Abstract
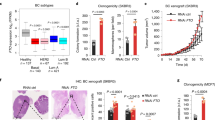
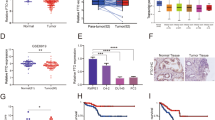
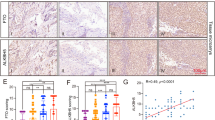
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO), which is closely linked with obesity and dietary intake, plays an important role in diet-related metabolic diseases. However, the underlying mechanism of the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethyltransferase FTO in tumor development and progression remains largely unexplored. Here, we demonstrated that FTO expression was largely lower in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) samples than in adjacent healthy tissues, and its expression negatively correlated with poor prognosis. Gain- and loss-of-function assays revealed that FTO inhibited NSCLC tumor cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, estrogen receptor alpha (ESR1) is a target of FTO, and increased FTO expression significantly impaired the m6A levels of ESR1 mRNA. There were two clear m6A modification sites (5247A and 5409A) in the 3′ untranslated region (3ʹUTR) of ESR1, and FTO could decrease their methylation. Moreover, the m6A readers YTHDF1 and IGF2BP3 recognized and bound the m6A sites in ESR1 mRNA, thereby enhancing its stability and facilitating tumor growth. We also showed that ESR1 has good diagnostic value for NSCLC. In conclusion, we uncovered an important mechanism of epitranscriptomic regulation by the FTO-YTHDF1-IGF2BP3-ESR1 axis and identified the potential of m6A-dependent therapeutic strategies for NSCLC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Source data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46.
Huang H, Weng H, Chen J. m6A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2020;37:270–88.
Liu X, Feng M, Hao X, Gao Z, Wu Z, Wang Y, et al. m6A methylation regulates hypoxia-induced pancreatic cancer glycolytic metabolism through ALKBH5-HDAC4-HIF1α positive feedback loop. Oncogene. 2023;42:2047–60.
Niu X, Yang Y, Ren Y, Zhou S, Mao Q, Wang Y. Crosstalk between m6A regulators and mRNA during cancer progression. Oncogene. 2022;41:4407–19.
An Y, Duan H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:14.
Deng X, Su R, Weng H, Huang H, Li Z, Chen J. RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in cancers: current status and perspectives. Cell Res. 2018;28:507–17.
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol. 2011;7:885–7.
Zheng G, Dahl J, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang C, Li C, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Jiang X, Liu B, Nie Z, Duan L, Xiong Q, Jin Z, et al. The role of m6A modification in the biological functions and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:74.
Yan H, Zhang L, Cui X, Zheng S, Li R. Roles and mechanisms of the m6A reader YTHDC1 in biological processes and diseases. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:237.
Deng LJ, Deng WQ, Fan SR, Chen MF, Qi M, Lyu WY, et al. m6A modification: recent advances, anticancer targeted drug discovery and beyond. Mol Cancer. 2022;21:52.
Tung YCL, Yeo Giles SH, O’Rahilly S, Coll Anthony P. Obesity and FTO: changing focus at a complex locus. Cell Metab. 2014;20:710–8.
Lin Z, Wan AH, Sun L, Liang H, Niu Y, Deng Y, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO enhances chemo-resistance in colorectal cancer through SIVA1-mediated apoptosis. Mol Ther. 2023;31:517–34.
Li Y, Su R, Deng X, Chen Y, Chen J. FTO in cancer: functions, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Trends in Cancer. 2022;8:598–614.
Tao L, Mu X, Chen H, Jin D, Zhang R, Zhao Y, et al. FTO modifies the m6A level of MALAT and promotes bladder cancer progression. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11:e310.
Zhou Y, Wang Q, Deng H, Xu B, Zhou Y, Liu J, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via m6A modification of caveolin-1 and metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13:72.
Huang J, Sun W, Wang Z, Lv C, Zhang T, Zhang D, et al. FTO suppresses glycolysis and growth of papillary thyroid cancer via decreasing stability of APOE mRNA in an N6-methyladenosine-dependent manner. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:42.
Tan Z, Shi S, Xu J, Liu X, Lei Y, Zhang B, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes pancreatic cancer progression by inducing the autocrine activity of PDGFC in an m6A-YTHDF2-dependent manner. Oncogene. 2022;41:2860–72.
Grinshpun A, Chen V, Sandusky ZM, Fanning SW, Jeselsohn R. ESR1 activating mutations: from structure to clinical application. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878:188830.
Li Z, Wu Y, Yates ME, Tasdemir N, Bahreini A, Chen J, et al. Hotspot ESR1 mutations are multimodal and contextual modulators of breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2022;82:1321–39.
