Abstract
Background/objectives
The phase angle, expressed through bioelectrical impedance, has been studied as a prognostic marker in several health conditions. As this issue is still conflicting, the question whether this parameter correlates with mortality in the most diverse clinical situations remains. Therefore, this study aimed to evaluate the relationship between phase angle and mortality through a systematic review of the literature.
Subjects/methods
This research was conducted in electronic databases (Pubmed, Embase, Cochrane, Lilacs, Scielo, e Scopus), and included studies that had phase angle as a variable of interest and mortality/survival as an outcome. Data were extracted independently by two reviewers and disagreements were assessed by a third reviewer.
Results
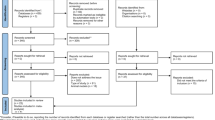
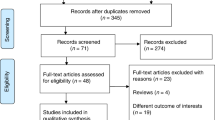
Forty-eight of 455 papers were assessed and an amount of 42 showed a correlation between phase angle and mortality.
Conclusions
Phase angle seems to be a good indicator for mortality in many clinical situations and can be used in screening individuals prone to this outcome.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbosa-Silva MCG, Barros AJD. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in clinical practice: a new perspective on its use beyond body composition equations. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2005;8:311–7.
Lee S, Gallagher D. Assessment methods in human body composition. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2009;11:566–72.
Kyle UG, Bosaeus I, Lorenzo A, Deurenberg P, Elia M, Manuel Gómez J, et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—part II: utilization in clinical practice. Clin Nutr. 2004;23:1430–53.
Llames L, Baldomero V, Iglesias ML, Rodota LP. Valores del ángulo de fase por bioimpedancia eléctrica; estado nutricional y valor prognóstico. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28:286–95.
Selberg O, Selberg D. Norms and correlates of bioimpedance phase angle in healthy human subjects, hospitalized patients, and patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2002;86:509–16.
Gupta D, Lammersfeld CA, Vashi PG, King J, Dahlk SL, Grutsch JF, et al. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle in clinical practice: implications for prognosis in stage IIIB and IV non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:1–6.
Pileggi VN, Scalize ARH, Camelo JS, Phase angle andWorld Health Organization. criteria for the assessment of nutritional status in children with osteogenesis imperfecta. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2016;34:484–8.
Lukaski HC, Kyle UG, Kondrup J. Assessment of adult malnutrition and prognosis with bioelectrical impedance analysis: phase angle and impedance ratio. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017;20:330–9.
Fernandes SA, de Mattos AA, Tovo CV, Marroni CA. Nutritional evaluation in cirrhosis: emphasis on the phase angle. World J Hepatol. 2016;8:1205–11.
Beberashvili I, Azar A, Sinuani I, Kadoshi H, Shapiro G, Feldman L, et al. Longitudinal changes in bioimpedance phase angle reflect inverse changes in serum IL-6 levels in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Nutrition. 2014;30:297–304.
Norman K, Stobäus N, Pirlich N, Bosy-Westphal M, Bioelectrical A. phase angle and impedance vector analysis - clinical relevance and applicability of impedance parameters. Clin Nutr. 2012;31:854–61.
Norman K, Wirth R, Neubauer M, Eckardt R, Stobäus N. The bioimpedance phase angle predicts low muscle strength impaired quality of life, and increased mortality in old patients with cancer. J Am Med. 2015;16:e17–22.
Beberashivili I, Azar A, Sinuani I, Shapiro G, Feldman L, Stav K, et al. Bioimpedance phase angle predicts muscle function, quality of life and clinical outcome in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014;68:683–9.
Alves FD, Souza GC, Clausell N, Biolo A. Prognostic role of phase angle in hospitalized patients with acute decompensated heart failure. Nutrition. 2016;35:1530–4.
Schwenk A, Beisenherz A, Romer K, Kremer G, Salzberger B, Elia M. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis remains an independent predictive marker in HIV-infected patients in the era of highly active antiretroviral treatment. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:496–501.
