each gene are listed in supplementary table 2.
Frozen coral samples were ground into a powder using a mortar and pestle chilled on a bed of dry ice. Total RNA was extracted and purified from each sample using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen) and an Aurum Total RNA Mini kit (Bio-Rad). Purified RNA samples were quantified by spectrophotometry (NanoDrop 2000, ThermoScientific). Only samples with concentrations greater than 50 ng μL−1 were used for subsequent analyses and samples typically had 260 nm:280 nm and 260 nm:230 nm ratios greater than 2.0 and 1.9 respectively. RNA samples were diluted to 20 ng μL−1 prior to cDNA synthesis. Reverse transcription PCR reactions were performed using the high capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems). For each sample, a total of 120 ng of total RNA was added to a single 10 μl cDNA reaction.
Quantitative PCR reactions were performed on 96 well plates with optical film, using a SensiMix real time detection system with 2X SYBR Hi-ROX Mastermix (BIOLINE) and an ABI Prism 7500 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems). Each 10 μL reaction contained 5 μL of SYBR Hi-ROX, 0.2 μL each of 10 mM forward and reverse primer, 2.6 μL nuclease-free water and 2 μL of 1:5 diluted cDNA. All qPCR reactions were performed with the following thermal profile: 50 °C for 2 min, 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 15s, 61 °C for 15s and 72 °C for 45s. Standards were constructed from pooled total RNA samples from multiple treatments and diluted in a 4-fold dilutions series. For each plate, standards were run in triplicate and samples run in duplicate. A dissociation curve between 61 °C and 95 °C (0.5 °C intervals) was performed immediately after each PCR reaction to ensure the absence of any non-specific, multi-product amplification. Negative control reactions were carried out on a subset of samples and pooled standards (not shown).
Standards were constructed from pooled total RNA samples from multiple time points and diluted in a 4-fold dilutions series prior to cDNA synthesis. Standards were run in triplicate and samples run in duplicate. Efficiency values for each gene were calculated using the formula E = 10(−1/slope) and are available in supplementary table S3. GeneEx expression software was used to normalize all data to total RNA and to the multiple house-keeping genes listed above and to account for differences in amplification efficiency. As the goal of this work was to compare gene expression across multiple variables and treatments rather than to a single control treatment, relative expression values for each gene of interest were calculated by dividing each value by the highest value within each gene assay76,77.
Statistical Analysis
For each species, the overall importance of elevated temperature and pCO2, were analyzed for their significance in separating samples using an ANalyses Of SIMilarities (ANOSIM) with 9,999 permutations. If resulting correlation from the ANOSIM was above 0.2, a subsequent SIMPER analysis was used to determine which variables contributed the greatest towards dissimilarity between treatment factor levels (2 temperature and 3 pCO2 levels) within each species. Lastly, physiological variables across all four coral species were analyzed using non-metric multidimensional scaling (nMDS) on Euclidean distances after log(x + 1) transformation78.
In order to better understand possible nuanced physiological changes within each species, individual variables were also analyzed. For each species, individual variables were tested for homogeneity of variance and normality of distribution using the Levene and Shapiro-Wilks tests, respectively. If either test was significant (p < 0.05), the data was log transformed. A two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was utilized to test for significant main and interactive effects of pCO2 and temperature. As our focus was primarily on the main effects and because only two temperatures were utilized, significant temperature effects were not followed up with post-hoc analyses. Significant differences for pCO2, were followed by Tukey post-hoc testing to distinguish between the three pCO2 treatments. Significant interactive effects were followed up by a pairwise comparison among all 6 treatments (Tukey post-hoc). Alternatively, if data failed to meet assumptions of normality even after log-transformation, a Kruskal-Wallis test with multiple comparisons was used. All statistical analyses were performed using R software with the ‘vegan’, ‘car’ and ‘pgirmess’ packages installed. Resulting output from SIMPER, ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis tests are provided as supplemental information.
Additional Information
How to cite this article: Hoadley, K. D. et al. Physiological response to elevated temperature and pCO2 varies across four Pacific coral species: Understanding the unique host+symbiont response. Sci. Rep. 5, 18371; doi: 10.1038/srep18371 (2015).
References
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. & Bruno, J. F. The impact of climate change on the world’s marine ecosystems. Science 328, 1523–1528 (2010).
