Abstract
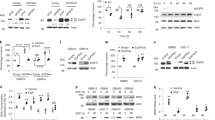
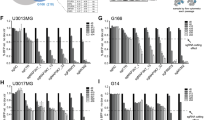
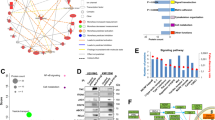
The microenvironment of glioblastoma (GBM) contains high levels of inflammatory cytokine interleukin 6 (IL-6), which contributes to promote tumour progression and invasion. The common epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII) mutation in GBM is associated with significantly higher levels of IL-6. Furthermore, elevated IL-1β levels in GBM tumours are also believed to activate GBM cells and enhance IL-6 production. However, the crosstalk between these intrinsic and extrinsic factors within the oncogene-microenvironment of GBM causing overproduction of IL-6 is poorly understood. Here, we show that EGFRvIII potentiates IL-1β-induced IL-6 secretion from GBM cells. Importantly, exacerbation of IL-6 production is most effectively attenuated in EGFRvIII-expressing GBM cells with inhibitors of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) and MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2). Enhanced IL-6 production and increased sensitivity toward pharmacological p38 MAPK and MK2 inhibitors in EGFRvIII-expressing GBM cells is associated with increased MK2-dependent nuclear–cytoplasmic shuttling and accumulation of human antigen R (HuR), an IL-6 mRNA-stabilising protein, in the cytosol. IL-1β-stimulated activation of the p38 MAPK–MK2-HuR pathway significantly enhances IL-6 mRNA stability in GBM cells carrying EGFRvIII. Further supporting a role for the p38 MAPK–MK2-HuR pathway in the development of inflammatory environment in GBM, activated MK2 is found in more than 50% of investigated GBM tissues and correlates with lower grade and secondary GBMs. Taken together, p38 MAPK–MK2-HuR signalling may enhance the potential of intrinsic (EGFRvIII) and extrinsic (IL-1β) factors to develop an inflammatory GBM environment. Hence, further improvement of brain-permeable and anti-inflammatory inhibitors targeting p38 MAPK, MK2 and HuR may combat progression of lower grade gliomas into aggressive GBMs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yeung YT, McDonald KL, Grewal T, Munoz L . Interleukins in glioblastoma pathophysiology: implications for therapy. Br J Pharmacol 2013; 168: 591–606.
The Cancer Genome Atlas Research, Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008; 455: 1061–1068.
Inda M, Bonavia R, Mukasa A, Narita Y, Sah D, Vandenberg S et al. Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 1731–1745.
Jin X, Yin J, Kim S-H, Sohn Y-W, Beck S, Lim YC et al. EGFR-AKT-Smad signaling promotes formation of glioma stem-like cells and tumor angiogenesis by ID3-driven cytokine induction. Cancer Res 2011; 71: 7125–7134.
Zhang J, Sarkar S, Cua R, Zhou Y, Hader W, Yong VW . A dialog between glioma and microglia that promotes tumor invasiveness through the CCL2/CCR2/interleukin-6 axis. Carcinogenesis 2012; 33: 312–319.
Schulz I, Engel C, Niestroj A, Zeitschel U, Menge K, Kehlen A et al. Heteroarylketones inhibit astroglial interleukin-6 expression via a STAT3/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. J Neuroinflammation 2011; 8: 86.
Spooren A, Mestdagh P, Rondou P, Kolmus K, Haegeman G, Gerlo S . IL-1β potently stabilizes IL-6 mRNA in human astrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 2011; 81: 1004–1015.
Yeung Y, Bryce N, Adams S, Braidy N, Konayagi M, McDonald K et al. p38 MAPK inhibitors attenuate pro-inflammatory cytokine production and invasiveness of human U251 glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 2012; 109: 35–44.
Nabors LB, Gillespie GY, Harkins L, King PH . HuR a RNA stability factor, is expressed in malignant brain tumors and binds to adenine- and uridine-rich elements within the 3-untranslated regions of cytokine and angiogenic factor mRNAs. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 2154–2161.
