Abstract
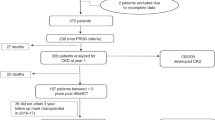
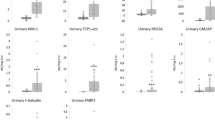
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Serum creatinine is an imprecise biomarker of AKI. We hypothesized that combining creatinine with serum cystatin C (cysC) and urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) more effectively characterizes AKI during the first 28 days of HSCT and better identifies patients at risk of adverse outcomes than creatinine alone. We prospectively assessed the type and severity of AKI in 80 consecutive allogeneic HSCT patients using weekly creatinine, cysC, and NGAL. We combined the biomarkers to define 7 Composite Types of AKI, including All Positive AKI (simultaneously detected creatinine, cysC, and NGAL AKI). Outcomes included renal replacement therapy and transplant-related mortality. In all, 75% of patients had AKI by at least one measure; 33% developed >1 type of AKI. Mild AKI often preceded Severe AKI. Patients with creatinine or NGAL AKI that were Severe or Repeated tended to have worse outcomes. The five patients with All Positive AKI had the highest rates of morbidity and mortality. AKI evaluation with creatinine, cysC, and NGAL provides a comprehensive profile of early AKI and narrowly identifies patients at highest risk of adverse outcomes, providing opportunities for early, impactful intervention.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Didsbury MS, Mackie FE, Kennedy SE. A systematic review of acute kidney injury in pediatric allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell recipients. Pediatr Transplant. 2015;19:460–70.
Laskin BL, Jodele S. Kidney disease in cancer survivors: focus on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Onco-Nephrol. 2017;1:163–9.
Hingorani S. Renal complications of hematopoietic-cell transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:2256–67.
Liu H, Li YF, Liu BC, Ding JH, Chen BA, Xu WL, et al. A multicenter, retrospective study of acute kidney injury in adult patients with nonmyeloablative hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010;45:153–8.
Parikh CR, McSweeney P, Schrier RW. Acute renal failure independently predicts mortality after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1999–2005.
Parikh CR, Sandmaier BM, Storb RF, Blume KG, Sahebi F, Maloney DG, et al. Acute renal failure after nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15:1868–76.
Zager RA, O’Quigley J, Zager BK, Alpers CE, Shulman HM, Gamelin LM, et al. Acute renal failure following bone marrow transplantation: a retrospective study of 272 patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 1989;13:210–6.
Hari P, Bagga A, Mahajan P, Lakshmy R. Effect of malnutrition on serum creatinine and cystatin C levels. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:1757–61.
Lagos-Arevalo P, Palijan A, Vertullo L, Devarajan P, Bennett M, Sabbisetti V, et al. Cystatin C in acute kidney injury diagnosis: early biomarker or alternative to serum creatinine? Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30:665–76.
Filler G, Lee M. Educational review: measurement of GFR in special populations. Pediatr Nephrol. 2018;33:2037–46.
Laskin BL, Nehus E, Goebel J, Furth S, Davies SM, Jodele S. Estimated versus measured glomerular filtration rate in children before hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20:2056–61.
Hazar V, Gungor O, Guven AG, Aydin F, Akbas H, Gungor F, et al. Renal function after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53:197–202.
Laskin BL, Goebel J, Davies SM, Khoury JC, Bleesing JJ, Mehta PA, et al. Early clinical indicators of transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in pediatric neuroblastoma patients undergoing auto-SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011;46:682–9.
Filler G, Bokenkamp A, Hofmann W, Le Bricon T, Martinez-Bru C, Grubb A. Cystatin C as a marker of GFR--history, indications, and future research. Clin Biochem. 2005;38:1–8.
Dharnidharka VR, Kwon C, Stevens G. Serum cystatin C is superior to serum creatinine as a marker of kidney function: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;40:221–6.
Laskin BL, Nehus E, Goebel J, Khoury JC, Davies SM, Jodele S. Cystatin C-estimated glomerular filtration rate in pediatric autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2012;18:1745–52.
Mishra J, Dent C, Tarabishi R, Mitsnefes MM, Ma Q, Kelly C, et al. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2005;365:1231–8.
Mishra J, Ma Q, Kelly C, Mitsnefes M, Mori K, Barasch J, et al. Kidney NGAL is a novel early marker of acute injury following transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol. 2006;21:856–63.
