Abstract
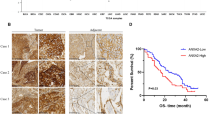
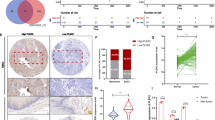
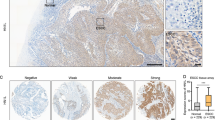
A-kinase-interacting protein 1 (AKIP1) is found to be overexpressed in breast and prostate cancers, suggesting that AKIP1 might act as a potent oncogenic protein. However, the clinical significance and biological role of AKIP1 in cancer progression remain largely unknown. Herein, we report that AKIP1 is markedly overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cell lines and clinical ESCC samples. AKIP1 expression significantly correlates with ESCC progression and patients’ shorter survival time. Furthermore, we find that overexpressing AKIP1 induces, whereas silencing AKIP1 reduces, ESCC angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, we demonstrate that AKIP1 transcriptionally upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) via interaction with its promoter through cooperation with multiple transcriptional factors, including SP1, AP2 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB). Importantly, significant correlation between levels of AKIP1 and VEGF-C is observed in a cohort of human ESCC, as well as in non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma and ovarian cancer. Hence, these findings indicate an important role for AKIP1 in ESCC angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, and uncover a novel mechanism for the upregulation of VEGF-C in cancers.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P . Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005; 55: 74–108.
Blot WJ, McLaughlin JK, Fraumeni JF Jr . Esophageal cancer. in Schottenfeld D, Fraumeni JF, (eds). Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, 2006;. p697–p706.
Ke L . Mortality and incidence trends from esophagus cancer in selected geographic areas of China circa 1970–90. Intl J cancer 2002; 102: 271–274.
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ . Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 2241–2252.
Mariette C, Balon JM, Piessen G, Fabre S, Van Seuningen I, Triboulet JP . Pattern of recurrence following complete resection of esophageal carcinoma and factors predictive of recurrent disease. Cancer 2003; 97: 1616–1623.
Ooki A, Yamashita K, Kobayashi N, Katada N, Sakuramoto S, Kikuchi S et al. Lymph node metastasis density and growth pattern as independent prognostic factors in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J Surg 2007; 31: 2184–2191.
Sato T, Iizuka N, Hamamoto Y, Yoshino S, Abe T, Takeda S et al. Esophageal squamous cell carcinomas with distinct invasive depth show different gene expression profiles associated with lymph node metastasis. Int J Oncol 2006; 28: 1043–1055.
Kimura H, Konishi K, Arakawa H, Oonishi I, Kaji M, Maeda K et al. Number of lymph node metastases influences survival in patients with thoracic esophageal carcinoma: therapeutic value of radiation treatment for recurrence. Dis Esophagus 1999; 12: 205–208.
Joukov V, Pajusola K, Kaipainen A, Chilov D, Lahtinen I, Kukk E et al. A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt-4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J 1996; 15: 290–298.
Lee J, Gray A, Yuan J, Luoh SM, Avraham H, Wood WI . Vascular endothelial growth factor-related protein: a ligand and specific activator of the tyrosine kinase receptor Flt4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1996; 93: 1988–1992.
Skobe M, Hawighorst T, Jackson DG, Prevo R, Janes L, Velasco P et al. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nat Med 2001; 7: 192–198.
Mandriota SJ, Jussila L, Jeltsch M, Compagni A, Baetens D, Prevo R et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J 2001; 20: 672–682.
Hirakawa S, Brown LF, Kodama S, Paavonen K, Alitalo K, Detmar M . VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites. Blood 2007; 109: 1010–1017.
Karpanen T, Egeblad M, Karkkainen MJ, Kubo H, Ylä-Herttuala S, Jäättelä M et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 1786–1790.
Achen MG, Stacker SA . Molecular control of lymphatic metastasis. Ann NY Acad Sci 2008; 1131: 225–234.
Cao Y, Linden P, Farnebo J, Cao R, Eriksson A, Kumar V et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1998; 95: 14389–14394.
Chien MH, Ku CC, Johansson G, Chen MW, Hsiao M, Su JL et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C (VEGF-C) promotes angiogenesis by induction of COX-2 in leukemic cells via the VEGF-R3/JNK/AP-1 pathway. Carcinogenesis 2009; 30: 2005–2013.
Kumar B, Chile SA, Ray KB, Reddy GE, Addepalli MK, Kumar AS et al. VEGF-C differentially regulates VEGF-A expression in ocular and cancer cells; promotes angiogenesis via RhoA mediated pathway. Angiogenesis 2011; 14: 371–380.
Saaristo A, Veikkola T, Enholm B, Hytönen M, Arola J, Pajusola K et al. Adenoviral VEGF-C overexpression induces blood vessel enlargement, tortuosity, and leakiness but no sprouting angiogenesis in the skin or mucous membranes. FASEB J 2002; 16: 1041–1049.
Feng Y, Hu J, Ma J, Feng K, Zhang X, Yang S et al. RNAi-mediated silencing of VEGF-C inhibits non-small cell lung cancer progression by simultaneously down-regulating the CXCR4, CCR7, VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3-dependent axes-induced ERK, p38 and AKT signalling pathways. Eur J Cancer 2011; 47: 2353–2363.
Su JL, Yang PC, Shih JY, Yang CY, Wei LH, Hsieh CY et al. The VEGF-C/Flt-4 axis promotes invasion and metastasis of cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006; 9: 209–223.
He Y, Kozaki K, Karpanen T, Koshikawa K, Yla-Herttuala S, Takahashi T et al. Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 94: 819–825.
Sastri M, Barraclough DM, Carmichael PT, Taylor SS . A-kinase-interacting protein localizes protein kinase A in the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 349–354.
