Abstract
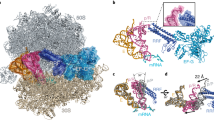
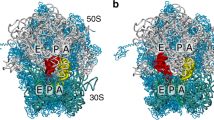
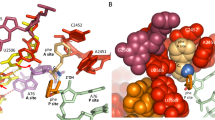
Discrimination of tRNA on the ribosome occurs in two consecutive steps: initial selection and proofreading. Here we propose a proofreading mechanism based on comparison of crystal structures of the 70S ribosome with an empty A site or with the A site occupied by uncharged cognate or near-cognate tRNA. We observe that ribosomal proteins S13, S19, L16, L25, L27 and L31 are actively involved in the proofreading of tRNA. We suggest that proofreading begins with the monitoring of the entire anticodon loop of tRNA by nucleotides from 16S rRNA (helices 18 and 44) of the small subunit and 23S rRNA (helix 69) of the large subunit with involvement of magnesium ions. Subsequently, the elbow region is scanned by rRNA (helices 38 and 89) and proteins from the large subunit determining whether to accommodate the acceptor end of tRNA in the peptidyl transferase center or not.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson, R.C. & Karim, A.M. The accuracy of protein biosynthesis is limited by its speed: high fidelity selection by ribosomes of aminoacyl-tRNA ternary complexes containing GTP γS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 4922–4926 (1982).
Ehrenberg, M., Kurland, C.G. & Ruusala, T. Counting cycles of EF-Tu to measure proofreading in translation. Biochimie 68, 261–273 (1986).
Hopfield, J.J. Kinetic proofreading: a new mechanism for reducing errors in biosynthetic processes requiring high specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71, 4135–4139 (1974).
Ninio, J. Kinetic amplification of enzyme discrimination. Biochimie 57, 587–595 (1975).
Koshland, D.E. Application of a theory of enzyme specificity to protein synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 44, 98–104 (1958).
Pape, T., Wintermeyer, W. & Rodnina, M. Induced fit in initial selection and proofreading of aminoacyl-tRNA on the ribosome. EMBO J. 18, 3800–3807 (1999).
Rodnina, M.V., Gromadski, K.B., Kothe, U. & Wieden, H.J. Recognition and selection of tRNA in translation. FEBS Lett. 579, 938–942 (2005).
Daviter, T., Gromadski, K.B. & Rodnina, M.V. The ribosome's response to codon-anticodon mismatches. Biochimie 88, 1001–1011 (2006).
Zaher, H.S. & Green, R. Fidelity at the molecular level: lessons from protein synthesis. Cell 136, 746–762 (2009).
Kramer, E.B. & Farabaugh, P.J. The frequency of translational misreading errors in E. coli is largely determined by tRNA competition. RNA 13, 87–96 (2007).
Rodnina, M.V. & Wintermeyer, W. Fidelity of aminoacyl-tRNA selection on the ribosome: kinetic and structural mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 70, 415–435 (2001).
Powers, T. & Noller, H.F. Selective perturbation of G530 of 16 S rRNA by translational miscoding agents and a streptomycin-dependence mutation in protein S12. J. Mol. Biol. 235, 156–172 (1994).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H.F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature 327, 389–394 (1987).
Moazed, D. & Noller, H.F. Binding of tRNA to the ribosomal A and P sites protects two distinct sets of nucleotides in 16 S rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 211, 135–145 (1990).
Yoshizawa, S., Fourmy, D. & Puglisi, J.D. Recognition of the codon-anticodon helix by ribosomal RNA. Science 285, 1722–1725 (1999).
Fourmy, D., Yoshizawa, S. & Puglisi, J.D. Paromomycin binding induces a local conformational change in the A-site of 16 S rRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 277, 333–345 (1998).
Ogle, J.M. et al. Recognition of cognate transfer RNA by the 30S ribosomal subunit. Science 292, 897–902 (2001).
Wimberly, B.T. et al. Structure of the 30S ribosomal subunit. Nature 407, 327–339 (2000).