Warner, M., Fitt, W. & Schmidt, G. Damage to photosystem II in symbiotic dinoflagellates: a determinant of coral bleaching. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 8007–8012 (1999).
Fitt, W., Brown, B. E., Warner, M. & Dunne, R. Coral bleaching: interpretation of thermal tolerance limits and thermal thresholds in tropical corals. Coral Reefs 20, 51–65 (2001).
Nishiyama, Y. et al. Oxidative stress inhibits the repair of photodamage to the photosynthetic machinery. EMBO J 20, 5587–5594 (2001).
Takahashi, S. & Murata, N. How do environmental stresses accelerate photoinhibition? Trends Plant Sci 13, 178–182 (2008).
Baird, A. H., Bhagooli, R., Ralph, P. J. & Takahashi, S. Coral bleaching: the role of the host. Trends Ecol Evol 24, 16–20 (2009).
Grottoli, A. G. et al. The cumulative impact of annual coral bleaching can turn some coral species winners into losers. Glob. Chang. Biol. 10.1111/gcb.12658 (2014).
Grottoli, A. G., Rodrigues, L. J. & Palardy, J. E. Heterotrophic plasticity and resilience in bleached corals. Nature 440, 1186–1189 (2006).
Anthony, K. R. N., Hoogenboom, M. O., Maynard, J. A., Grottoli, A. G. & Middlebrook, R. Energetics approach to predicting mortality risk from environmental stress: a case study of coral bleaching. Funct Ecol 23, 539–550 (2009).
Levas, S. J., Grottoli, A. G., Hughes, A., Osburn, C. L. & Matsui, Y. Physiological and biogeochemical traits of bleaching and recovery in the mounding species of coral Porites lobata: Implications for resilience in mounding corals. PloS one 8, 10.1371/journal.pone.0063267 (2013).
Schoepf, V. et al. Coral energy reserves and calcification in a high-CO2 world at two temperatures. PLoS one 8, 10.1371/journal.pone.0075049 (2013).
Gigova, L., Ivanova, N., Gacheva, G., Andreeva, R. & Furnadzhieva, S. Response of Trachydiscus minutus (Xanthophyceae) to temperature and light. J Phycol 48, 85–93 (2012).
Carvalho, A. P., Monteiro, C. M. & Malcata, F. X. Simultaneous effect of irradiance and temperature on biochemical composition of the microalga Pavlova lutheri. J Appl Phycol 21, 543–552 (2009).
Comeau, S., Edmunds, P. J., Spindel, N. B. & Carpenter, R. C. The responses of eight coral reef calcifiers to increasing partial pressure of CO2 do not exhibit a tipping point. Limnol Oceanogr 589, 388–398 (2013).
Anthony, K. R. N., Kline, D. I., Diaz-Pulido, G., Dove, S. & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Ocean acidification causes bleaching and productivity loss in coral reef builders. Proc. Natl. Acad. USA 105, 17442–17446 (2008).
Edmunds, P. J., Carpenter, R. C. & Comeau, S. Understanding the threats of ocean acidification to coral reefs. Oceanogr. 26, 149–152 (2013).
Cohen, A. L. & Holcomb, M. Why corals care about ocean acidification: uncovering the mechanism. Oceanogr. 22, 118–127 (2009).
Suggett, D. J. et al. Sea anemones may thrive in a high CO2 world. Glob. Chang. Biol. 18, 3015–3025 (2012).
Towanda, T. & Thuesen, E. V. Prolonged exposure to elevated CO2 promotes growth of the algal symbiont Symbiodinium muscatinei in the intertidal sea anemone Anthopleura elegantissima. Open Biol. 1, 615–621 (2012).
Brading, P. et al. Differential effects of ocean acidification on growth and photosynthesis among phylotypes of Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae). Limnol. Oceangr. 56, 927–938 (2011).
Brading, P., Warner, M. E., Smith, D. J. & Suggett, D. J. Contrasting modes of inorganic carbon acquisition amongst Symbiodinium (Dinophyceae) phylotypes. New Phytol 200, 432–442 (2013).
Moya, A. et al. Whole transcriptome analysis of the coral Acropora millepora reveals complex responses to CO2‐driven acidification during the initiation of calcification. Mol Ecol 21, 2440–2454 (2012).
