Abstract
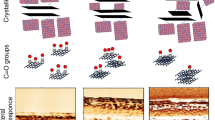
The results of comprehensive research on the thermal behavior and molecular and crystalline structures of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHB-HV) films of different thicknesses, their molecular weights (Mw) and 3-hydroxyvalerate (3-HV) contents are reported. Increasing film thickness from 30 to 100 µm resulted in an isotropic crystal orientation, reducing the crystallite size of the orthorhombic α-phase in the b direction from 22 to 17 nm and increasing the degree of crystallinity of the PHB films without affecting their thermal behavior. Furthermore, despite resulting in the same degree of crystallinity and roughness, an ~8-fold decrease in PHB Mw from 803 kDa to 102 kDa resulted in a decreased number of piezoactive domains. The addition of 5.9% 3-HV resulted in anisotropy in the PHB crystalline structure and increased D(020) from 19 nm to 24 nm. Additionally, a further increase in the 3-HV content to 17.5% in the PHB-HV films led to a decrease in the melting temperature and a decrease in the degree of crystallinity from 57% to 23%, which resulted in the absence of local piezoresponse. Notably, the decrease in the Mw of PHB-HV (~17%) from 1177 kDa to 756 kDa resulted in an increase in the degree of crystallinity from 23% to 32%. Moreover, the PHB-HV films became smoother with increasing 3-HV content.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mohandas SP, Balan L, Gopi J, Anoop B, Mohan PS, Philip R, et al. Biocompatibility of polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate films generated from Bacillus cereus MCCB 281 for medical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;176:244–52.
Zhuikov V, Bonartsev A, Bagrov D, Yakovlev S, Myshkina V, Makhina T, et al. Mechanics and surface ultrastructure changes of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) films during enzymatic degradation in pancreatic lipase solution. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst. 2017;648:236–43.
Vieyra H, Juárez E, López UF, Morales AG, Torres M. Cytotoxicity and biocompatibility of biomaterials based in polyhydroxybutyrate reinforced with cellulose nanowhiskers determined in human peripheral leukocytes. Biomed Mater. 2018;13:045011.
Shishatskaya EI, Voinova ON, Goreva AV, Mogilnaya OA, Volova TG. Biocompatibility of polyhydroxybutyrate microspheres: in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2008;19:2493–502.
Altaee N, El-Hiti GA, Fahdil A, Sudesh K, Yousif E. Biodegradation of different formulations of polyhydroxybutyrate films in soil. SpringerPlus. 2016;5:1–12.
Meischel M, Eichler J, Martinelli E, Karr U, Weigel J, Schmöller G, et al. Adhesive strength of bone-implant interfaces and in-vivo degradation of PHB composites for load-bearing applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;53:104–18.
Koller M. Biodegradable and biocompatible polyhydroxy-alkanoates (PHA): Auspicious microbial macromolecules for pharmaceutical and therapeutic applications. Molecules. 2018;23:362.
Zhuikov VA, Zhuikova YV, Makhina TK, Myshkina VL, Rusakov A, Useinov A, et al. Comparative structure-property characterization of poly (3-Hydroxybutyrate-Co-3-Hydroxyvalerate) s films under hydrolytic and enzymatic degradation: Finding a transition point in 3-hydroxyvalerate content. Polymers. 2020;12:728.
Zviagin AS, Chernozem RV, Surmeneva MA, Pyeon M, Frank M, Ludwig T, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric response of hybrid biodegradable 3D poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds coated with hydrothermally deposited ZnO for biomedical applications. Eur Polym J. 2019;117:272–9.
Chernozem R, Guselnikova O, Surmeneva M, Postnikov P, Abalymov A, Parakhonskiy B, et al. Diazonium chemistry surface treatment of piezoelectric polyhydroxybutyrate scaffolds for enhanced osteoblastic cell growth, Eur. Polym J. 2020;20:100758.