Schmeing, T.M. et al. The crystal structure of the ribosome bound to EF-Tu and aminoacyl-tRNA. Science 326, 688–694 (2009).
Ogle, J.M., Murphy, F.V., Tarry, M.J. & Ramakrishnan, V. Selection of tRNA by the ribosome requires a transition from an open to a closed form. Cell 111, 721–732 (2002).
Yusupov, M.M. et al. Crystal structure of the ribosome at 5.5 Å resolution. Science 292, 883–896 (2001).
Voorhees, R.M., Weixlbaumer, A., Loakes, D., Kelley, A.C. & Ramakrishnan, V. Insights into substrate stabilization from snapshots of the peptidyl transferase center of the intact 70S ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 528–533 (2009).
Plant, E.P. et al. Differentiating between near- and non-cognate codons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . PLoS ONE 2, e517 (2007).
Jenner, L.B., Demeshkina, N., Yusupova, G. & Yusupov, M. Structural aspects of messenger RNA reading frame maintenance by the ribosome. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 17, 555–560 (2010).
Klein, D.J., Moore, P.B. & Steitz, T.A. The contribution of metal ions to the structural stability of the large ribosomal subunit. RNA 10, 1366–1379 (2004).
Selmer, M. et al. Structure of the 70S ribosome complexed with mRNA and tRNA. Science 313, 1935–1942 (2006).
Korostelev, A. et al. Crystal structure of a translation termination complex formed with release factor RF2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 19684–19689 (2008).
Brodersen, D.E., Clemons, W.M. Jr., Carter, A.P., Wimberly, B.T. & Ramakrishnan, V. Crystal structure of the 30 S ribosomal subunit from Thermus thermophilus: structure of the proteins and their interactions with 16 S RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 316, 725–768 (2002).
Schmeing, T.M., Huang, K.S., Strobel, S.A. & Steitz, T.A. An induced-fit mechanism to promote peptide bond formation and exclude hydrolysis of peptidyl-tRNA. Nature 438, 520–524 (2005).
Erlacher, M.D. & Polacek, N. Ribosomal catalysis: the evolution of mechanistic concepts for peptide bond formation and peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis. RNA Biol. 5, 5–12 (2008).
Varshney, U., Lee, C.P., Seong, B.L. & RajBhandary, U.L. Mutants of initiator tRNA that function both as initiators and elongators. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18018–18024 (1991).
Lee, C.P., Seong, B.L. & RajBhandary, U.L. Structural and sequence elements important for recognition of Escherichia coli formylmethionine tRNA by methionyl-tRNA transformylase are clustered in the acceptor stem. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18012–18017 (1991).
Wrede, P., Woo, N.H. & Rich, A. Initiator tRNAs have a unique anticodon loop conformation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76, 3289–3293 (1979).
Marck, C. & Grosjean, H. tRNomics: analysis of tRNA genes from 50 genomes of Eukarya, Archaea, and Bacteria reveals anticodon-sparing strategies and domain-specific features. RNA 8, 1189–1232 (2002).
Rozenski, J., Crain, P.F. & McCloskey, J.A. The RNA modification database: 1999 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 27, 196–197 (1999).
Jukes, T.H. Possibilities for the evolution of the genetic code from a preceding form. Nature 246, 22–26 (1973).
Berk, V., Zhang, W., Pai, R.D. & Cate, J.H. Structural basis for mRNA and tRNA positioning on the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 15830–15834 (2006).
Blaha, G., Stanley, R.E. & Steitz, T.A. Formation of the first peptide bond: the structure of EF-P bound to the 70S ribosome. Science 325, 966–970 (2009).
Thompson, R.C., Dix, D.B., Gerson, R.B. & Karim, A.M. Effect of Mg2+ concentration, polyamines, streptomycin, and mutations in ribosomal proteins on the accuracy of the two-step selection of aminoacyl-tRNAs in protein biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 6676–6681 (1981).
Gromadski, K.B., Daviter, T. & Rodnina, M.V. A uniform response to mismatches in codon-anticodon complexes ensures ribosomal fidelity. Mol. Cell 21, 369–377 (2006).
