Abstract
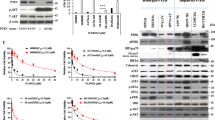
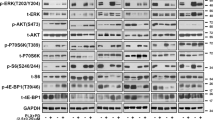
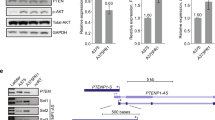
Multiple genetic mutations within melanoma not only cause lesion-specific responses to targeted therapy but also alter the molecular route of resistance to that therapy. Inactivation of PTEN occurs in up to 30% of melanomas, frequently with a concurrent activating BRAF mutation. PTEN loss regulates both acquired and intrinsic drug resistance. Here we show that AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor (BRAFi) depends upon PTEN status in melanoma. Hyperactivation of both ERK and AKT pathways was associated with BRAFi resistance in melanoma with wildtype PTEN. The PTEN-impaired melanoma cells required only the ERK resistance mechanism. Moreover, we identified AXL as a key upstream effector of AKT pathway-associated resistance to BRAFi in melanoma with wildtype PTEN, but not in melanoma with impaired PTEN. Notably, we confirmed that blocking AXL by shRNA and a small molecular inhibitor could rescue the sensitivity of resistant melanoma cells with wildtype PTEN to BRAFi and inhibit their growth in vitro and in vivo. Our study has uncovered a mechanism by which PTEN status contributes to acquired resistance to BRAFi and offers a rational strategy to guide clinical testing in pre-identified subsets of patients who relapse during treatment with BRAFi. The identified protein AXL represents a promising therapeutic target for BRAF mutant melanoma patients with wildtype PTEN.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, et al. Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 2002;417:949–54.
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:2507–16.
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A, McArthur GA, Sosman JA, et al. Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:809–19.
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, Gonzalez R, Pavlick AC, Weber JS, et al. Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with vemurafenib. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:707–14.
Nazarian R, Shi H, Wang Q, Kong X, Koya RC, Lee H, et al. Melanomas acquire resistance to B-RAF(V600E) inhibition by RTK or N-RAS upregulation. Nature. 2010;468:973–7.
Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, Thomas SR, Wardwell L, Johnson LA, et al. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature. 2010;468:968–72.
Sun C, Wang L, Huang S, Heynen GJ, Prahallad A, Robert C, Haanen J, et al. Reversible and adaptive resistance to BRAF(V600E) inhibition in melanoma. Nature. 2014;508:118–22.
Girotti MR, Pedersen M, Sanchez-Laorden B, Viros A, Turajlic S, Niculescu-Duvaz D, et al. Inhibiting EGF receptor or SRC family kinase signaling overcomes BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:158–67.
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, Somasundaram R, Fukunaga-Kalabis M, Cipolla AK, et al. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:683–95.
Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, Gonzalez R, Kefford RF, Sosman J, et al. Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations. N Engl J Med. 2012;367:1694–703.
Chen G, Davies MA. Targeted therapy resistance mechanisms and therapeutic implications in melanoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014;28:523–36.
Ribas A, Gonzalez R, Pavlick A, Hamid O, Gajewski TF, Daud A, et al. Combination of vemurafenib and cobimetinib in patients with advanced BRAF(V600)-mutated melanoma: a phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:954–65.
Sullivan RJ, Fisher DE. Understanding the biology of melanoma and therapeutic implications. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2014;28:437–53.
Wu H, Goel V, Haluska FG. PTEN signaling pathways in melanoma. Oncogene. 2003;22:3113–22.
Healy E, Rehman I, Angus B, Rees JL. Loss of heterozygosity in sporadic primary cutaneous melanoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1995;12:152–6.
Herbst RA, Weiss J, Ehnis A, Cavenee WK, Arden KC. Loss of heterozygosity for 10q22-10qter in malignant melanoma progression. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3111–4.
Tsao H, Zhang X, Benoit E, Haluska FG. Identification of PTEN/MMAC1 alterations in uncultured melanomas and melanoma cell lines. Oncogene. 1998;16:3397–402.
Haluska FG, Tsao H, Wu H, Haluska FS, Lazar A, Goel V. Genetic alterations in signaling pathways in melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:S2301–07.
Marsh Durban V, Deuker MM, Bosenberg MW, Phillips W, McMahon M. Differential AKT dependency displayed by mouse models of BRAFV600E-initiated melanoma. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:5104–18.
Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. Cancer genes and the pathways they control. Nat Med. 2004;10:789–99.
Paraiso KH, Xiang Y, Rebecca VW, Abel EV, Chen YA, Munko AC, et al. PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through the suppression of BIM expression. Cancer Res. 2011;71:2750–60.
Van Allen EM, Wagle N, Sucker A, Treacy DJ, Johannessen CM, Goetz EM, et al. The genetic landscape of clinical resistance to RAF inhibition in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:94–109.
Shi H, Hugo W, Kong X, Hong A, Koya RC, Moriceau G, et al. Acquired resistance and clonal evolution in melanoma during BRAF inhibitor therapy. Cancer Discov. 2014;4:80–93.
Poulikakos PI, Rosen N. Mutant BRAF melanomas--dependence and resistance. Cancer Cell. 2011;19:11–15.
Linger RM, Keating AK, Earp HS, Graham DK. TAM receptor tyrosine kinases: biologic functions, signaling, and potential therapeutic targeting in human cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 2008;100:35–83.
Müller J, Krijgsman O, Tsoi J, Robert L, Hugo W, Song C, et al. Low MITF/AXL ratio predicts early resistance to multiple targeted drugs in melanoma. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5712.
