Abstract
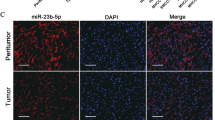
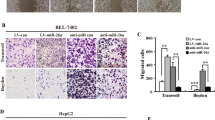
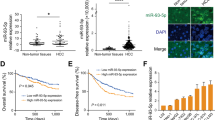
Due to the lack of early diagnostic and effective treatment modalities, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still the most lethal cancer with a high mortality on a global scale. Recent studies have highlighted the key roles of microRNAs (miRs) in HCC development. In the study, we attempted to investigate the potential role of miR-9-5p in the progression of HCC. Expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) and miR-9-5p was examined in HCC tissues collected from HCC patients and cell lines. The proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis of HCC cells, and levels of oxygen consumption rate, extracellular acidification rate and reactive oxygen species (ROS) as well as the tumorigenicity of transfected cells in vivo were measured after gain- and loss-of-function experiments in HCC cells. It was revealed that miR-9-5p was upregulated, while PDK4 was poorly expressed in HCC tissues and cells, associating with a poor prognosis of HCC patients. miR-9-5p directly targeted PDK4 and could downregulate its expression, thus leading to promoted cell proliferation, invasion and migration, enhanced mitochondrial activity and energy metabolism, and suppressed apoptosis in HCC cells, along with increased tumorigenicity in mouse xenograft models. Altogether, miR-9-5p facilitated mitochondrial energy metabolism of HCC cells by downregulating PDK4, promoting the development of HCC. miR-9-5p and PDK4 may serve as potential therapeutic targets for preventing recurrence and metastasis of HCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerbes A, Zoulim F, Tilg H, Dufour JF, Bruix J, Paradis V, et al. Gut roundtable meeting paper: selected recent advances in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut. 2018;67:380–8.
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424.
Kulik L, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019;156:477–91.e1.
Kon S, Ishibashi K, Katoh H, Kitamoto S, Shirai T, Tanaka S, et al. Cell competition with normal epithelial cells promotes apical extrusion of transformed cells through metabolic changes. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:530–41.
Wu J, Zhao Y, Park YK, Lee JY, Gao L, Zhao J, et al. Loss of PDK4 switches the hepatic NF-kappaB/TNF pathway from pro-survival to pro-apoptosis. Hepatology 2018;68:1111–24.
Choiniere J, Wu J, Wang L. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 deficiency results in expedited cellular proliferation through E2F1-mediated increase of cyclins. Mol Pharm. 2017;91:189–96.
Lee SJ, Jeong JY, Oh CJ, Park S, Kim JY, Kim HJ, et al. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 promotes vascular calcification via SMAD1/5/8 phosphorylation. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16577.
Li G, Wu F, Yang H, Deng X, Yuan Y. MiR-9-5p promotes cell growth and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer through the repression of TGFBR2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;96:1170–8.
Chen L, Hu W, Li G, Guo Y, Wan Z, Yu J. Inhibition of miR-9-5p suppresses prostate cancer progress by targeting StarD13. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:20.
Liu Z, Chen JY, Zhong Y, Xie L, Li JS. lncRNA MEG3 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by sponging miR-9-5p to upregulate SOX11. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2019;52:e8631.
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi B, et al. UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 2017;19:649–58.
Tang B, Liang X, Tang F, Zhang J, Zeng S, Jin S, et al. Expression of USP22 and Survivin is an indicator of malignant behavior in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2015;47:2208–16.
Vasuri F, Visani M, Acquaviva G, Brand T, Fiorentino M, Pession A, et al. Role of microRNAs in the main molecular pathways of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24:2647–60.
Huang S, He X. The role of microRNAs in liver cancer progression. Br J Cancer. 2011;104:235–40.
Koens L, Qin Y, Leung WY, Corver WE, Jansen PM, Willemze R, et al. MicroRNA profiling of primary cutaneous large B-cell lymphomas. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e82471.
Yang C, Wang S, Ruan H, Li B, Cheng Z, He J, et al. Downregulation of PDK4 increases lipogenesis and associates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2019;10:918–26.
Han H, Li W, Shen H, Zhang J, Zhu Y, Li Y. microRNA-129-5p, a c-Myc negative target, affects hepatocellular carcinoma progression by blocking the Warburg effect. J Mol Cell Biol. 2016;8:400–10.
Wang M, Gao Q, Chen Y, Li Z, Yue L, Cao Y. PAK4, a target of miR-9-5p, promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019;24:58.
Drakaki A, Hatziapostolou M, Polytarchou C, Vorvis C, Poultsides GA, Souglakos J, et al. Functional microRNA high throughput screening reveals miR-9 as a central regulator of liver oncogenesis by affecting the PPARA-CDH1 pathway. BMC Cancer. 2015;15:542.
Cai K, Li T, Guo L, Guo H, Zhu W, Yan L, et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00467 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression by modulating miR-9-5p/PPARA expression. Open Biol. 2019;9:190074.
Grassian AR, Metallo CM, Coloff JL, Stephanopoulos G, Brugge JS. Erk regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase flux through PDK4 modulates cell proliferation. Genes Dev. 2011;25:1716–33.
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Geng L, Yi H, Huo W, Talmon G, et al. Transforming growth factor beta mediates drug resistance by regulating the expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 in colorectal cancer. J Biol Chem. 2016;291:17405–16.
Wang W, Zhu M, Xu Z, Li W, Dong X, Chen Y, et al. Ropivacaine promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through damaging mitochondria and activating caspase-3 activity. Biol Res. 2019;52:36.
Ma WQ, Han XQ, Wang Y, Wang X, Zhu Y, Liu NF. Nepsilon-carboxymethyl-lysine promotes calcium deposition in VSMCs via intracellular oxidative stress-induced PDK4 activation and alters glucose metabolism. Oncotarget 2017;8:112841–54.
Zhu H, Xue H, Jin QH, Guo J, Chen YD. MiR-138 protects cardiac cells against hypoxia through modulation of glucose metabolism by targetting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1. Biosci Rep. 2017;37: BSR20170296:
Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Ke B, Wan L, Wang H, Ye J. Induction of posttranslational modifications of mitochondrial proteins by ATP contributes to negative regulation of mitochondrial function. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0150454.
Xu W, Li L, Sun J, Zhu S, Yan Z, Gao L, et al. Putrescine delays postovulatory aging of mouse oocytes by upregulating PDK4 expression and improving mitochondrial activity. Aging. 2018;10:4093–106.
Li G, Li M, Hu J, Lei R, Xiong H, Ji H, et al. The microRNA-182-PDK4 axis regulates lung tumorigenesis by modulating pyruvate dehydrogenase and lipogenesis. Oncogene 2017;36:989–98.
Kim MY, Koh DI, Choi WI, Jeon BN, Jeong DY, Kim KS, et al. ZBTB2 increases PDK4 expression by transcriptional repression of RelA/p65. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:1609–25.
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere appreciation to our colleagues for their valuable suggestions on this study.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82060856) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Grant No. 2020JJA140194).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, T., Ning, X., Zhao, H. et al. microRNA-9-5p regulates the mitochondrial function of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through suppressing PDK4. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 706–718 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00253-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00253-w
This article is cited by
-
Non-coding RNAs regulating mitochondrial function in cardiovascular diseases
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
MicroRNA-mediated reprogramming of glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism in cancer
Genome Instability & Disease (2022)