Brett JO, Spring LM, Bardia A, Wander SA. ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2021;23:85.
Huang Y-M, Wang W, Hsieh P-P, Chen H-H. Haplotype of ESR1 and PPARD genes is associated with higher anthropometric changes in Han Chinese obesity by adjusting dietary factors-an 18-month follow-up. Nutrients. 2022;14:4425.
Nakada D, Oguro H, Levi BP, Ryan N, Kitano A, Saitoh Y, et al. Oestrogen increases haematopoietic stem-cell self-renewal in females and during pregnancy. Nature. 2014;505:555–8.
Deng X, Qing Y, Horne D, Huang H, Chen J. The roles and implications of RNA m6A modification in cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2023;20:507–26.
Zeng L, Huang X, Zhang J, Lin D, Zheng J. Roles and implications of mRNA N6‐methyladenosine in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2023;43:729–48.
Ma L, Xue X, Zhang X, Yu K, Xu X, Tian X, et al. The essential roles of m6A RNA modification to stimulate ENO1-dependent glycolysis and tumorigenesis in lung adenocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:36.
Ma L, Chen T, Zhang X, Miao Y, Tian X, Yu K, et al. The m6A reader YTHDC2 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis by suppressing SLC7A11-dependent antioxidant function. Redox Biol. 2021;38:101801.
Burns KA, Korach KS. Estrogen receptors and human disease: an update. Arch Toxicol. 2012;86:1491–504.
El-Botty R, Morriset L, Montaudon E, Tariq Z, Schnitzler A, Bacci M, et al. Oxidative phosphorylation is a metabolic vulnerability of endocrine therapy and palbociclib resistant metastatic breast cancers. Nat Commun. 2023;14:4221.
Li A, Chen YS, Ping XL, Yang X, Xiao W, Yang Y, et al. Cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017;27:444–7.
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon G, Yue Y, Han D, et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature. 2014;505:117–20.
Yang Y, Hsu PJ, Chen YS, Yang YG. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018;28:616–24.
Chen M, Wei L, Law CT, Tsang FH, Shen J, Cheng CL, et al. RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase-like 3 promotes liver cancer progression through YTHDF2-dependent posttranscriptional silencing of SOCS2. Hepatology. 2018;67:2254–70.
Shi H, Wei J, He C. Where, when, and how: context-dependent functions of RNA methylation writers, readers, and erasers. Mol Cell. 2019;74:640–50.
Xu X, Cui J, Wang H, Ma L, Zhang X, Guo W, et al. IGF2BP3 is an essential N6-methyladenosine biotarget for suppressing ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mater Today Bio. 2022;17:100503.
Burstein HJ, DeMichele A, Somerfield MR, Henry NL. Testing for ESR1 mutations to guide therapy for hormone receptor–positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative metastatic breast cancer: ASCO guideline rapid recommendation update. J Clin Oncol. 2023;41:3423–5.
Gou X, Kim BJ, Anurag M, Lei JT, Young MN, Holt MV, et al. Kinome reprogramming is a targetable vulnerability in ESR1 fusion-driven breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2023;83:3237–51.
Liu J, Eckert MA, Harada BT, Liu S-M, Lu Z, Yu K, et al. m6A mRNA methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:1074–83.
Chang G, Shi L, Ye Y, Shi H, Zeng L, Tiwary S, et al. YTHDF3 induces the translation of m6A-enriched gene transcripts to promote breast cancer brain metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2020;38:857–71.e857.
Shen C, Sheng Y, Zhu AC, Robinson S, Jiang X, Dong L, et al. RNA demethylase ALKBH5 selectively promotes tumorigenesis and cancer stem cell self-renewal in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:64–80.e69.
Frye M, Harada BT, Behm M, He C. RNA modifications modulate gene expression during development. Science. 2018;361:1346–9.
Chen H, Pan Y, Zhou Q, Liang C, Wong C-C, Zhou Y, et al. METTL3 inhibits antitumor immunity by targeting m6A-BHLHE41-CXCL1/CXCR2 axis to promote colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2022;163:891–907.
Ni Z, Sun P, Zheng J, Wu M, Yang C, Cheng M, et al. JNK signaling promotes bladder cancer immune escape by regulating METTL3-mediated m6A modification of PD-L1 mRNA. Cancer Res. 2022;82:1789–802.
Li Z-X, Zheng Z-Q, Yang P-Y, Lin L, Zhou G-Q, Lv J-W, et al. WTAP-mediated m6A modification of lncRNA DIAPH1-AS1 enhances its stability to facilitate nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:1137–51.