Konevega, A.L. et al. Purine bases at position 37 of tRNA stabilize codon-anticodon interaction in the ribosomal A site by stacking and Mg2+-dependent interactions. RNA 10, 90–101 (2004).
Cochella, L. & Green, R. An active role for tRNA in decoding beyond codon:anticodon pairing. Science 308, 1178–1180 (2005).
Smith, D. & Yarus, M. Transfer RNA structure and coding specificity. I. Evidence that a D-arm mutation reduces tRNA dissociation from the ribosome. J. Mol. Biol. 206, 489–501 (1989).
Vacher, J. & Buckingham, R.H. Effect of photochemical crosslink S4U(8)-C(13) on suppressor activity of su+ tRNATrp from Escherichia coli . J. Mol. Biol. 129, 287–294 (1979).
Agirrezabala, X. et al. Visualization of the hybrid state of tRNA binding promoted by spontaneous ratcheting of the ribosome. Mol. Cell 32, 190–197 (2008).
Cukras, A.R. & Green, R. Multiple effects of S13 in modulating the strength of intersubunit interactions in the ribosome during translation. J. Mol. Biol. 349, 47–59 (2005).
Frank, J. & Agrawal, R.K. A ratchet-like inter-subunit reorganization of the ribosome during translocation. Nature 406, 318–322 (2000).
Zhang, W., Dunkle, J.A. & Cate, J.H. Structures of the ribosome in intermediate states of ratcheting. Science 325, 1014–1017 (2009).
Spahn, C.M. et al. Domain movements of elongation factor eEF2 and the eukaryotic 80S ribosome facilitate tRNA translocation. EMBO J. 23, 1008–1019 (2004).
Gromadski, K.B. & Rodnina, M.V. Kinetic determinants of high-fidelity tRNA discrimination on the ribosome. Mol. Cell 13, 191–200 (2004).
Blanchard, S.C., Gonzalez, R.L., Kim, H.D., Chu, S. & Puglisi, J.D. tRNA selection and kinetic proofreading in translation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 11, 1008–1014 (2004).
Lang, K., Erlacher, M., Wilson, D.N., Micura, R. & Polacek, N. The role of 23S ribosomal RNA residue A2451 in peptide bond synthesis revealed by atomic mutagenesis. Chem. Biol. 15, 485–492 (2008).
Gogia, Z.V., Yusupov, M.M. & Spirina, T.N. Structure of Thermus thermophilus ribosomes. Method of isolation and purification of ribosomes. Mol. Biol. (Mosk.) 20, 519–526 (1986).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Schulze-Briese and the staff at the Swiss Light Source for help during synchrotron X-ray data collection, M. Rodnina and R. Green for the critical reading of the manuscript and advice, S. Duclaud for assistance in ribosome preparation, S. Melnikov for helpful discussions and the staff of the Structural Biology Department core facility at the Institut de Génétique et de Biologie Moléculaire et Cellulaire. This work was supported by the Agence Nationale de la Recherche BLAN07-3_190451 (M.Y.), ANR-07-PCVI-0015-01 (G.Y.) and by the European Commission SPINE2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.J. and N.D. contributed equally to the study; L.J. purified the ribosomes, collected, processed and refined X-ray data and performed model building; N.D. collected X-ray data, performed model building and wrote the manuscript; G.Y. designed the study, and crystallized and performed model building; M.Y. designed the study; L.J., G.Y. and M.Y. corrected the manuscript; all authors discussed the results.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–8, Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 1930 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jenner, L., Demeshkina, N., Yusupova, G. et al. Structural rearrangements of the ribosome at the tRNA proofreading step. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17, 1072–1078 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1880
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1880
This article is cited by
-
Geometric alignment of aminoacyl-tRNA relative to catalytic centers of the ribosome underpins accurate mRNA decoding
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Contact networks in RNA: a structural bioinformatics study with a new tool
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design (2022)
-
ArfB can displace mRNA to rescue stalled ribosomes
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Phenotypic effects of paralogous ribosomal proteins bL31A and bL31B in E. coli
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the 70S ribosome from Enterococcus faecalis
Scientific Reports (2020)