Chernozem R, Surmeneva M, Shkarina S, Loza K, Epple M, Ulbricht M, et al. Piezoelectric 3-D fibrous poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)-based scaffolds ultrasound-mineralized with calcium carbonate for bone tissue engineering: inorganic phase formation, osteoblast cell adhesion, and proliferation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:19522–33.
Castellano D, Sanchis A, Blanes M, Pérez del Caz MD, Ruiz‐Saurí A, Piquer‐Gil M, et al. Electrospun poly (hydroxybutyrate) scaffolds promote engraftment of human skin equivalents via macrophage M2 polarization and angiogenesis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12:e983–94.
Castellano D, Blanes M, Marco B, Cerrada I, Ruiz-Saurí A, Pelacho B, et al. A comparison of electrospun polymers reveals poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) fiber as a superior scaffold for cardiac repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23:1479–90.
Gorodzha SN, Muslimov AR, Syromotina DS, Timin AS, Tcvetkov NY, Lepik KV, et al. A comparison study between electrospun polycaprolactone and piezoelectric poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B. 2017;160:48–59.
Young R, Terenghi G, Wiberg M. Poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB): a resorbable conduit for long-gap repair in peripheral nerves. Br J Surg. 2002;55:235–40.
Wang AC, Wu C, Pisignano D, Wang ZL, Persano L. Polymer nanogenerators: opportunities and challenges for large‐scale applications. J Appl Polym Sci. 2018;135:45674.
Huang NF, Lee RJ, Li S. Engineering of aligned skeletal muscle by micropatterning. Am J Transl Res. 2010;2:43.
Kumar S, Sharma M, Kumar A, Powar S, Vaish R. Rapid bacterial disinfection using low frequency piezocatalysis effect. J Ind Eng Chem. 2019;77:355–64.
Vatlin IS, Chernozem RV, Timin AS, Chernova AP, Plotnikov EV, Mukhortova YR, et al. Bacteriostatic effect of piezoelectric poly-3-hydroxybutyrate and polyvinylidene fluoride polymer films under ultrasound treatment. Polymers. 2020;12:240.
Raza ZA, Khalil S, Abid S. Recent progress in development and chemical modification of poly (hydroxybutyrate) based blends for potential medical applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;160:77–100.
Steinbüchel A, Debzi E-M, Marchessault RH, Timm A. Synthesis and production of poly (3-hydroxyvaleric acid) homopolyester by Chromobacterium violaceum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1993;39:443–9.
Köse GT, Kenar H, Hasırcı N, Hasırcı V. Macroporous poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) matrices for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2003;24:1949–58.
Valappil SP, Misra SK, Boccaccini AR, Roy I. Biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates, an overview of animal testing and in vivo responses. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2006;3:853–68.
Rossi S, Azghani AO, Omri A. Antimicrobial efficacy of a new antibiotic-loaded poly (hydroxybutyric-co-hydroxyvaleric acid) controlled release system. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;54:1013–8.
Leong YK, Show PL, Ooi CW, Ling TC, Lan JC-W. Current trends in polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) biosynthesis: insights from the recombinant Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol 2014;180:52–65.
Kunioka M, Tamaki A, Doi Y. Crystalline and thermal properties of bacterial copolyesters: poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules. 1989;22:694–7.
Napolitano S, Wübbenhorst M. Deviation from bulk behaviour in the cold crystallization kinetics of ultrathin films of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate). J Phys Condens Matter. 2007;19:205121.
Dai X, Li H, Ren Z, Russell TP, Yan S, Sun X. Confinement effects on the crystallization of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate). Macromolecules. 2018;51:5732–41.
Frank C, Rao V, Despotopoulou M, Pease R, Hinsberg W, Miller R, et al. Structure in thin and ultrathin spin-cast polymer films. Science. 1996;273:912–5.
Hong S-G, Hsu H-W, Ye M-T. Thermal properties and applications of low molecular weight polyhydroxybutyrate. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;111:1243–50.
Bonartsev A, Bonartseva G, Reshetov I, Kirpichnikov M, Shaitan K. Application of polyhydroxyalkanoates in medicine and the biological activity of natural poly (3-hydroxybutyrate). Acta Naturae. 2019;11:4–16.
