Abstract
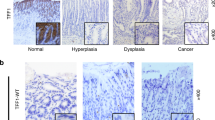
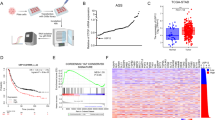
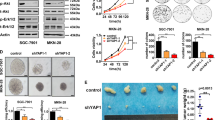
Dopamine and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein, Mr 32000 (DARPP-32), is frequently overexpressed in early stages of gastric cancers. We utilized in vitro assays, 3D gastric gland organoid cultures, mouse models, and human tissue samples to investigate the biological and molecular impact of DARPP-32 on activation of IGF1R and STAT3 signaling and gastric tumorigenesis. DARPP-32 enhanced phosphorylation of IGF1R (Y1135), a step that was critical for STAT3 phosphorylation at Y705, nuclear localization, and transcription activation. By using proximity ligation and co-immunoprecipitation assays, we found that IGF1R and DARPP-32 co-existed in the same protein complex. Binding of DARPP-32 to IGF1R promoted IGF1R phosphorylation with subsequent activation of downstream SRC and STAT3. Analysis of gastric tissues from the TFF1 knockout (KO) mouse model of gastric neoplasia, demonstrated phosphorylation of STAT3 in the early stages of gastric tumorigenesis. By crossing the TFF1 KO mice with DARPP-32 (DP) knockout (KO) mice, that have normal stomach, we obtained double knockout (TFF1 KO/DP KO). The gastric mucosa from the double KO mice did not show phosphorylation of IGF1R or STAT3. In addition, the TFF1 KO/DP KO mice had a significant delay in developing neoplastic gastric lesions. Analysis of human gastric cancer tissue microarrays, showed high levels of DARPP-32 and positive immunostaining for nuclear STAT3 in cancer tissues, as compared to non-cancer histologically normal tissues. In summary, the DARPP-32–IGF1R signaling axis plays a key role in regulating the STAT3 signaling, a critical step in gastric tumorigenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 December 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-023-02916-y
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA. Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108.
El-Rifai W, Smith MF Jr., Li G, Beckler A, Carl VS, Montgomery E, et al. Gastric cancers overexpress DARPP-32 and a novel isoform, t-DARPP. Cancer Res. 2002;62:4061–4.
Mukherjee K, Peng D, Brifkani Z, Belkhiri A, Pera M, Koyama T, et al. Dopamine and cAMP regulated phosphoprotein MW 32 kDa is overexpressed in early stages of gastric tumorigenesis. Surgery. 2010;148:354–63.
Beckler A, Moskaluk CA, Zaika A, Hampton GM, Powell SM, Frierson HF, et al. Overexpression of the 32-kilodalton dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein in common adenocarcino mas. Cancer. 2003;98:1547–51.
Belkhiri A, Zaika A, Pidkovka N, Knuutila S, Moskaluk C, El-Rifai W. Darpp-32: a novel antiapoptotic gene in upper gastrointestinal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2005;65:6583–92.
Chen Z, Zhu S, Hong J, Soutto M, Peng D, Belkhiri A, et al. Gastric tumour-derived ANGPT2 regulation by DARPP-32 promotes angiogenesis. Gut. 2016;65:925–34.
Vangamudi B, Peng DF, Cai Q, El-Rifai W, Zheng W, Belkhiri A. t-DARPP regulates phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-dependent cell growth in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 2010;9:240.
Zhu S, Belkhiri A, El-Rifai W. DARPP-32 Increases Interactions Between Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor and ERBB3 to Promote Tumor Resistance to Gefitinib. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1738–48 e1732.
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 2010;140:883–99.
Yoshimura A, Nishinakamura H, Matsumura Y, Hanada T. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling and immune responses by SOCS proteins. Arthritis Res Ther. 2005;7:100–10.
Yoshimura A, Mori H, Ohishi M, Aki D, Hanada T. Negative regulation of cytokine signaling influences inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15:704–8.
O’Shea JJ, Plenge R. JAK and STAT signaling molecules in immunoregulation and immune-mediated disease. Immunity. 2012;36:542–50.
Ahn JH, Choi YS, Choi JH. Leptin promotes human endometriotic cell migration and invasion by up-regulating MMP-2 through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Hum Reprod. 2015;21:792–802.
Yang C, He L, He P, Liu Y, Wang W, He Y, et al. Increased drug resistance in breast cancer by tumor-associated macrophages through IL-10/STAT3/bcl-2 signaling pathway. Med Oncol. 2015;32:352.
Li CJ, Li YC, Zhang DR, Pan JH. Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 function in lung cancer. J Cancer Res Ther. 2013;9(Suppl 2):S67–73.
Darnell JE Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science. 1997;277:1630–5.
Li S, Lei X, Zhang J, Yang H, Liu J, Xu C. Insulin-like growth factor 1 promotes growth of gastric cancer by inhibiting foxo1 nuclear retention. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:4519–23.
Chen Z, Soutto M, Rahman B, Fazili MW, Peng D, Blanca Piazuelo M, et al. Integrated expression analysis identifies transcription networks in mouse and human gastric neoplasia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2017;56:535–47.