Rong D, Wu F, Lu C, Sun G, Shi X, Chen X, et al. m6A modification of circHPS5 and hepatocellular carcinoma progression through HMGA2 expression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021;26:637–48.
Deng D, You A, Tian W, Yuan H, Gu L, Zhou J. TTC22 promotes m6A-mediated WTAP expression and colon cancer metastasis in an RPL4 binding-dependent pattern. Oncogene. 2022;41:3925–38.
Yu H, Zhao K, Zeng H, Li Z, Chen K, Zhang Z, et al. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) methyltransferase WTAP accelerates the Warburg effect of gastric cancer through regulating HK2 stability. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:111075.
Sheng Y, Wei J, Yu F, Xu H, Yu C, Wu Q, et al. A critical role of nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 in leukemogenesis by regulating MCM complex-mediated DNA replication. Blood. 2021;138:2838–52.
Liu T, Wei Q, Jin J, Luo Q, Liu Y, Yang Y, et al. The m6A reader YTHDF1 promotes ovarian cancer progression via augmenting EIF3C translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:3816–31.
Zhang L, Wan Y, Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Gu Z, Ma X, et al. IGF2BP1 overexpression stabilizes PEG10 mRNA in an m6A-dependent manner and promotes endometrial cancer progression. Theranostics. 2021;11:1100–14.
Zheng G, Dahl JA, Niu Y, Fedorcsak P, Huang CM, Li CJ, et al. ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility. Mol Cell. 2013;49:18–29.
Gerken T, Girard CA, Tung Y-CL, Webby CJ, Saudek V, Hewitson KS, et al. The obesity-associated FTO gene encodes a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent nucleic acid demethylase. Science. 2007;318:1469–72.
Duan X, Yang L, Wang L, Liu Q, Zhang K, Liu S, et al. m6A demethylase FTO promotes tumor progression via regulation of lipid metabolism in esophageal cancer. Cell Biosci. 2022;12:60.
Cui Y, Zhang C, Ma S, Li Z, Wang W, Li Y, et al. RNA m6A demethylase FTO-mediated epigenetic up-regulation of LINC00022 promotes tumorigenesis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021;40:294.
Angus L, Beije N, Jager A, Martens JWM, Sleijfer S. ESR1 mutations: Moving towards guiding treatment decision-making in metastatic breast cancer patients. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;52:33–40.
Li Z, McGinn O, Wu Y, Bahreini A, Priedigkeit NM, Ding K, et al. ESR1 mutant breast cancers show elevated basal cytokeratins and immune activation. Nat Commun. 2022;13:2011.
Shen M, Li Y, Wang Y, Shao J, Zhang F, Yin G, et al. N6-methyladenosine modification regulates ferroptosis through autophagy signaling pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Redox Biol. 2021;47:102151.
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol. 2018;20:285–95.
Hu X, Nadalin G, De Luise M, Martin T, Wakeling A, Huggins R, et al. Circumvention of doxorubicin resistance in multi-drug resistant human leukaemia and lung cancer cells by the pure antioestrogen ICI 164384. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27:773–7.
Xu X, Ma L, Zhang X, Guo S, Guo W, Wang Y, et al. A positive feedback circuit between RN7SK snRNA and m6A readers is essential for tumorigenesis. Mol Ther. 2023;31:1615–35.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82273139, 82303043), Shanghai Science and Technology Committee Rising-Star Program (22QA1408300), Excellent Talents Nurture Project of Shanghai Chest Hospital (2021YNZYY02, 2021YNZYY01, 2021YNZYJ01), and the Talent Training Plan of Shanghai Chest Hospital in 2022 (RC-202301-130), The Nurture Projects for Basic Research of Shanghai Chest Hospital (2022YNJCQ08).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LM and JW conceived and designed the experiments; LM, JW and XZ developed the methodology; SQ, BZ and YH collected clinical samples and information; XX, XW, FL, YY, LC and XZ performed analysis of data and statistical; XX, BZ, CL and SQ were responsible for animal experiment; LM, JW and XZ supervised the study; LM and XX wrote, reviewed and revised the manuscript; LM, JW, XZ, XX and BZ provided financial support. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All the animal experiments and collection of specimens were approved by the ethical committee of the Shanghai Chest Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Qiu, S., Zeng, B. et al. N6-methyladenosine demethyltransferase FTO mediated m6A modification of estrogen receptor alpha in non-small cell lung cancer tumorigenesis. Oncogene 43, 1288–1302 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-02992-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-024-02992-8