Chernozem RV, Romanyuk KN, Grubova I, Chernozem PV, Surmeneva MA, Mukhortova YR, et al. Enhanced piezoresponse and surface electric potential of hybrid biodegradable polyhydroxybutyrate scaffolds functionalized with reduced graphene oxide for tissue engineering. Nano Energy. 2021;89:106473.
Cai Z, Xiong P, He S, Zhu C. Improved piezoelectric performances of highly orientated poly (β-hydroxybutyrate) electrospun nanofiber membrane scaffold blended with multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Mater Lett. 2019;240:213–6.
Bonartsev A, Bonartseva G, Makhina T, Myshkina V, Luchinina E, Livshits V, et al. New poly (3-hydroxybutyrate)-based systems for controlled release of dipyridamole and indomethacin. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2006;42:625–30.
Bonartsev A, Zharkova I, Yakovlev S, Myshkina V, Mahina T, Voinova V, et al. Biosynthesis of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) copolymers by Azotobacter chroococcum 7B: A precursor feeding strategy. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017;47:173–84.
Chen L, Wang M. Production and evaluation of biodegradable composites based on PHB–PHV copolymer. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2631–9.
Furukawa T, Sato H, Murakami R, Zhang J, Noda I, Ochiai S, et al. Raman microspectroscopy study of structure, dispersibility, and crystallinity of poly (hydroxybutyrate)/poly (l-lactic acid) blends. Polymer. 2006;47:3132–40.
Furukawa T, Sato H, Murakami R, Zhang J, Duan Y-X, Noda I, et al. Structure, dispersibility, and crystallinity of poly (hydroxybutyrate)/poly (L-lactic acid) blends studied by FT-IR microspectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Macromolecules. 2005;38:6445–54.
Sato H, Murakami R, Noda I, Ozaki Y. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy and quantum chemistry calculation studies of C–H⋯ O hydrogen bondings and thermal behavior of biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoate. J Mol Struct. 2005;744:35–46.
Phongtamrug S, Tashiro K. X-ray crystal structure analysis of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) β-Form and the proposition of a mechanism of the stress-induced α-to-β phase transition. Macromolecules. 2019;52:2995–3009.
Liu C, Noda I, Martin DC, Chase DB, Ni C, Rabolt JF. Growth of anisotropic single crystals of a random copolymer, poly [(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-(R)-3-hydroxyhexanoate] driven by cooperative–CH··· O H-bonding. Polymer. 2018;154:111–8.
Sun X, Tokuda A, Oji Y, Nakatani T, Tsuji H, Ozaki Y, et al. Effects of molar mass of poly (l-lactide acid) on the crystallization of poly [(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] in Their Ultrathin Blend Films. Macromolecules. 2012;45:2485–93.
Sato H, Ando Y, Dybal JI, Iwata T, Noda I, Ozaki Y. Crystal structures, thermal behaviors, and C− H··· O· C hydrogen bondings of poly (3-hydroxyvalerate) and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) studied by infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction. Macromolecules. 2008;41:4305–12.
Wellen RM, Rabello MS, Fechine GJ, Canedo EL. The melting behaviour of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) by DSC. Reproducibility study. Polym Test. 2013;32:215–20.
Gunaratne L, Shanks R. Melting and thermal history of poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) using step-scan DSC. Thermochim Acta. 2005;430:183–90.
Wang MM, Braun H, Meyer E, Zhu J. Morphogenesis and chain behaviors related to crystallization in ultrathin polymer films. World Sci Tech R D. 2006;28:5–18.
Anbukarasu P, Sauvageau D, Elias AL. Enzymatic degradation of dimensionally constrained polyhydroxybutyrate films. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2017;19:30021–30.
Reddy KR, Ogawa S, Sato H, Takahashi I, Ozaki Y. Evolution of intermediate and highly ordered crystalline states under spatial confinement in poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) ultrathin films. Macromolecules. 2016;49:4202–10.
