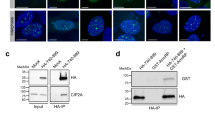
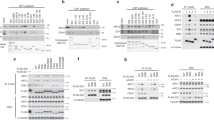
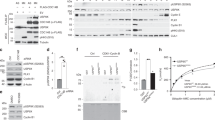
Abstract
CtBPs form NADH-sensitive chromatin-modifying complexes, which link cellular metabolism to gene transcription. They also function in the cytoplasm to regulate Golgi fissioning; their inhibition can consequently cause a Golgi-dependent checkpoint in G2. We have recently identified a novel role of CtBPs in the maintenance of mitotic fidelity; inhibition of CtBP synthesis resulting in reduced association of aurora B with mitotic chromatin and aberrant segregation of chromosomes. Here, we demonstrate that it is the interaction of CtBPs with transcriptional regulators and/or chromatin-modifying enzymes in the cell nucleus, rather than their role in Golgi fission, which is critical for the maintenance of mitotic fidelity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergman LM, Birts CN, Darley M, Gabrielli B, Blaydes JP . (2009). CtBPs promote cell survival through the maintenance of mitotic fidelity. Mol Cell Biol 29: 4539–4551.
Bergman LM, Blaydes JP . (2006). C-terminal binding proteins: Emerging roles in cell survival and tumorigenesis. Apoptosis 11: 879–888.
Bergman LM, Morris L, Darley M, Mirnezami AH, Gunatilake SC, Blaydes JP . (2006). Role of the unique N-terminal domain of CtBP2 in determining the subcellular localisation of CtBP family proteins. BMC Cell Biol 7: 35.
Blaydes JP, Gire V, Rowson J, Wynford-Thomas D . (1997). Tolerance of high levels of wild-type p53 in transformed epithelial cells dependent on auto-regulation by mdm-2. Oncogene 14: 1859–1868.
Boyd JM, Subramanian T, Schaeper U, La Regina M, Bayley S, Chinnadurai G . (1993). A region in the C-terminus of adenovirus 2/5 E1a protein is required for association with a cellular phosphoprotein and important for the negative modulation of T24-ras mediated transformation, tumorigenesis and metastasis. Embo J 12: 469–478.
Chen YW, Paliwal S, Draheim K, Grossman SR, Lewis BC . (2008). p19Arf inhibits the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by binding to C-terminal binding protein. Cancer Res 68: 476–482.
Cheok CF, Kua N, Kaldis P, Lane DP . (2010). Combination of nutlin-3 and VX-680 selectively targets p53 mutant cells with reversible effects on cells expressing wild-type p53. Cell Death Differ 17: 1486–14500.
Chinnadurai G . (2007). Transcriptional regulation by C-terminal binding proteins. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 39: 1593–1607.
Chinnadurai G . (2009). The transcriptional corepressor CtBP: a foe of multiple tumor suppressors. Cancer Res 69: 731–734.
Colanzi A, Carcedo CH, Persico A, Cericola C, Turacchio G, Bonazzi M et al. (2007). The Golgi mitotic checkpoint is controlled by BARS-dependent fission of the Golgi ribbon into separate stacks in G2. EMBO J 26: 2465–2476.
Ditchfield C, Keen N, Taylor SS . (2005). The Ipl1/Aurora kinase family: methods of inhibition and functional analysis in mammalian cells. Methods Mol Biol 296: 371–381.
Eot-Houllier G, Fulcrand G, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Jaulin C . (2009). Histone deacetylase inhibitors and genomic instability. Cancer Lett 274: 169–176.
Grooteclaes M, Deveraux Q, Hildebrand J, Zhang Q, Goodman RH, Frisch SM . (2003). C-terminal-binding protein corepresses epithelial and proapoptotic gene expression programs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100: 4568–4573.
Hidalgo Carcedo C, Bonazzi M, Spano S, Turacchio G, Colanzi A, Luini A et al. (2004). Mitotic Golgi partitioning is driven by the membrane-fissioning protein CtBP3/BARS. Science 305: 93–96.