Dankort D, Curley DP, Cartlidge RA, Nelson B, Karnezis AN, Damsky WE Jr, et al. Braf(V600E) cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma. Nat Genet. 2009;41:544–52.
Stahl JM, Cheung M, Sharma A, Trivedi NR, Shanmugam S, Robertson GP. Loss of PTEN promotes tumor development in malignant melanoma. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2881–90.
Nathanson KL, Martin AM, Wubbenhorst B, Greshock J, Letrero R, D’Andrea K, et al. Tumor genetic analyses of patients with metastatic melanoma treated with the BRAF inhibitor dabrafenib (GSK2118436). Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:4868–78.
Bucheit AD, Chen G, Siroy A, Tetzlaff M, Broaddus R, Milton D, et al. Complete loss of PTEN protein expression correlates with shorter time to brain metastasis and survival in stage IIIB/C melanoma patients with BRAFV600 mutations. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:5527–36.
Gopal YN, Deng W, Woodman SE, Komurov K, Ram P, Smith PD, et al. Basal and treatment-induced activation of AKT mediates resistance to cell death by AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in Braf-mutant human cutaneous melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 2010;70:8736–47.
Deng W, Gopal YN, Scott A, Chen G, Woodman SE, Davies MA. Role and therapeutic potential of PI3K-mTOR signaling in de novo resistance to BRAF inhibition. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012;25:248–58.
Sullivan R, LoRusso P, Boerner S, Dummer R. Achievements and challenges of molecular targeted therapy in melanoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2015; 177–86.
Wagle N, Emery C, Berger MF, Davis MJ, Sawyer A, Pochanard P, et al. Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3085–96.
Byron SA, Loch DC, Wellens CL, Wortmann A, Wu J, Wang J, et al. Sensitivity to the MEK inhibitor E6201 in melanoma cells is associated with mutant BRAF and wildtype PTEN status. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:75.
Turke AB, Song Y, Costa C, Cook R, Arteaga CL, Asara JM, et al. MEK inhibition leads to PI3K/AKT activation by relieving a negative feedback on ERBB receptors. Cancer Res. 2012;72:3228–37.
Li Y, Ye X, Tan C, Hongo JA, Zha J, Liu J, et al. AXL as a potential therapeutic target in cancer: role of AXL in tumor growth, metastasis and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2009;28:3442–55.
Sensi M, Catani M, Castellano G, Nicolini G, Alciato F, Tragni G, et al. Human cutaneous melanomas lacking MITF and melanocyte differentiation antigens express a functional Axl receptor kinase. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:2448–57.
Brand TM, Iida M, Stein AP, Corrigan KL, Braverman CM, Luthar N, et al. AXL mediates resistance to cetuximab therapy. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5152–64.
Meyer AS, Zweemer AJ, Lauffenburger DA. The AXL receptor is a sensor of ligand spatial heterogeneity. Cell Syst. 2015;1:25–36.
Zhang Z, Lee JC, Lin L, Olivas V, Au V, LaFramboise T, et al. Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in lung cancer. Nat Genet. 2012;44:852–60.
Giles KM, Kalinowski FC, Candy PA, Epis MR, Zhang PM, Redfern AD, et al. Axl mediates acquired resistance of head and neck cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor erlotinib. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:2541–58.
Meyer AS, Miller MA, Gertler FB, Lauffenburger DA. The receptor AXL diversifies EGFR signaling and limits the response to EGFR-targeted inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Sci Signal. 2013;6:ra66.
Yao TW, Zhang J, Prados M, Weiss WA, James CD, Nicolaides T. Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibition in BRAFV600E mutant gliomas. Oncotarget. 2017;8:583–95.
Miller MA, Oudin MJ, Sullivan RJ, Wang SJ, Meyer AS, Im H, et al. Reduced proteolytic shedding of receptor tyrosine kinases is a post-translational mechanism of kinase inhibitor resistance. Cancer Discov. 2016;6:382–99.
Yu Y, Davicioni E, Triche TJ, Merlino G. The homeoprotein six1 transcriptionally activates multiple protumorigenic genes but requires ezrin to promote metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1982–9.
Yu Y, Khan J, Khanna C, Helman L, Meltzer PS, Merlino G. Expression profiling identifies the cytoskeletal organizer ezrin and the developmental homeoprotein Six-1 as key metastatic regulators. Nat Med. 2004;10:175–81.
Sheskin DJ. Handbook of parametric and nonparametric statistical procedures. 3rd ed. Boca Raton:CRC Press; 2003.
Hather G. et al. Growth rate analysis and efficient experimental design for tumor xenograft studies. Cancer Inf. 2014;13:65–72.
Chou TC. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010;70:440–6.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by funding from the NIH intramural research program. Thanks, are due to Dr. Miriam Anver for assistance with immunohistochemistry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, Q., Liu, J., Huang, L. et al. AXL/AKT axis mediated-resistance to BRAF inhibitor depends on PTEN status in melanoma. Oncogene 37, 3275–3289 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0205-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0205-4
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic targeting of the functionally elusive TAM receptor family
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2024)
-
The journey from melanocytes to melanoma
Nature Reviews Cancer (2023)
-
TAM family kinases as therapeutic targets at the interface of cancer and immunity
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2023)
-
Disrupting cellular memory to overcome drug resistance
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Autophagy in BRAF-mutant cutaneous melanoma: recent advances and therapeutic perspective
Cell Death Discovery (2023)