Kossack W, Seidlitz A, Thurn-Albrecht T, Kremer F. Interface and confinement induced order and orientation in thin films of poly (ϵ-caprolactone). Macromolecules. 2016;49:3442–51.
Sato H, Murakami R, Padermshoke A, Hirose F, Senda K, Noda I, et al. Infrared spectroscopy studies of CH⊙⊙⊙ O hydrogen bondings and thermal behavior of biodegradable poly (hydroxyalkanoate). Macromolecules. 2004;37:7203–13.
van Drongelen M, Van Erp T, Peters G. Quantification of non-isothermal, multi-phase crystallization of isotactic polypropylene: The influence of cooling rate and pressure. Polymer. 2012;53:4758–69.
Hoshina H, Morisawa Y, Sato H, Minamide H, Noda I, Ozaki Y, et al. Polarization and temperature dependent spectra of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoate)s measured at terahertz frequencies. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2011;13:9173.
Hoshina H, Morisawa Y, Sato H, Kamiya A, Noda I, Ozaki Y, et al. Higher order conformation of poly(3-hydroxyalkanoates) studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Appl Phys Lett. 2010;96:101904.
Owen A, Heinzel J, Škrbić Ž, Divjaković V. Crystallization and melting behaviour of PHB and PHB/HV copolymer. Polymer. 1992;33:1563–7.
Sato H, Ando Y, Mitomo H, Ozaki Y. Infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction studies of thermal behavior and lamella structures of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)(P (HB-co-HV)) with PHB-type crystal structure and PHV-type crystal structure. Macromolecules. 2011;44:2829–37.
Choi Y-Y, Sharma P, Phatak C, Gosztola DJ, Liu Y, Lee J, et al. Enhancement of local piezoresponse in polymer ferroelectrics via nanoscale control of microstructure. ACS Nano. 2015;9:1809–19.
Jesse S, Guo S, Kumar A, Rodriguez B, Proksch R, Kalinin SV. Resolution theory, and static and frequency-dependent cross-talk in piezoresponse force microscopy. Nanotechnology. 2010;21:405703.
Bonartsev A, Voinova V, Bonartseva G. Poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) and human microbiota. Appl Biochem Microbiol. 2018;54:547–68.
Voinova V, Bonartseva G, Bonartsev A. Effect of poly (3-hydroxyalkanoates) as natural polymers on mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2019;11:764.
Manna SS, Ghanty C, Baindara P, Barik TK, Mandal SM. Electrochemical communication in biofilm of bacterial community. J Basic Microbiol. 2020;60:819–27.
Acknowledgements
This research was performed at Tomsk Polytechnic University within the framework of the Tomsk Polytechnic University Development Program (infrastructure provided for research activities) and was financially supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project number 20-63-47096, sample fabrication and characterization of their properties) and Ministry of Science and Higher Education (#075-15-2021-588 from 1.06.2021, piezoresponse study). RC, VS and RS acknowledge support from the German-Russian Interdisciplinary Science Center (G-risc) funded by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD). This work was developed within the scope of the project CICECO-Aveiro Institute of Materials, UIDB/50011/2020, UIDP/50011/2020 & LA/P/0006/2020, financed by national funds through the FCT/MEC (PIDDAC). We also acknowledge Alexey Rusakov and Alexey Useinov from the Federal State Budgetary Institution “Technological Institute for Superhard and Novel Carbon Materials” for their help in performing previous measurements of the Young’s modulus of the PHB and PHB-HV films by nanoindentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
41428_2022_662_MOESM1_ESM.docx
A comprehensive study on the structure and piezoelectric response of biodegradable polyhydroxybutyrate-based films for tissue engineering applications
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chernozem, R.V., Pariy, I.O., Pryadko, A. et al. A comprehensive study of the structure and piezoelectric response of biodegradable polyhydroxybutyrate-based films for tissue engineering applications. Polym J 54, 1225–1236 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00662-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-022-00662-8