Kovi RC, Paliwal S, Pande S, Grossman SR . (2010). An ARF/CtBP2 complex regulates BH3-only gene expression and p53-independent apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 17: 513–521.
Kuppuswamy M, Vijayalingam S, Zhao LJ, Zhou Y, Subramanian T, Ryerse J et al. (2008). Role of the PLDLS-binding cleft region of CtBP1 in recruitment of core and auxiliary components of the corepressor complex. Mol Cell Biol 28: 269–281.
Mirnezami AH, Campbell SJ, Darley M, Primrose JN, Johnson PWM, Blaydes JP . (2003). Hdm2 recruits a hypoxia sensitive co-repressor to negatively regulate p53-dependent transcription. Curr Biol 13: 1234–1239.
Mroz EA, Baird AH, Michaud WA, Rocco JW . (2008). COOH-terminal binding protein regulates expression of the p16INK4A tumor suppressor and senescence in primary human cells. Cancer Res 68: 6049–6053.
Nardini M, Spano S, Cericola C, Pesce A, Massaro A, Millo E et al. (2003). CtBP/BARS: a dual-function protein involved in transcription co-repression and Golgi membrane fission. Embo J 22: 3122–3130.
Paliwal S, Pande S, Kovi RC, Sharpless NE, Bardeesy N, Grossman SR . (2006). Targeting of C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) by ARF results in p53-independent apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 26: 2360–2372.
Phelps RA, Chidester S, Dehghanizadeh S, Phelps J, Sandoval IT, Rai K et al. (2009). A two-step model for colon adenoma initiation and progression caused by APC loss. Cell 137: 623–634.
Quinlan KGR, Verger A, Kwok A, Lee SHY, Perdomo J, Nardini M et al. (2006). Role of the C-terminal binding protein PXDLS motif binding cleft in protein interactions and transcriptional repression. Molecular and Cellular Biology 26: 8202–8213.
Schaeper U, Boyd JM, Verma S, Uhlmann E, Subramanian T, Chinnadurai G . (1995). Molecular cloning and characterization of a cellular phosphoprotein that interacts with a conserved C-terminal domain of adenovirus E1A involved in negative modulation of oncogenic transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 10467–10471.
Shi Y, Sawada J, Sui G, Affar el B, Whetstine JR, Lan F et al. (2003). Coordinated histone modifications mediated by a CtBP co-repressor complex. Nature 422: 735–738.
Stevens FE, Beamish H, Warrener R, Gabrielli B . (2008). Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce mitotic slippage. Oncogene 27: 1345–1354.
Warrener R, Beamish H, Burgess A, Waterhouse NJ, Giles N, Fairlie D et al. (2003). Tumor cell-selective cytotoxicity by targeting cell cycle checkpoints. FASEB J 17: 1550–1552.
Yang JS, Gad H, Lee SY, Mironov A, Zhang L, Beznoussenko GV et al. (2008). A role for phosphatidic acid in COPI vesicle fission yields insights into Golgi maintenance. Nat Cell Biol 10: 1146–1153.
Zhang Q, Piston DW, Goodman RH . (2002). Regulation of corepressor function by nuclear NADH. Science 295: 1895–1897.
Zhang Q, Yoshimatsu Y, Hildebrand J, Frisch SM, Goodman RH . (2003). Homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 promotes apoptosis by downregulating the transcriptional corepressor CtBP. Cell 115: 177–186.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Matthew Darley for the generation of plasmid reagents, Patrick Duriez for the preparation of GST fusion proteins for microinjection, and the Southampton School of Medicine Bioimaging Unit for assistance with live cell imaging. Funding for the work was from the UK Breast Cancer Campaign.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birts, C., Bergman, L. & Blaydes, J. CtBPs promote mitotic fidelity through their activities in the cell nucleus. Oncogene 30, 1272–1280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.507
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.507
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
CtBP1/2 differentially regulate genomic stability and DNA repair pathway in high-grade serous ovarian cancer cell
Oncogenesis (2021)
-
Different Functions of HIPK2 and CtBP2 in Traumatic Brain Injury
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience (2013)