Robeau V, Blasco H, Maillot F, Corcia P, Praline J. Nutritional assessment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in routine practice: value of weighing and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Muscle Nerve. 2015;51:479–84.
Hui D, Bansal S, Morgado M, Dev R, Chisholm G, Bruera E. Phase angle for prognostication of survival in patients with advanced cancer: preliminary findings. Cancer. 2014;120:2207–14.
Visser M, Van Venrooij LM, Wanders DC, de Vos R, Wisselink W, van Leeuwen PA, et al. The bioelectrical impedance phase angle as indicator of undernutrition and adverse clinical outcome in cardiac surgical patients. Clin Nutr. 2012;31:981–6.
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology - a proposal for reporting. JAMA. 2000;283:2008–12.
Wells GA, Shea B, O’Connell D. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 9 Dec 2016.
Rodrigues R, Oliveira B, Pedroso S, Azevedo JN, Azevedo P, Oliveira JP, et al. Predictive value of bioelectrical impedance analysis parameters in the mortality of patients on hemodialysis. Port J Nephrol Hypert. 2014;28:309–17.
Colín-Ramírez E, Castillo-Martínez L, Orea-Tejeda A, Vázquez-Durán M, Rodríguez AE, Keirns-Davis C. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic marker in chronic heart failure. Nutrition. 2012;28:901–5.
Lee Y, Kwon O, Shin CS, Lee SM. Use of bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of nutritional status in critically ill patients. Clin Nutr Res. 2015;4:32–40.
Büntzel J, Krauß T, Büntzel H, Küttner K, Fröhlich D, Oehler W, et al. Nutritional parameters for patients with head and neck cancer. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:2119–24.
Gupta D, Lammersfeld CA, Burrows JL, Dahlk SL, Vashi PG, Grutsch JF, et al. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle in clinical practice: implications for prognosis in advanced colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:1634–8.
Gupta D, Lis CG, Dahlk SL, Vashi PG, Grutsch JF, Lammersfeld CA. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic indicator advanced pancreatic cancer. Br J Nutr. 2004;92:957–62.
Gupta D, Lammersfeld CA, Vashi PG, King J, Dahlk SL, Grutsch JF, et al. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:249.
Hui D, Dev R, Pimental L, Park M, Cerana MA, Liu D, et al. Association between multi-frequency phase angle and survival in patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2017;53:571–7.
Generoso SV, Rodrigues AM, Maia F, Armani B, Costa AC, Jansen AK, et al. Phase angle as prognostic indicator in surgical cancer patients. Nutr Cancer. 2014;33:53.
Skowronek P, Kuhberg M, Richter R, Chen F, Braicu EI, Sehouli J. Preoperative malnutrition as criteria for tumor resection completeness and overall survival in patients with ovarian cancer: results of a prospective study. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:e16532.
Abad S, Sotomayor G, Vega A, Pérez de José A, Verdalles U, Jofré R, et al. The phase angle of the electrical impedance is a predictor of long-term survival in dialysis patients. Nefrologia. 2011;31:670–6.
Caravaca F, Martínez del Viejo C, Villa J, Gallardo RM, Ferreira F. Hydration status assessment by multi-frequency bioimpedance in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Nefrologia. 2011;31:537–44.
Chertow GM, Jacobs DO, Lazarus MJ, Lew NL, Lowrie EG. Phase angle predicts survival in hemodialysis patients. J Ren Nutr. 1997;7:204–7.
Di Iorio B, Cillo N, Cirillo M, De Santo NG. Charlson comorbidity index is a predictor of outcomes in incident hemodialysis patients and correlates with phase angle and hospitalization. Int J Artif Organs. 2004;27:330–6.
Dumler F. A low bioimpedance phase angle predicts a higher mortality and lower nutritional status in chronic dialysis patients. J Phys Conf Ser. 2010;224:012104.
Koh K, Wong H, Go K, Morad Z. Normalized bioimpedance indices are better predictors of outcome in perioneal dialysis patients. Perit Dial Int. 2011;31:574–82.
