Abstract
Background
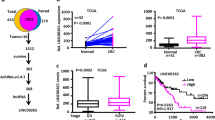
Circβ-catenin, our first reported circRNA, has been reported to mediate tumorigenesis in various cancers. However, its biological functions and underlying mechanisms in colorectal cancer (CRC) remain unknown.
Methods
The qRT-PCR examination was used to detect the expression of circβ-catenin, miR-197-3p, and CTNND1 in cells and human tissues. Western blot was conducted to detect the protein expression levels. The biological function of circβ-catenin was verified by MTT, colony formation, wound healing, and transwell assays. The in vivo effects of circβ-catenin were verified by nude mice xenograft and metastasis models. The regulatory network of circβ-catenin/miR-197-3p/CTNND1 was confirmed via dual-luciferase reporter and RIP assays.
Results
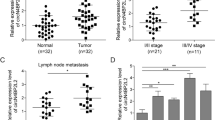
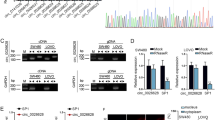
In the present study, circβ-catenin was found to promote CRC cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, circβ-catenin served as miRNA decoy to directly bind to miR-197-3p, then antagonized the repression of the target gene CTNND1, and eventually promoted the malignant phenotype of CRC. More interestingly, the inverted repeated Alu pairs termed AluJb1/2 and AluY facilitated the biogenesis of circβ-catenin, which could be partially reversed by EIF4A3 binding to Alu element AluJb2.
Conclusions
Our findings illustrated a novel mechanism of circβ-catenin in modulating CRC tumorigenesis and metastasis, which provides a potential therapeutic target for CRC patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xi Y, Xu P. Global colorectal cancer burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol. 2021;14:101174.
Wang Y, Liu J, Ma J, Sun T, Zhou Q, Wang W, et al. Exosomal circRNAs: biogenesis, effect and application in human diseases. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:116.
Arnold M, Sierra MS, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global patterns and trends in colorectal cancer incidence and mortality. Gut. 2017;66:683–91.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Du WW, Yang W, Liu E, Yang Z, Dhaliwal P, Yang BB. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44:2846–58.
Abdelmohsen K, Panda AC, Munk R, Grammatikakis I, Dudekula DB, De S, et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017;14:361–9.
Pamudurti NR, Bartok O, Jens M, Ashwal-Fluss R, Stottmeister C, Ruhe L, et al. Translation of CircRNAs. Mol Cell. 2017;66:9–21.e7.
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK, et al. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 2013;495:384–8.
Li P, Chen S, Chen H, Mo X, Li T, Shao Y, et al. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;444:132–6.
Meng S, Zhou H, Feng Z, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P, et al. CircRNA: functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:94.
Wilusz JE, Sharp PA. Molecular biology. A circuitous route to noncoding RNA. Science. 2013;340:440–1.
You X, Vlatkovic I, Babic A, Will T, Epstein I, Tushev G, et al. Neural circular RNAs are derived from synaptic genes and regulated by development and plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2015;18:603–10.
Liang WC, Wong CW, Liang PP, Shi M, Cao Y, Rao ST, et al. Translation of the circular RNA circbeta-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol. 2019;20:84.
Zhao W, Zhang Y, Zhu Y. Circular RNA circbeta-catenin aggravates the malignant phenotype of non-small-cell lung cancer via encoding a peptide. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35:e23900.
Wang S, Su T, Tong H, Zhou D, Ma F, Ding J, et al. Circbeta-catenin promotes tumor growth and Warburg effect of gallbladder cancer by regulating STMN1 expression. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7:233.
Wang S, Chao F, Zhang C, Han D, Xu G, Chen G. Circular RNA circPFKP promotes cell proliferation by activating IMPDH2 in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022;524:109–20.
Wang R, Zhang S, Chen X, Li N, Li J, Jia R, et al. EIF4A3-induced circular RNA MMP9 (circMMP9) acts as a sponge of miR-124 and promotes glioblastoma multiforme cell tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:166.
Zhao J, Jiang Y, Zhang H, Zhou J, Chen L, Li H, et al. The SRSF1/circATP5B/miR-185-5p/HOXB5 feedback loop regulates the proliferation of glioma stem cells via the IL6-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:134.
Zhou T, Wu L, Ma N, Tang F, Yu Z, Jiang Z, et al. SOX9-activated FARSA-AS1 predetermines cell growth, stemness, and metastasis in colorectal cancer through upregulating FARSA and SOX9. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:1071.
Kim ES, Choi JY, Hwang SJ, Bae IH. Hypermethylation of miR-205-5p by IR governs aggressiveness and metastasis via regulating Bcl-w and Src. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2019;14:450–64.
Zheng Q, Bao C, Guo W, Li S, Chen J, Chen B, et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat Commun. 2016;7:11215.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009;136:215–33.
Errichelli L, Dini Modigliani S, Laneve P, Colantoni A, Legnini I, Capauto D, et al. FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons. Nat Commun. 2017;8:14741.