Kaniewska, P. et al. Major cellular and physiological impacts of ocean acidification on a reef building coral. PLoS one 7, 10.1371/journal.pone.0034659 (2012).
Vidal-Dupiol, J. et al. Genes related to ion-transport and energy production are upregulated in response to CO2-driven pH decrease in corals: new insights from transcriptome analysis. PloS one 8, 10.1371/journal.pone.0058652 (2013).
Muller-Parker, G., McCloskey, L. R., Hoegh-Guldberg, O. & McAuley, P. J. The effect of ammonium enrichment on animal and algal biomass of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Pac Sci 48, 273–283 (1994).
Hoegh-Guldberg, O. & Williamson, J. Availability of two forms of dissolved nitrogen to the coral Pocillopora damicornis and its symbiotic zooxanthellae. Mar Biol 133, 561–570 (1999).
Moya, A. et al. Carbonic anhydrase in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: characterization, localization and role in biomineralization. J Biol Chem 283, 25475–25484 (2008).
Grover, R., Maguer, J. F., Allemand, D. & Ferrier-Pages, C. Nitrate uptake in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Limnol Oceanogr 48, 2266–2274 (2003).
Miller, D. J., Ball, E. E., Forêt, S. & Satoh, N. Coral genomics and transcriptomics—ushering in a new era in coral biology. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 408, 114–119 (2011).
Reynaud, S. et al. Interacting effects of CO2 partial pressure and temperature on photosynthesis and calcification in a scleractinian coral. Glob. Chang. Biol. 9, 1660–1668 (2003).
Rodolfo-Metalpa, R., Martin, S., Ferrier-Pagès, C. & Gattuso, J.-P. Response of the temperate coral Cladocora caespitosa to mid-and long-term exposure to pCO 2 and temperature levels projected for the year 2100 AD. Biogeosciences 7, 289–300 (2010).
LaJeunesse, T. C., Smith, R. T., Finney, J. & Oxenford, H. Outbreak and persistence of opportunistic symbiotic dinoflagellates during the 2005 Caribbean mass coral ‘bleaching’ event. Proc R Soc B 276, 4139–4148 (2009).
Wall, C. B., Fan, T. Y. & Edmunds, P. J. Ocean acidification has no effect on thermal bleaching in the coral Seriatopora caliendrum. Coral Reefs 33, 119–130 (2014).
Mumby, P. J., Chisholm, J. R. M., Edwards, A. J., Andrefouet, S. & Jaubert, J. Cloudy weather may have saved Society Island reef corals during the 1998 ENSO event. Marine Ecology-Progress Series 222, 209–216 (2001).
Suggett, D. J. et al. Light availability determines susceptibility of reef building corals to ocean acidification. Coral Reefs 32, 327–337 (2012).
Enriquez, S., Mendez, E. R. & Iglesias-Prieto, R. Multiple scattering on corals enhances light absorption by symbiotic algae. Limnol Oceanogr 50, 1025–1032 (2005).
Rodriguez-Román, A., Hernández-Pech, X., Thomé, P. E., Enriquez, S. & Iglesias-Prieto, R. Photosynthesis and light utilization in the Caribbean coral Montastraea faveolata recovering from a bleaching event. Limnol Oceanogr 51, 2702–2710 (2006).
Thompson, P. A., Harrison, P. J. & Parslow, J. S. Influence of irradiance on cell volume and carbon quota for ten species of marine phytoplankton. J Phycol 27, 351–360 (1991).
Finkel, Z. V. Light absorption and size scaling of light-limited metabolism in marine diatoms. Limnol Oceanogr 46, 86–94 (2001).
Toseland, A. D. S. J. et al. The impact of temperature on marine phytoplankton resource allocation and metabolism. Nat. Clim. Change 3, 979–984 (2013).
Berges, J. A., Varela, D. E. & Harrison, P. J. Effects of temperature on growth rate, cell composition and nitrogen metabolism in the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana (Bacillariophyceae). Mar Ecol Prog Ser 225, 139–146 (2002).
Renaud, S. M., Zhou, H. C., Parry, D. L., Thinh, L.-V. & Woo, K. C. Effect of temperature on the growth, total lipid content and fatty acid composition of recently isolated tropical microalgae Isochrysis sp., Nitzschia closterium, Nitzschia paleacea and commercial species Isochrysis sp.(clone T. ISO). J Appl Phycol 7, 595–602 (1995).