Maggiore Q, Nigrelli S, Ciccarelli C, Grimaldi C, Rossi GA, Michelassi C. Nutritional and prognostic correlates of bioimpedance indexes in hemodialysis patients. Kidney Int. 1996;50:2103–8.
Mushnick R, Fein PA, Mittman N, Goel N, Chattopadhyay J, Avram MM. Relationship of bioelectrical impedance parameters to nutrition and survival in peritoneal dialysis patients. Kidney Int Suppl. 2003;87:53–56.
Pupim LB, Caglar K, Hakim RM, Shyr Y, Ikizler TA. Uremic malnutrition is a predictor of death independent of inflammatory status. Kidney Int. 2004;66:2054–60.
Segall L, Mardare N, Ungureanu S, Busuioc M, Nistor I, Enache R, et al. Nutritional status evaluation and survival in haemodialysis patients in one centre from Romania. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24:2536–40.
Doesch C, Suselbeck T, Leweling H, Fluechter S, Haghi D, Schoenberg SO, et al. Bioimpedance analysis parameters and epicardial adipose tissue assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging in patients with heart failure. Obesity. 2010;18:2326–32.
Berbigier MC, Pasinato VF, Rubin BA, Moraes RB, Perry ID. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle in septic patients admitted to intensive care units. Rev Bras Ter Intens. 2013;25:25–31.
Da Silva TK, Berbigier MC, Rubin BA, Moraes RB, Souza GC, Perry ID. Phase angle as a prognostic marker in patients with critical illness. Nutr Clin Pract. 2015;30:261–5.
Díaz-De Los Santos M, Cieza J, Valenzuela R. Correlación entre índices de bioimpedancia elétrica y score Apache II en pacientes con shock séptico. Rev Med Hered. 2011;21:111–7.
Thibault R, Makhlouf A, Mulliez A, Gonzalez MC, Kekstas G, Kozjek N, et al. Fat-free mass at admission predicts 28-day mortality in intensive care unit patients: the international prospective observational study Phase Angle Project. Intensive Care Med. 2016;42:1445–53.
Davis MP, Yavuzsen T, Khoshknabi D, Kirkova J, Walsh D, Lasheen W, et al. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle changes during hydration and prognosis in advanced cancer. Am J Hosp Palliat Med. 2009;26:180–6.
Lee SY, Lee YJ, Yang J, Kim CM, Choi WS. The association between phase angle of bioelectrical Impedance analysis and survival time in advanced cancer patients: preliminary study. Korean J Fam Med. 2014;35:251–6.
Santarpia L, Marra M, Montagnese C, Alfonsi L, Pasanisi F, Contaldo F. Prognostic significance of bioelectrical impedance phase angle in advanced cancer: preliminary observations. Nutrition. 2009;25:930–1.
Martin L, Lagergren J, Blomberg J, Johar A, Bosaeus I, Lagergren P. Phase angle as a prognostic marker after percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) in a prospective cohort study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2016;51:1013–6.
Sánchez-Lara K, Turcott JG, Juárez E, Guevara P, Núñez-Valencia C, Oñate-Ocaña LF, et al. Association of nutrition parameters including bioelectrical impedance and systemic inflammatory response with quality of life and prognosis in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a prospective study. Nutr Cancer. 2012;64:526–34.
Toso S, Piccoli A, Gusella M, Menon D, Bononi A, Crepaldi G, et al. Altered tissue electric properties in lung cancer patients as detected by bioelectric impedance vector analysis. Nutrition. 2000;16:120–4.
Desport JC, Marin B, Funalot B, Preux PM, Couratier P. Phase angle is a prognostic factor for survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2008;9:273–8.
Krause L, Becker MO, Brueckner CS, Bellinghausen CJ, Becker C, Schneider U, et al. Nutritional status as marker for disease activity and severity predicting mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:1951–7.
Marin B, Desport JC, Kajeu P, Jesus P, Nicolaud B, Nicol M, et al. Alteration of nutritional status at diagnosis is a prognostic factor for survival of ALS patients. J Neurol Psychiatry. 2011;82:628–34.