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM, Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, et al. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell. 2015;160:1125–34.
Zhang XO, Wang HB, Zhang Y, Lu X, Chen LL, Yang L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell. 2014;159:134–47.
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC, Ji ZL. CircRNA: a novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer. 2018;25:1–7.
Zhu M, Dang Y, Yang Z, Liu Y, Zhang L, Xu Y, et al. Comprehensive RNA sequencing in Adenoma-cancer transition identified predictive biomarkers and therapeutic targets of human CRC. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;20:25–33.
Shi C-J, Li S-Y, Shen C-H, Pan F-F, Deng L-Q, Fu W-M, et al. Icariside II suppressed tumorigenesis by epigenetically regulating the circβ-catenin-Wnt/β-catenin axis in colorectal cancer. Bioorg Chem. 2022;124:105800.
Ma Z, Han C, Xia W, Wang S, Li X, Fang P, et al. circ5615 functions as a ceRNA to promote colorectal cancer progression by upregulating TNKS. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11:356.
Zhang J, Wang H, Wu K, Zhan F, Zeng H. Dysregulated circRNA_100876 contributes to proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting microRNA-516b (miR-516b). Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21:733–40.
Zhou N, Sun Z, Li N, Ge Y, Zhou J, Han Q, et al. miR‑197 promotes the invasion and migration of colorectal cancer by targeting insulin‑like growth factor‑binding protein 3. Oncol Rep. 2018;40:2710–21.
Wang W, Zhou L, Li Z, Lin G. Circ_0014130 is involved in the drug sensitivity of colorectal cancer through miR-197-3p/PFKFB3 axis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;37:908–18.
Wang M, Hu H, Wang Y, Huang Q, Huang R, Chen Y, et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 mediates 5-fluorouracil resistance by acting as a ceRNA of miR-197-3p in colorectal cancer. J Cancer. 2019;10:4603–13.
Yang T, Li H, Chen T, Ren H, Shi P, Chen M. LncRNA MALAT1 depressed chemo-sensitivity of NSCLC cells through directly functioning on miR-197-3p/p120 Catenin axis. Mol Cells. 2019;42:270–83.
Wu L, Cao M, Pu X, Liu B, Wang J. The sponge interaction between circular RNA and microRNA serves as a fast-evolving mechanism that suppresses non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) in humans. J Mol Evol. 2022;90:362–74.
Shen Q, He T, Yuan H. Hsa_circ_0002577 promotes endometrial carcinoma progression via regulating miR-197/CTNND1 axis and activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:1229–40.
Reynolds AB, Roesel DJ, Kanner SB, Parsons JT. Transformation-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel cellular protein in chicken cells expressing oncogenic variants of the avian cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989;9:629–38.
Park JI, Kim SW, Lyons JP, Ji H, Nguyen TT, Cho K, et al. Kaiso/p120-catenin and TCF/beta-catenin complexes coordinately regulate canonical Wnt gene targets. Dev Cell. 2005;8:843–54.
Hernandez-Martinez R, Ramkumar N, Anderson KV. p120-catenin regulates WNT signaling and EMT in the mouse embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019;116:16872–81.
Casagolda D, Del Valle-Perez B, Valls G, Lugilde E, Vinyoles M, Casado-Vela J, et al. A p120-catenin-CK1epsilon complex regulates Wnt signaling. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:2621–31.
Han L, Li Z, Jiang Y, Jiang Z, Tang L. SNHG29 regulates miR-223-3p/CTNND1 axis to promote glioblastoma progression via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019;19:345.
Yamada N, Noguchi S, Mori T, Naoe T, Maruo K, Akao Y. Tumor-suppressive microRNA-145 targets catenin delta-1 to regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in human colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2013;335:332–42.
Chan CC, Dostie J, Diem MD, Feng W, Mann M, Rappsilber J, et al. eIF4A3 is a novel component of the exon junction complex. RNA. 2004;10:200–9.
Liu Q, Dong H. EIF4A3-mediated hsa_circ_0088088 promotes the carcinogenesis of breast cancer by sponging miR-135-5p. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2021;35:e22909.
Xing W, Zhou PC, Zhang HY, Chen LM, Zhou YM, Cui XF, et al. Circular RNA circ_GLIS2 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis. Liver Int. 2022;42:682–95.
Funding
This work was supported by the Futian Healthcare Research Project (FTWS2023065), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82772526) and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2020A1515010961, 2021A1515012111).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HL and JZ conceived and designed the whole project and the experiments. LD, CS, SZ, and WL conducted the experiments. YX, YW, WF, WZ, and LD performed data analysis. CS and LD wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by Ethics Committee from Sun Yat-sen University approved this study, and patient consent was obtained before the samples were taken. The usage and treatment of animals were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Southern Medical University.
Consent to publish
All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, LQ., Shi, CJ., Zhou, ST. et al. EIF4A3-negatively driven circular RNA β-catenin (circβ-catenin) promotes colorectal cancer progression via miR-197-3p/CTNND1 regulatory axis. Br J Cancer (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02612-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-024-02612-y