Loya, Y. et al. Coral bleaching: the winners and the losers. Ecol Lett 4, 122–131 (2001).
Dimond, J. L., Holzman, B. J. & Bingham, B. L. Thicker host tissues moderate light stress in a cnidarian endosymbiont. J. Exp. Biol. 215, 2247–2254 (2012).
Helmuth, B. S. T., Timmerman, B. E. H. & Sebens, K. P. Interplay of host morphology and symbiont microhabitat in coral aggregations. Mar Biol 130, 1–10 (1997).
Roche, R. C., Abel, R. L., Johnson, K. G. & Perry, C. T. Spatial variation in porosity and skeletal element characteristics in apical tips of the branching coral Acropora pulchra (Brook 1891). Coral Reefs 30, 195–201 (2011).
Stimson, J. S. Location, Quantity and rate of change in quantity of lipids in tissue of Hawaiian hermatypic corals. Bull Mar Sci 41, 889–904 (1987).
Roberty, S., Berne, N., Bailleul, B. & Cardol, P. PSI Mehler reaction is the main alternative photosynthetic electron pathway in Symbiodinium sp., symbiotic dinoflagellates of cnidarians. New Phytol 204, 81–91 (2014).
Oakley, C. A., Hopkinson, B. M. & Schmidt, G. W. Mitochondrial terminal alternative oxidase and its enhancement by thermal stress in the coral symbiont Symbiodinium. Coral Reefs 33, 543–552 (2014).
Hennige, S. J., McGinley, M. P., Grottoli, A. G. & Warner, M. E. Photoinhibition of Symbiodinium spp. within the reef corals Montastraea faveolata and Porites astreoides: implications for coral bleaching. Mar Biol 158, 2515–2526 (2011).
Edge, S. E., Morgan, M. B., Gleason, D. F. & Snell, T. W. Development of a coral cDNA array to examine gene expression profiles in Montastraea faveolata exposed to environmental stress. Mar Pollut Bull 51, 507–523 (2005).
Leggat, W. et al. Differential responses of the coral host and their algal symbiont to thermal stress. PloS one 6, 10.1371/journal.pone.0026687 (2011).
Ogawa, D., Bobeszko, T., Ainsworth, T. & Leggat, W. The combined effects of temperature and CO2 lead to altered gene expression in Acropora aspera. Coral Reefs 32, 895–907 (2013).
Bertucci, A., Tambutte, S., Supuran, C. T., Allemand, D. & Zoccola, D. A new coral carbonic anhydrase in Stylophora pistillata. Mar Biotechnol 13, 992–1002 (2011).
Osovitz, C. J. & Hofmann, G. E. Thermal history-dependent expression of the HSP70 gene in purple sea urchins: Biogeographic patterns and the effect of temperature acclimation. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 327, 134–143 (2005).
Rosic, N. N., Pernice, M., Dove, S., Dunn, S. & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Gene expression profiles of cytosolic heat shock proteins Hsp70 and Hsp90 from symbiotic dinoflagellates in response to thermal stress: possible implications for coral bleaching. Cell Stress Chaperon 16, 69–80 (2011).
Seveso, D. et al. Exploring the effect of salinity changes on the levels of Hsp60 in the tropical coral Seriatopora caliendrum. Mar Environ Res 90, 96–103 (2013).
Seneca, F. O. et al. Patterns of gene expression in a scleractinian coral undergoing natural bleaching. Mar Biotechnol 12, 594–604 (2010).
Rosic, N. N., Pernice, M., Rodriguez-Lanetty, M. & Hoegh-Guldberg, O. Validation of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in Symbiodinium exposed to thermal and light stress. Mar Biotechnol 13, 355–365 (2011).
Boldt, L., Yellowlees, D. & Leggat, W. Measuring Symbiodinium sp. gene expression patterns with quantitative real-time PCR. Proc of the 11th Internatl Coral Reef Symposium. 118–122 (2009).
Bachvaroff, T. R. & Place, A. R. From stop to start: tandem gene arrangement, copy number and trans-splicing sites in the dinoflagellate Amphidinium carterae. PLoS One 3, 10.1371/journal.pone.0002929 (2008).