Meisner N-C, Hintersteiner M, Mueller K, Bauer R, Seifert J-M, Naegeli H-U et al. Identification and mechanistic characterization of low-molecular-weight inhibitors for HuR. Nat Chem Biol 2007; 3: 508–516.
Doller A, Pfeilschifter J, Eberhardt W . Signalling pathways regulating nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the mRNA-binding protein HuR. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 2165–2173.
Lin W-N, Lin C-C, Cheng H-Y, Yang C-M . Regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 and cytosolic phospholipase A2 gene expression by lipopolysaccharide through the RNA-binding protein HuR: involvement of NADPH oxidase, reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Br J Pharmacol 2011; 163: 1691–1706.
Fernau NS, Fugmann D, Leyendecker M, Reimann K, Grether-Beck S, Galban S et al. Role of HuR and p38 MAPK in ultraviolet B-induced post-transcriptional regulation of COX-2 expression in the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 3896–3904.
Wang S, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Kern S, Danner RL . Nitric oxide-p38 MAPK signaling stabilizes mRNA through AU-rich element-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Leukocyte Biol 2008; 83: 982–990.
Ramgolam VS, DeGregorio SD, Rao GK, Collinge M, Subaran SS, Markovic-Plese S et al. T Cell LFA-1 engagement induces HuR-dependent cytokine mRNA stabilization through a Vav-1, Rac1/2, p38MAPK and MKK3 signaling cascade. PLoS ONE 2010; 5: e14450.
Winzen R, Kracht M, Ritter B, Wilhelm A, Chen CY, Shyu AB et al. The p38 MAP kinase pathway signals for cytokine-induced mRNA stabilization via MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 2 and an AU-rich region-targeted mechanism. EMBO J 1999; 18: 4969–4980.
Neininger A, Kontoyiannis D, Kotlyarov A, Winzen R, Eckert R, Volk HD et al. MK2 targets AU-rich elements and regulates biosynthesis of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-6 independently at different post-transcriptional levels. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 3065–3068.
Gaestel M . MAPKAP kinases - MKs- two's company, three's a crowd. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2006; 7: 120–130.
Miyata Y, Watanabe S, Sagara Y, Mitsunari K, Matsuo T, Ohba K et al. High expression of HuR in cytoplasm, but not nuclei, is associated with malignant aggressiveness and prognosis in bladder cancer. PLoS ONE 2013; 8: e59095.
Bolognani F, Gallani A-I, Sokol L, Baskin D, Meisner-Kober N . mRNA stability alterations mediated by HuR are necessary to sustain the fast growth of glioma cells. J Neurooncol 2012; 106: 531–542.
Filippova N, Yang X, Wang Y, Gillespie GY, Langford C, King PH et al. The RNA-binding protein HuR promotes glioma growth and treatment resistance. Mol Cancer Res 2011; 9: 648–659.
Bonavia R, Inda MM, Vandenberg S, Cheng S-Y, Nagane M, Hadwiger P et al. EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NFkB, interleukin-8 pathway. Oncogene 2011; 31: 4054–4066.
Avraham R, Yarden Y . Feedback regulation of EGFR signalling: decision making by early and delayed loops. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2011; 12: 104–117.
Brzezinska AA, Johnson JL, Munafo DB, Ellis BA, Catz SD . Signalling mechanisms for Toll-like receptor-activated neutrophil exocytosis: key roles for interleukin-1-receptor-associated kinase-4 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase but not Toll/IL-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β (TRIF). Immunology 2009; 127: 386–397.
Sumara G, Formentini I, Collins S, Sumara I, Windak R, Bodenmiller B et al. Regulation of PKD by the MAPK p38δ in insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis. Cell 2009; 136: 235–248.
Cheng C, Kuo C, Lin C, Hsieh H, Yang C . IL-1β induces expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and cell migration via a c-Src-dependent, growth factor receptor transactivation in A549 cells. Br J Pharmacol 2010; 160: 1595–1610.