Hirsch R, Dent C, Pfriem H, Allen J, Beekman RH 3rd, Ma Q, et al. NGAL is an early predictive biomarker of contrast-induced nephropathy in children. Pediatr Nephrol. 2007;22:2089–95.
Wheeler DS, Devarajan P, Ma Q, Harmon K, Monaco M, Cvijanovich N, et al. Serum neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury in critically ill children with septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:1297–303.
Haase M, Devarajan P, Haase-Fielitz A, Bellomo R, Cruz DN, Wagener G, et al. The outcome of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin-positive subclinical acute kidney injury: a multicenter pooled analysis of prospective studies. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;57:1752–61.
Basu RK, Wong HR, Krawczeski CD, Wheeler DS, Manning PB, Chawla LS, et al. Combining functional and tubular damage biomarkers improves diagnostic precision for acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014;64:2753–62.
Larsson A, Malm J, Grubb A, Hansson LO. Calculation of glomerular filtration rate expressed in mL/min from plasma cystatin C values in mg/L. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 2004;64:25–30.
Schwartz GJ, Munoz A, Schneider MF, Mak RH, Kaskel F, Warady BA, et al. New equations to estimate GFR in children with CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;20:629–37.
Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130:461–70.
Schuh MP, Nehus E, Ma Q, Haffner C, Bennett M, Krawczeski CD, et al. Long-term stability of urinary biomarkers of acute kidney injury in children. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;67:56–61.
Kellum JA, Lameire N, Aspelin P, Barsoum RS, Burdmann EA, Goldstein SL, et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int Suppl. 2012;2:1–138.
Kaddourah A, Basu RK, Bagshaw SM, Goldstein SL. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill children and young adults. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:11–20.
Bennett M, Nehus E, Haffner C, Ma Q, Devarajan P. Pediatric reference ranges for acute kidney injury biomarkers. Pediatr Nephrol. 2015;30:677–85.
Haase M, Bellomo R, Devarajan P, Schlattmann P, Haase-Fielitz A. Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2009;54:1012–24.
McCullough PA, Shaw AD, Haase M, Bouchard J, Waikar SS, Siew ED, et al. Diagnosis of acute kidney injury using functional and injury biomarkers: workgroup statements from the tenth Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative Consensus Conference. Contrib Nephrol. 2013;182:13–29.
Ronco C, Kellum JA, Haase M. Subclinical AKI is still AKI. Crit Care. 2012;16:313.
Nehus E, Kaddourah A, Bennett M, Pyles O, Devarajan P. Subclinical kidney injury in children receiving nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after cardiac surgery. J Pediatr. 2017;189:175–80.
Jodele S, Davies SM, Lane A, Khoury J, Dandoy C, Goebel J, et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults. Blood. 2014;124:645–53.
Taghizadeh-Ghehi M, Sarayani A, Ashouri A, Ataei S, Moslehi A, Hadjibabaie M. Urine neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as an early marker of acute kidney injury in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients. Ren Fail. 2015;37:994–8.
Deger SM, Erten Y, Suyani E, Aki SZ, Ulusal Okyay G, Pasaoglu OT, et al. Early diagnostic markers for detection of acute kidney injury in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Exp Clin Transplant. 2017.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Center for Acute Care Nephrology, Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH, USA for purchasing biomarker assay supplies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
SLG consults for and has received grant support from Bioporto, Inc. The other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benoit, S.W., Dixon, B.P., Goldstein, S.L. et al. A novel strategy for identifying early acute kidney injury in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 54, 1453–1461 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0428-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41409-018-0428-6
This article is cited by
-
Acute kidney injury following treatment with CD19-specific CAR T-cell therapy in children, adolescent, and young adult patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Pediatric Nephrology (2024)
-
Risk factors for acute kidney injury in pediatric patients after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pediatric Nephrology (2024)
-
Risk factors for severe acute kidney injury after pediatric hematopoietic cell transplantation
Pediatric Nephrology (2023)
-
Pharmacokinetics in Critically Ill Children with Acute Kidney Injury
Pediatric Drugs (2023)
-
Acute kidney injury in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplantation: critical appraisal and consensus
Pediatric Nephrology (2022)