Kitching R, Li H, Wong MJ, Kanaganayakam S, Kahn H, Seth A . Characterization of a novel human breast cancer associated gene (BCA3) encoding an alternatively spliced proline-rich protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 2003; 1625: 116–121.
Gao N, Asamitsu K, Hibi Y, Ueno T, Okamoto T . AKIP1 enhances NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression by promoting the nuclear retention and phosphorylation of p65. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 7834–7843.
Gao N, Hibi Y, Cueno M, Asamitsu K, Okamoto T . A-kinase-interacting protein 1 (AKIP1) acts as a molecular determinant of PKA in NF-kappaB signaling. J Biol Chem 2010; 285: 28097–28104.
Scavelli C, Vacca A, Di Pietro G, Dammacco F, Ribatti D . Crosstalk between angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in tumor progression. Leukemia 2004; 18: 1054–1058.
Gomes FG, Nedel F, Alves AM, Nör JE, Tarquinio SB . Tumor angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis: tumor/endothelial crosstalk and cellular/microenvironmental signaling mechanisms. Life Sci 2013; 92: 101–107.
Cao Y . Opinion: emerging mechanisms of tumour lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5: 735–743.
Alitalo K, Tammela T, Petrova TV . Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 2005; 438: 946–953.
Krzystek-Korpacka M, Matusiewicz M, Diakowska D, Grabowski K, Blachut K, Banas T . Up-regulation of VEGF-C secreted by cancer cells and not VEGF-A correlates with clinical evaluation of lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Cancer Lett 2007; 249: 171–177.
Zhang HL, Chen LQ, Liu RL, Shi YT, He M, Meng XL et al. The number of lymph node metastases influences survival and International Union Against Cancer tumor-node-metastasis classification for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 2010; 23: 53–58.
Hosch SB, Stoecklein NH, Pichlmeier U, Rehders A, Scheunemann P, Niendorf A et al. Esophageal cancer: the mode of lymphatic tumor cell spread and its prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 1970–1975.
Albini A, Tosetti F, Li VW, Noonan DM, Li WW . Cancer prevention by targeting angiogenesis. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2012; 9: 498–509.
Kubota Y, Kaneko K, Konishi K, Ito H, Yamamoto T, Katagiri A et al. The onset of angiogenesis in a multistep process of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Front Biosci 2009; 14: 3872–3878.
Tanigawa N, Matsumura M, Amaya H, Kitaoka A, Shimomatsuya T, Lu C et al. Tumor vascularity correlates with the prognosis of patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 1997; 79: 220–225.
Kitadai Y, Onogawa S, Kuwai T, Matsumura S, Hamada H, Ito M et al. Angiogenic switch occurs during the precancerous stage of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep 2004; 11: 315–319.
Tsai PW, Shiah SG, Lin MT, Wu CW, Kuo ML . Up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor C in breast cancer cells by heregulin-beta 1. A critical role of p38/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 5750–5759.
Lin C, Song L, Gong H, Liu A, Lin X, Wu J et al. Nkx2-8 downregulation promotes angiogenesis and activates NF-κB in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res 2013; 73: 3638–3648.
Zhang Y, Du XL, Wang CJ, Lin DC, Ruan X, Feng YB et al. Reciprocal activation between PLK1 and Stat3 contributes to survival and proliferation of esophageal cancer cells. Gastroenterology 2012; 142: 521–530 e523.
Chen X, Ying Z, Lin X, Lin H, Wu J, Li M et al. Acylglycerol kinase augments JAK2/STAT3 signaling in esophageal squamous cells. J Clin Invest 2013; 123: 2576–2589.
Andl CD, Mizushima T, Nakagawa H, Oyama K, Harada H, Chruma K et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mediates increased cell proliferation, migration, and aggregation in esophageal keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 2003; 278: 1824–1830.
Miebach S, Grau S, Hummel V, Rieckmann P, Tonn JC, Goldbrunner RH . Isolation and culture of microvascular endothelial cells from gliomas of different WHO grades. J Neurooncol 2006; 76: 39–48.
Shimada Y, Imamura M, Wagata T, Yamaguchi N, Tobe T . Characterization of 21 newly established esophageal cancer cell lines. Cancer 1992; 69: 277–284.
Sobin LH, Wittekind CH (eds). International Union Against Cancer (UICC). TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours 5th edn. Wiley, New York, 1997, pp 54–58.
Li J, Zhang N, Song LB, Liao WT, Jiang LL, Gong LY et al. Astrocyte elevated gene-1 is a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer progression and overall patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 3319–3326.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Guangdong Province Universities and Colleges Pearl River Scholar Funded Scheme (GDUPS, 2012), Natural Science Foundation of China (81325013, 81071780, 81030048, 91229101, U1201121, 81272196 and 81272198), the Science and Technology Department of Guangdong Province (S2011020002757 and S2012020010946) and Ministry of Education of China (20130171110085, 20120171110055).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, C., Song, L., Liu, A. et al. Overexpression of AKIP1 promotes angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 34, 384–393 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.559
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.559
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Lymphangiogenesis in gastric cancer: function and mechanism
European Journal of Medical Research (2023)
-
AKIP1 accelerates glioblastoma progression through stabilizing EGFR expression
Oncogene (2023)
-
IL-1RA inhibits esophageal carcinogenesis and lymphangiogenesis via downregulating VEGF-C and MMP9
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2023)
-
Lymphatic Drainage System and Lymphatic Metastasis of Cancer Cells in the Mouse Esophagus
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2023)
-
Exosomal LINC00161 promotes angiogenesis and metastasis via regulating miR-590-3p/ROCK axis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Cancer Gene Therapy (2021)