Abstract
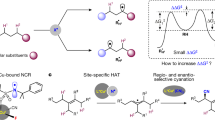
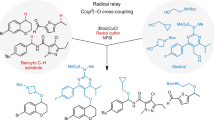
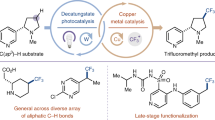
Cytochrome P450 enzymes are known to catalyze bimodal oxidation of aliphatic acids via radical intermediates, which partition between pathways of hydroxylation and desaturation5,6. Developing analogous catalytic systems for remote C−H functionalization remains a significant challenge14,15,16. Here we report the development of Cu(I)-catalyzed bimodal dehydrogenation/lactonization reactions of synthetically common N-methoxyamides via radical abstractions of the γ-aliphatic C−H bonds. The feasibility of switching from dehydrogenation to lactonization has also been demonstrated by altering reaction conditions. The use of a readily available amide as both radical precursor and internal oxidant allowed for the development of a redox-neutral C−H functionalization reactions with methanol as the sole side product. These C−H functionalization reactions using Cu(I) catalyst of loading as low as 0.5 mol% have been applied to the diversification of a wide range of aliphatic acids including drug molecules and natural products. The exceptional compatibility of this catalytic system with a wide range of oxidatively sensitive functionality demonstrates the unique advantage of using simple amide substrate as the mild internal oxidant.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
from$1.95
to$39.95
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures S1-19; Supplementary Tables S1-8 and Supplementary References.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Zhang, ZJ. & Yu, JQ. Copper-catalyzed dehydrogenation or lactonization of C(sp3)−H bonds. Nature (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07341-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-024-07341-z
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.