Okamoto, O. K., Robertson, D. L., Fagan, T. F., Hastings, J. W. & Colepicolo, P. Different regulatory mechanisms modulate the expression of a dinoflagellate iron-superoxide dismutase. J Biol Chem 276, 19989–19993 (2001).
Parker, M. S. & Armbrust, E. Synergistic effects of light, temperature and nitrogen source on transcription of genes for carbon and nitrogen metabolism in the centric diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana (Baccillariophyceae). J Phycol 41, 1142–1153 (2005).
Cornwall, C. E. & Hurd, C. L. Experimental design in ocean acidification research: problems and solutions. ICES J Mar Sci 10.1093/icesjms/fsv118, (2015).
IPCC. Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA. (2013).
Cai, W. J. et al. Alkalinity distribution in the western North Atlantic Ocean margins. J Geophys Res 115, 10.1029/2009JC005482 (2010).
Johannes, R. E. & Wiebe, W. J. Method for determination of coral tissue biomass and composition. Limnol Oceanogr 15, 822–15:824 (1970).
Marsh, J. Primary productivity of reef-building calcareous and red algae. Ecology 55, 255–263 (1970).
Stimson, J. & Kinzie, R. A. The temporal pattern and rate of release of zooxanthellae from the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis (Linnaeus) under nitrogen-enrichment and control conditions. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 153, 63–74 (1991).
Smith, P. K. et al. Determination of protein concentration by the bicinchoninic acid method. Anal Biochem 150, 76–85 (1985).
Folch, J., Lees, M. & Sloane-Stanley, G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226, 497–509 (1957).
Cheng, Y.-S., Zheng, Y. & VanderGheynst, J. Rapid quantitative analysis of lipids using a colorimetric method in a microplate format. Lipids 46, 95–103 (2011).
Dubois, M., Giles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Pevers, P. A. & Smith, F. Colorimetric method for determination of sugar and related substances. Anal Chem 28, 350–356 (1956).
LaJeunesse, T. C. et al. Low symbiont diversity in southern Great Barrier Reef corals, relative to those of the Caribbean. Limnol Oceanogr 48, 2046–2054 (2003).
Zoccola, D. et al. Molecular cloning and localization of a PMCA P-type calcium ATPase from the coral Stylophora pistillata. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) 1663, 117–126 (2004).
Levy, O. et al. Light-responsive cryptochromes from a simple multicellular animal, the coral Acropora millepora. Sci. Signal. 318, 467–472 (2007).
Hoadley, K. D., Szmant, A. M. & Pyott, S. J. Circadian clock gene expression in the coral Favia fragum over diel and lunar reproductive cycles. PloS one 6, 10.1371/journal.pone.0019755 (2011).
Ziegler, M., Roder, C. M., Buchel, C. & Voolstra, C. R. Limits to physiological plasticity of the coral Pocillopora verrucosa from the central Red Sea. Coral Reefs 33, 1115–1129 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.G.G., W.J.C. and M.E.W. conceived and designed the experiments. T.F.M., Y.W. and Y.M. constructed the experimental systems. K.D.H. performed lab work and analyzed the data. K.D.H., D.T.P., A.G.G., W.J.C., V.S., X.H., Q.L., H.X., Y.W., Y.M., J.H.B. and M.E.W. conducted the experiment and wrote the manuscript.
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is not included under the Creative Commons license, users will need to obtain permission from the license holder to reproduce the material. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/
About this article
Cite this article
Hoadley, K., Pettay, D., Grottoli, A. et al. Physiological response to elevated temperature and pCO2 varies across four Pacific coral species: Understanding the unique host+symbiont response. Sci Rep 5, 18371 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18371
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18371
This article is cited by
-
Host starvation and in hospite degradation of algal symbionts shape the heat stress response of the Cassiopea-Symbiodiniaceae symbiosis
Microbiome (2024)
-
Branching coral growth and visual health during bleaching and recovery on the central Great Barrier Reef
Coral Reefs (2023)
-
Long-term exposure to an extreme environment induces species-specific responses in corals’ photosynthesis and respiration rates
Marine Biology (2022)
-
Moderate nutrient concentrations are not detrimental to corals under future ocean conditions
Marine Biology (2021)
-
Resilience of the temperate coral Oculina arbuscula to ocean acidification extends to the physiological level
Coral Reefs (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.