Abstract
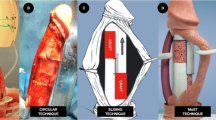
Peyronie’s disease is often comorbid with erectile dysfunction and can cause significant penile shortening. We describe our modified tunica expansion procedure (TEP) technique of penile length preservation and girth enhancement with correction of penile angulation in patients with mild Peyronie’s disease (<30 degree angulation, or hourglass deformity, no hinging) and erectile dysfunction presenting for inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) surgery. A retrospective review of IPP placement from one high volume surgeon was performed. A total of 474 patients’ charts from June 2017 to June 2021 were reviewed and those charts of patients undergoing modified TEP in the setting of Peyronie’s disease were analyzed. Average increase in length and girth were measured and means with standard deviations calculated. The modified TEP is performed through a scrotal approach and involves complete eversion of the penis with dissection of Buck’s fascia off the underlying tunica. Subsequently, staggered scorings of the underlying tunica are performed allowing for circumferential girth enhancement and length preservation. In men with Peyronie’s disease, these scorings are preferentially concentrated on the side of the plaque to allow straightening without loss of length. A total of 32 patients with Peyronie’s disease from the larger cohort underwent the modified TEP. Mean increase in length of distal corpora was 2.8 ± 0.8 cm (range 2.0–3.4 cm) (measured using Furlow before and after penile eversion with TEP), while mean increase in girth (measured at midphallus prior to prosthesis insertion and after IPP inflation) was 1.6 ± 0.4 cm (range 1.2–2.2 cm). There were no reported complications. A scrotal approach to TEP is an easy to perform technique that can be used to restore length and enhance girth in men with Peyronie’s disease undergoing insertion of IPP. Additionally, it is a customizable approach that can also be used to correct mild penile angulation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gaffney CD, Pagano MJ, Weinberg AC, Small AC, Kuehas FE, Egydio PH, et al. Lengthening strategies for Peyronie’s disease. Transl Androl Urol. 2016;5:351.
Taylor FL, Levine LA. Peyronie’s Disease. Urol Clin North Am. 2007;34:517.
Patel DP, Christensen MB, Hotaling JM, Pastuszak AW. A review of inflammation and fibrosis: implications for the pathogenesis of Peyronie’s disease. World J Urol. 2020;38:253.
Krakhotkin DV, Chernylovskyi VA, Mottrie A, Greco F, Bugaev RA. New insights into the pathogenesis of Peyronie’s disease: A narrative review. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2020;6:165.
Rew KT, Heidelbaugh JJ. Erectile Dysfunction. Am Fam Phys. 2016;94:820.
Akakpo W, Pineda MA, Burnett AL. Critical Analysis of Satisfaction Assessment After Penile Prosthesis Surgery. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:244.
Shah T, Wang R. A Review of Factors Affecting Patient Satisfaction With Inflatable Penile Prosthesis. Sex Med Rev. 2021;9:350.
Montorsi F, Rigatti P, Carmignani G, Corbu C, Campo B, Ordesi G, et al. AMS three-piece inflatable implants for erectile dysfunction: a long-term multi-institutional study in 200 consecutive patients. Eur Urol. 2000;37:50.
Egydio PH. An Innovative Strategy for Non-Grafting Penile Enlargement: A Novel Paradigm for Tunica Expansion Procedures. J Sex Med. 2020;17:2093.
Warner JN. A Contemporary Evaluation of Peyronie’s Disease During Penile Prosthesis Placement: MOST, MUST, and More. Curr Urol Rep. 2019;20:9.
Hehemann MC, Towe M, Huynh LM, El-Khatib FM, Yafi FA. Penile Girth Enlargement Strategies: What’s the Evidence? Sex Med Rev. 2019;7:535.
Shah BB, Kent M, Valenzuela R. Advanced Penile Length Restoration Techniques to Optimize Penile Prosthesis Placement Outcomes. Sex Med Rev. 2021;9:641–9.
Tran H, Goldfarb R, Ackerman A, Valenzuela RJ. Penile Lengthening, Girth, and Size Preservation at the Time of Penile Prosthesis Insertion. Sex Med Rev. 2017;5:403.
Baumgarten AS, Beilan JA, Shah BB, Loeb A, Bickell M, Parker J, et al. Suprapubic Fat Pad Excision with Simultaneous Placement of Inflatable Penile Prosthesis. J Sex Med. 2019;16:333.
Adham MN, Teimourian B, Mosca P. Buried penis release in adults with suction lipectomy and abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;106:840.
Miranda-Sousa A, Keating M, Moreira S, Baker M, Carrion R. Concomitant ventral phalloplasty during penile implant surgery: a novel procedure that optimizes patient satisfaction and their perception of phallic length after penile implant surgery. J Sex Med. 2007;4:1494.
Rolle L, Falcone M, Ceruti C, Timpano M, Sedigh O, Ralph DJ, et al. A prospective multicentric international study on the surgical outcomes and patients’ satisfaction rates of the ‘sliding’ technique for end-stage Peyronie’s disease with severe shortening of the penis and erectile dysfunction. BJU Int. 2016;117:814.
Egydio PH, Kuehhas FE. Penile lengthening and widening without grafting according to a modified ‘sliding’ technique. BJU Int. 2015;116:965.
Wilson SK, Mora-Estaves C, Egydio P, Ralph D, Habous M, Love C, et al. Glans Necrosis Following Penile Prosthesis Implantation: Prevention and Treatment Suggestions. Urology. 2017;107:144.
Sansalone S, Garaffa G, Djinovic R, Egydio P, Vespasiani G, Miano R, et al. Simultaneous penile lengthening and penile prosthesis implantation in patients with Peyronie’s disease, refractory erectile dysfunction, and severe penile shortening. J Sex Med. 2012;9:316.
Levine LA, Becher EF, Bella AJ, Brant WO, Kohler TS, Martinez-Salamanca JI, et al. Penile Prosthesis Surgery: Current Recommendations From the International Consultation on Sexual Medicine. J Sex Med. 2016;13:489.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SR: data analysis and paper writing. AZ: data analysis and paper writing. RV: study design and final paper review and approval.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Razdan, S., Zisman, A. & Valenzuela, R. Scrotal approach for tunica expansion procedure (TEP) for penile girth and length restoration during penile prosthesis implantation in patients with penile angulation due to Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: technique and outcomes. Int J Impot Res 36, 146–150 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-022-00652-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-022-00652-7
This article is cited by
-
Comment on: “Scrotal approach for tunica expansion procedure (TEP) for penile girth and length restoration in patients with penile angulation due to Peyronie’s disease and erectile dysfunction: technique and outcomes”
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)
-
Unveiling treatment horizons and contemporary perspectives in Peyronie’s disease – take home messages from Laurance A. Levine special issue
International Journal of Impotence Research (2024)