Ma Y, Tang N, Thompson RC, Mobley BC, Clark SW, Sarkaria JN, et al. InsR/IGF1R Pathway Mediates Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors in Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1767–76.
Werner H. Tumor suppressors govern insulin-like growth factor signaling pathways: implications in metabolism and cancer. Oncogene. 2012;31:2703–14.
Gryko M, Kisluk J, Cepowicz D, Zinczuk J, Kamocki Z, Guzinska-Ustymowicz K, et al. Expression of insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 correlate with lymphatic metastases in human gastric cancer. Pol J Pathol. 2014;65:135–40.
Adachi Y, Li R, Yamamoto H, Min Y, Piao W, Wang Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor blockade reduces the invasiveness of gastrointestinal cancers via blocking production of matrilysin. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1305–13.
Ge J, Chen Z, Huang J, Yuan W, Den Z. Silencing insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor expression inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:633–8.
Soutto M, Belkhiri A, Piazuelo MB, Schneider BG, Peng D, Jiang A, et al. Loss of TFF1 is associated with activation of NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation and gastric neoplasia in mice and humans. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:1753–67.
Szasz AM, Lanczky A, Nagy A, Forster S, Hark K, Green JE, et al. Cross-validation of survival associated biomarkers in gastric cancer using transcriptomic data of 1065 patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:49322–33.
Wang MS, Pan Y, Liu N, Guo C, Hong L, Fan D. Overexpression of DARPP-32 in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Pr. 2005;59:58–61.
Adachi Y, Ohashi H, Imsumran A, Yamamoto H, Matsunaga Y, Taniguchi H, et al. The effect of IGF-I receptor blockade for human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:973–85.
Numata K, Oshima T, Sakamaki K, Yoshihara K, Aoyama T, Hayashi T, et al. Clinical significance of IGF1R gene expression in patients with Stage II/III gastric cancer who receive curative surgery and adjuvant chemotherapy with S-1. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2016;142:415–22.
Mitchell TJ, John S. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) signalling and T-cell lymphomas. Immunology. 2005;114:301–12.
Cafferkey C, Chau I. Novel STAT 3 inhibitors for treating gastric cancer. Expert Opin Invest Drugs. 2016;25:1023–31.
Jones SA, Scheller J, Rose-John S. Therapeutic strategies for the clinical blockade of IL-6/gp130 signaling. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:3375–83.
Menting JG, Lawrence CF, Kong GK, Margetts MB, Ward CW, Lawrence MC. Structural congruency of ligand binding to the insulin and insulin/type 1 insulin-like growth factor hybrid receptors. Structure. 2015;23:1271–82.
Carboni JM, Lee AV, Hadsell DL, Rowley BR, Lee FY, Bol DK, et al. Tumor development by transgenic expression of a constitutively active insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Cancer Res. 2005;65:3781–7.
Yadav A, Kalita A, Dhillon S, Banerjee K. JAK/STAT3 pathway is involved in survival of neurons in response to insulin-like growth factor and negatively regulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling-3. J Biol Chem. 2005;280:31830–40.
Zhao G, Zhu G, Huang Y, Zheng W, Hua J, Yang S, et al. IL-6 mediates the signal pathway of JAK-STAT3-VEGF-C promoting growth, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in gastric cancer. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:1787–95.
He G, Karin M. NF-kappaB and STAT3 - key players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 2011;21:159–68.
Grivennikov SI, Karin M. Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010;21:11–19.
Zhu S, Soutto M, Chen Z, Peng D, Romero-Gallo J, Krishna US, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced cell death is counteracted by NF-kappaB-mediated transcription of DARPP-32. Gut. 2017;66:761–2.
Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:e45.
Fienberg AA, Hiroi N, Mermelstein PG, Song W, Snyder GL, Nishi A, et al. DARPP-32: regulator of the efficacy of dopaminergic neurotransmission. Science. 1998;281:838–42.
Lefebvre O, Chenard MP, Masson R, Linares J, Dierich A, LeMeur M, et al. Gastric mucosa abnormalities and tumorigenesis in mice lacking the pS2 trefoil protein. Science. 1996;274:259–62.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health (R01CA93999), Research Career Scientist award (1IK6BX003787), and a merit award (I01BX001179) from the U.S. Department of Veterans affairs (W. El-Rifai). The contents of this work are solely the responsibility of the authors and do not necessarily represent the official views of the Department of Veterans Affairs, National Institutes of Health, or the University of Miami.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Soutto, M., Chen, Z. et al. Activation of IGF1R by DARPP-32 promotes STAT3 signaling in gastric cancer cells. Oncogene 38, 5805–5816 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0843-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0843-1
This article is cited by
-
cAMP-PKA/EPAC signaling and cancer: the interplay in tumor microenvironment
Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2024)
-
Dopamine receptors gene overexpression in the microenvironment of invasive gastric cancer and its potential implications
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
DARPP-32 promotes ERBB3-mediated resistance to molecular targeted therapy in EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma
Oncogene (2022)
-
ASCL1-regulated DARPP-32 and t-DARPP stimulate small cell lung cancer growth and neuroendocrine tumour cell proliferation
British Journal of Cancer (2020)