Munoz L, Selig R, Yeung Y, Peifer C, Laufer SA . Fluorescence polarisation binding assay to develop inhibitors of inactive p38a mitogen-activated protein kinase. Anal Biochem 2010; 401: 125–133.
Mourey RJ, Burnette BL, Brustkern SJ, Daniels JS, Hirsch JL, Hood WF et al. A Benzothiophene inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 inhibits tumor necrosis factor α production and has oral anti-inflammatory efficacy in acute and chronic models of inflammation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010; 333: 797–807.
Gurgis FMS, Ziaziaris W, Munoz L . Mitogen-activated protein kinase–activated protein kinase 2 in neuroinflammation, heat shock protein 27 phosphorylation, and cell cycle: role and targeting. Mol Pharmacol 2014; 85: 345–356.
Kim HH, Abdelmohsen K, Lal A, Pullmann R, Yang X, Galban S et al. Nuclear HuR accumulation through phosphorylation by Cdk1. Genes Dev 2008; 22: 1804–1815.
Li L, Dutra A, Pak E, Labrie JE, Gerstein RM, Pandolfi PP et al. EGFRvIII expression and PTEN loss synergistically induce chromosomal instability and glial tumors. Neuro Oncol 2009; 11: 9–21.
Turner JG, Dawson J, Sullivan DM . Nuclear export of proteins and drug resistance in cancer. Biochem Pharmacol 2012; 83: 1021–1032.
Liao W, Wang W, Chang W, Tseng JT . The RNA-binding protein HuR stabilizes cytosolic phospholipase A2α mRNA under interleukin-1β treatment in non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Biol Chem 2011; 286: 35499–35508.
Tran H, Maurer F, Nagamine Y . Stabilization of urokinase and urokinase receptor mRNAs by HuR is linked to its cytoplasmic accumulation induced by activated mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2. Mol Cell Biol 2003; 23: 7177–7188.
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P . The definition of primary and secondary glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2013; 19: 764–772.
Munoz L, Ralay Ranaivo H, Roy SM, Hu W, Craft JM, McNamara LK et al. A novel p38alpha MAPK inhibitor suppresses brain proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation and attenuates synaptic dysfunction and behavioral deficits in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. J Neuroinflammation 2007; 4: 21.
Munoz L, Ramsay E, Manetsch M, Ge Q, Peifer C, Laufer SA et al. Novel p38 MAPK inhibitor ML3403 has potent anti-inflammatory activity in airway smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 2010; 635: 212–218.
Guillemin GJ, Smythe G, Takikawa O, Brew BJ . Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and production of quinolinic acid by human microglia, astrocytes, and neurons. Glia 2005; 49: 15–23.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from National Foundation for Medical Research and Innovation and the University of Sydney Brown Fellowship to LM. TG acknowledges support from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (510294) and the University of Sydney (2010-02681). GJG is supported by the Australian Research Council (FT120100397) and Tour de Cure. AJA is supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (1025637). We would like to thank Maggie Lee for technical assistance with immunohistochemistry and Myriam Gorospe for pHuR(S202) antibody.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurgis, F., Yeung, Y., Tang, M. et al. The p38-MK2-HuR pathway potentiates EGFRvIII–IL-1β-driven IL-6 secretion in glioblastoma cells. Oncogene 34, 2934–2942 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.225
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.225
This article is cited by
-
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation enhances HuR oligomerization and contributes to pro-inflammatory gene mRNA stabilization
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
MAPKAPK2: the master regulator of RNA-binding proteins modulates transcript stability and tumor progression
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2019)
-
Erlotinib overcomes paclitaxel-resistant cancer stem cells by blocking the EGFR-CREB/GRβ-IL-6 axis in MUC1-positive cervical cancer
Oncogenesis (2019)
-
MAPKAPK2 (MK2) inhibition mediates radiation-induced inflammatory cytokine production and tumor growth in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Oncogene (2019)
-
NFAT1-regulated IL6 signalling contributes to aggressive phenotypes of glioma
Cell Communication and Signaling (2017)