Abstract
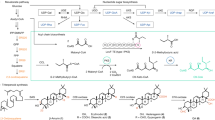
The crude extract of the Arctic fungus Phoma muscivora CPCC 401424 displayed anti-influenza A virus activities which led us to investigated their secondary metabolites. Four new chromone derivatives, phomarcticones A–D (1–4) and five known chromone analogs (5–9) have been isolated from Arctic fungus Phoma muscivora CPCC 401424. Compounds 3 and 4 possess rare sulfoxide groups in chromone derivatives. Their structures and absolute configurations were elucidated by extensive analysis of spectroscopic data, electronic circular dichroism, and comparison with reported data. Compounds 3, 7, and 9 showed significant anti-influenza A virus activities with the IC50 values of 24.4, 4.2, and 2.7 μM, respectively.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schueffler A, Anke T. Fungal natural products in research and development. Nat Prod Rep. 2014;31:1425–48.
El-Elimat T, Raja HA, Figueroa M, Al Sharie AH, Bunch RL, Oberlies NH. Freshwater fungi as a source of chemical diversity: a review. J Nat Prod. 2021;84:898–916.
Boerema GH, de Gruyter J, Noordeloos ME, Hamers MEC. Phoma identification manual, 1st edn. Wallingford, UK: CABI Publishing; 2004.
Rai M, Gade A, Zimowska B, Ingle AP, Ingle P. Marine-derived Phoma-the gold mine of bioactive compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;102:9053–66.
Rai M, Zimowska B, Kövics GJ Phoma: Diversity, Taxonomy, Bioactivities, and Nanotechnology. Springer, 2022, pp 205–19.
Rai M, Zimowska B, Gade A, Ingle P. Promising antimicrobials from Phoma spp.: progress and prospects. AMB Express. 2022;12:60.
Wang LW, Xu BG, Wang JY, Su ZZ, Lin FC, Zhang CL, et al. Bioactive metabolites from Phoma species, an endophytic fungus from the Chinese medicinal plant Arisaema erubescens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012;93:1231–9.
Mohamed IE, Gross H, Pontius A, Kehraus S, Krich A, Kelter G, et al. Epoxyphomalin A and B, prenylated polyketides with potent cytotoxicity from the marine-derived fungus Phoma sp. Org Lett. 2009;11:5014–7.
Kong F, Wang Y, Liu P, Dong T, Zhu W. Thiodiketopiperazines from the marine-derived fungus Phoma sp. OUCMDZ-1847. J Nat Prod. 2014;77:132–7.
Peng X, He Y, Gao Y, Duan F, Chen J, Ruan H. Cytochalasins from an endophytic fungus Phoma multirostrata XJ-2-1 with cell cycle arrest and TRAIL-resistance-overcoming activities. Bioorg Chem. 2020;104:104317.
Shi T, Qi J, Shao CL, Zhao DL, Hou XM, Wang CY. Bioactive diphenyl ethers and isocoumarin derivatives from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Mar Drugs. 2017;15:146.
Arora P, Wani ZA, Nalli Y, Ali A, Riyaz-UI-Hassan S. Antimicrobial potential of thiodiketopiperazine derivatives produced by Phoma sp., an endophyte of Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn. Micro Ecol. 2016;72:802–12.
Lee MS, Wang SW, Wang GJ, Pang KL, Lee CK, Kuo YH, et al. Angiogenesis inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents from Phoma sp. NTOU4195. J Nat Prod. 2016;79:2983–90.
Peng X, Duan F, He Y, Gao Y, Chen J, Chang J, et al. Ergocytochalasin A, a polycyclic merocytochalasan from an endophytic fungus Phoma multirostrata XJ-2-1. Org Biomol Chem 2020;18:4056–62.
Tan Y, Wang YD, Li Q, Xing XK, Niu SB, Sun BD, et al. Undescribed diphenyl ethers betaethrins A–I from a desert plant endophytic strain of the fungus Phoma betae A.B. Frank (Didymellaceae). Phytochemistry 2021;201:113264.
Gubiani JR, Wijeratne EMK, Shi T, Arauji AR, Arnold AE, Chapman E, et al. An epigenetic modifier induces production of (10’S)-verruculide B, an inhibitor of protein tyrosine phosphatases by Phoma sp. nov. LG0217, a fungal endophyte of Parkinsonia microphylla. Bioorg Med Chem. 2017;25:1860–6.
Cimmino A, Andolfi A, Zonno MC, Avolio F, Berestetskiy A, Vurro M, et al. Chenopodolans A–C: phytotoxic furopyrans produced by Phoma chenopodiicola, a fungal pathogen of Chenopodium album. Phytochemsitry. 2013;96:208–13.
Zhang D, Wang Y, Hu X, Wang X, Li L, Gu G, et al. Cyclic and linear thiopeptides from soil-derived Streptomyces sp. CPCC 203702 with antiviral and antibacterial activities. Chin J Chem. 2021;39:3277–84.
Gu G, Zhang T, Zhao J, Zhao W, Tang Y, Wang L, et al. New dimeric chromanone derivatives from the mutant strains of Penicillium oxalicum and their bioactivities. RSC Adv. 2022;12:22377–84.
Wang L, Huang Y, Zhang L, Liu Z, Liu W, Xu H, et al. Structures and absolute configurations of phomalones from the coral-associated fungus Parengyodontium album sp. SCSIO 40430. Org Biomol Chem. 2021;19:6030–7.
Chandler IM, Mclntyre CR, Simpson TJ. Biosynthesis of LL-D253α, a polyketide chromanone metabolite of Phoma pigmentivora: incorporation of 13C, 2H and l8O labelled precursors. J Chem Soc Perkin Trans 1992;18:2285–93.
McGahren WJ, Ellestad GA, Morton GO, Kunstmann MP. Structure of a new fungal lactone, LL-P880, from an unidentified Penicillium sp. J Org Chem. 1972;37:1636–9.
Kim JW, Ko W, Kim E, Kim GS, Hwang GJ, Son S, et al. Anti-inflammatory phomalichenones from an endolichenic fungus Phoma sp. J Antibiot. 2018;71:753–6.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82073744), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (2021-I2M-1-055), the Non-profit Central Research Institute Fund of CAMS (2021-PT350-001), and the National Microbial Resource Center (NMRC-2021-3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, Y., Gu, G., Wang, J. et al. Four new chromone derivatives from the Arctic fungus Phoma muscivora CPCC 401424 and their antiviral activities. J Antibiot 76, 88–92 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00588-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-022-00588-6