Belarmino G, Gonzalez MC, Torrinhas RS, Sala P, Andraus W, D’Albuquerque LA, et al. Phase angle obtained by bioelectrical impedance analysis independently predicts mortality in patients with cirrhosis. World J Hepatol. 2017;9:401–8.
Peres WAF, Lento DF, Baluz K, Ramalho A. Phase angle as a nutritional evaluation tool in all stages of chronic liver disease. Nutr Hosp. 2012;27:2072–8.
Ruiz-Margáin A, Marcias-Rodrigues RU, Rios-Torres SL, Espinosa-Cuevas A, Duarte-Rojo A, Torre A. Phase angle as a nutritional marker related to prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis: a cut-off value for Mexican population. Gastroenterol. 2014;146:931.
Maddocks M, Kon SS, Jones SE. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle relates to function, disease severity and prognosis in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Nutr. 2015;34:1245–50.
Ott M, Fischer H, Polat H, Helm EB, Frenz M, Caspary WF, et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis as a predictor of survival in patients with human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr Hum Retrovirol. 1995;9:20–5.
Baumgartner RN, Chumlea WC, Roche AF. Bioelectric impedance phase angle and body composition. Am J Clin Nutr. 1988;48:16–23.
Ortiz CL, Montejo JC, Jiménez FJ, Lopez JM, García de Lorenzo AM, Grau TC, et al. Recommendations for nutritional assessment and specialized nutritional support of critically ill patients. Nutr Hosp. 2005;20:1–3.
American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.) Board of Directors. Guidelines for the use of parenteral andenteral nutrition in adult and pediatric patients [erratum in JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002;26:144]. JPEN J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2002;26:1SA–138SA.
Chio A, Calvo A, Moglia C, Mazzini L, Mora G. Phenotypic heterogeneity of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2011;82:740–6.
Schmidt K, Martinez-Gamboa L, Meier S, Witt C, Meisel C, Hanitsch LG, et al. Bronchoalveoloar lavage fluid cytokines and chemokines as markers and predictors for the outcome of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R111.
Bosy-Westphal A, Danielzik S, Dörhöfer RP, Later W, Wiese S, Müller MJ. Phase angle from bioelectrical impedance analysis: population reference values by age, sex, and body mass index. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2006;30:309–16.
Kyle UG, Soundar EP, Genton L, Pichard C. Can phase angle determined by bioelectrical impedance analysis assess nutritional risk? A comparison between healthy and hospitalized subjects. Clin Nutr. 2012;31:875–81.
Kuchnia AJ, Teigen LM, Cole AJ, Mulasi U, Gonzalez MC, Heymsfield SB, et al. Phase angle and impedance ratio: reference cut-points from the United States National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1999-2004 from bioimpedance spectroscopy data. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2016;41:1310–5.
Mialich MS, Sicchieri JF, Junior AA. Analysis of body composition: a critical review of the use of bioelectrical impedance analysis. Int J Clin Nutr. 2014;2:1–10.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre.
Author contributions
L.M.G. and F.D.A. designed the study, collected and analyzed the data, interpreted the data, wrote, read, and approved the final version of the article. I.S.P., G.C.S., and N.C. contributed to the work conception and design, interpreted and analyzed the data, contributed to the writing of the article, revised critically, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). and Fundo de Incentivo a Pesquisa (FIPE).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garlini, L.M., Alves, F.D., Ceretta, L.B. et al. Phase angle and mortality: a systematic review. Eur J Clin Nutr 73, 495–508 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0159-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0159-1
This article is cited by
-
Association of resting energy expenditure with phase angle in hospitalized older patients: a cross-sectional analysis
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024)
-
Is phase angle associated with visceral adiposity and cardiometabolic risk in cardiology outpatients?
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024)
-
Phase angle and anthropometric indicators of cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2024)
-
The use of phase angle in patients with digestive and liver diseases
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders (2023)
-
Association of 24-h movement behaviors with phase angle in community-dwelling older adults: a compositional data analysis
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research (2023)