Abstract
Objectives
To compare the repeatability of Cone Location and Magnitude Index expanded (CLMI.X) parameters of 2 mm diameter zone of greatest corneal curvature (Cspot-Axi) and 1 mm diameter zone of thinnest pachmymetry (Spot-Pach) with the maximum single point keratometry (Kmax), 3 mm Zonal Kmax (Z-Kmax3), and thinnest single point pachymetry (TP) in keratoconus (KC).
Methods
In this Comparative repeatability study, data from 36 eyes of 36 normal individuals and 72 eyes of 72 KC patients (28 eyes with ≤50.0D and 44 eyes with >50.0D Z-Kmax3) were analyzed. For each enrolled eye, imaging was done 6 times (3 consecutive acquisitions with a half hour break). For each parameter, the within-subject standard deviation (Sw) was calculated from the data of the six exams.
Results
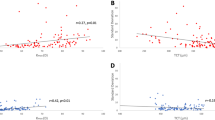
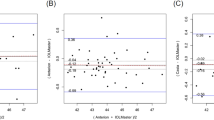
In the normal group, Cspot-Axi-Sw was different from Kmax-Sw (p = 0.0004). Also, Z-Kmax3-Sw was different from Kmax-Sw (p = 0.0297). The difference between Cspot-Axi-Sw and Z-Kmax3-Sw was statistically significant (p = 0.0482). In the KC group, Sw were significantly different between Cspot-Axi and Kmax (p < 0.0001), and between Z-Kmax3 and Kmax (p < 0.0001). In the Z-Kmax3 ≤ 50.0D subgroup, Sw were different between Cspot-Axi and Kmax (p = 0.0002). In the Z-Kmax3 > 50.0D subgroup, Sw were different between Cspot-Axi and Kmax (p < 0.0001), and between Z-Kmax3 and Kmax (p < 0.0001). Sw differences between Spot-Pach and TP were not significant in any of the study groups (all P > 0.05).
Conclusions
In the diagnosis and follow up of KC, the zonal averages of Cspot-Axi and Z-Kmax3 are more reliable than the single point Kmax. The repeatability of Spot-Pach is similar to TP and both variables should suit the purpose equally.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 18 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $14.39 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Gomes JA, Tan D, Rapuano CJ, Belin MW, Ambrósio R Jr., Guell JL, et al. Global consensus on keratoconus and ectatic diseases. Cornea. 2015;34:359–69.
Roberts. Error in the estimation of ablation centration using pachymetric difference maps. J Refract Surg. 2015;31:138–9.
Miraftab M, Fotouhi A, Hashemi H, Jafari F, Shahnazi A, Asgari S. A modified risk assessment scoring system for post laser in situ keratomileusis ectasia in topographically normal patients. J Ophthalmic Vis Res. 2014;9:434–8.
Randleman JB, Russell B, Ward MA, Thompson KP, Stulting RD. Risk factors and prognosis for corneal ectasia after LASIK. Ophthalmology. 2003;110:267–75.
Piñero DP, Nieto JC, Lopez-Miguel A. Characterization of corneal structure in keratoconus. J Cataract Refrct Surg. 2012;38:2167–83.
Ambrosio R Jr., Caiado AL, Guerra FP, Louzada R, Sinha RA, Luz A, et al. Novel pachymetric parameters based on corneal tomography for diagnosing keratoconus. J Refract Surg. 2011;27:753–8.
Mahmoud AM, Roberts CJ, Lembach RG, Twa MD, Herderick EE, McMahon TT, CLEK Study Group. CLMI: the cone location and magnitude index. Cornea. 2008;27:480–7.
Crawford AZ, Patel DV, McGhee CNJ. Comparison and repeatability of keratometric and corneal power measurements obtained by Orbscan II, Pentacam, and Galilei corneal tomography systems. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:53–60.
Guber I, McAlinden C, Majo F, Bergin C. Identifying more reliable parameters for the detection of change during the follow-up of mild to moderate keratoconus patients. Eye Vis. 2017;4:24.
Hashemi H, Yekta A, Khabazkhoob M. Effect of keratoconus grades on repeatability of keratometry readings: Comparison of 5 devices. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2015;41:1065–72.
Hashemi H, Asgari S, Roberts CJ. Zonal Kmax Is More Reliable Than Single-Point Kmax. J Refract Surg. 2021;37:286–7.
Mahmoud AM, Roberts C, Henderick EE. The Ohio State University Corneal Topography Tool. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:S677.
Mahmoud AM, Nuñez MX, Blanco C, Koch DD, Wang L, Weikert MP, et al. Expanding the cone location and magnitude index to include corneal thickness and posterior surface information for the detection of keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2013;156:1102–11.
Ferdi AC, Nguyen V, Gore DM, Allan BD, Rozema JJ, Watson SL. Keratoconus natural progression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 11 529 eyes. Ophthalmology. 2019;126:935–45.
Burns DM, Johnston FM, Frazer DG, Patterson C, Jackson AJ. Keratoconus: an analysis of corneal asymmetry. Br J Ophthalmol. 2004;88:1252–5.
Asroui L, Mehanna CJ, Salloum A, Chalhoub RM, Roberts CJ, Awwad ST. Repeatability of Zone Averages Compared to Single-Point Measurements of Maximal Curvature in Keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2021;221:226–34.
Hick S, Laliberté JF, Meunier J, Chagnon M, Brunette I. Effects of misalignment during corneal topography. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:1522–9.
Miháltz K, Kránitz K, Kovács I, Takács A, Németh J, Nagy ZZ. Shifting of the line of sight in keratoconus measured by a hartmann-shack sensor. Ophthalmology. 2010;117:41–48.
Kreps EO, Jimenez-Garcia M, Issarti I, Claerhout I, Koppen C, Rozema JJ. Repeatability of the Pentacam HR in Various Grades of Keratoconus. Am J Ophthalmol. 2020;219:154–62.
Liljequist D, Elfving B, Skavberg Roaldsen K. Intraclass correlation—a discussion and demonstration of basic features. PLoS One. 2019;14:e0219854.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Concept and design (HH, CJR), acquisition of data (HH, SA), statistical analysis (AMM), interpretation of result (HH, CJR, SM, and SA), drafting the manuscript (SA, CJR, and SM), critical revision and final approve (all authors).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
CJR is consultant for Oculus Optikgeräte GmbH and Ziemer Ophthalmic Systems AG, Germany. None of the remaining authors have any financial disclosures.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hashemi, H., Asgari, S., Mahmoud, A.M. et al. Variability of CLMI-X parameters, zonal Kmax, and single-point Kmax in keratoconus progression. Eye 37, 3197–3202 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02476-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41433-023-02476-1