Abstract
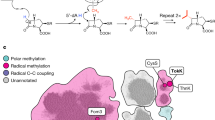
The N-sulfonated monocyclic β-lactam ring characteristic of the monobactams confers resistance to zinc metallo-β-lactamases and affords the most effective class to combat carbapenem-resistant enterobacteria (CRE). Here we report unprecedented nonribosomal peptide synthetase activities, wherein an assembled tripeptide is N-sulfonated in trans before direct synthesis of the β-lactam ring in a noncanonical, cysteine-containing thioesterase domain. This means of azetidinone synthesis is distinct from the three others known in nature.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair, J.M., Webber, M.A., Baylay, A.J., Ogbolu, D.O. & Piddock, L.J. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 13, 42–51 (2015).
Buller, A.R. & Townsend, C.A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 110, E653–E661 (2013).
Nordmann, P., Dortet, L. & Poirel, L. Trends Mol. Med. 18, 263–272 (2012).
Townsend, C.A. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 35, 97–108 (2016).
Sattely, E.S., Fischbach, M.A. & Walsh, C.T. Nat. Prod. Rep. 25, 757–793 (2008).
Hur, G.H., Vickery, C.R. & Burkart, M.D. Nat. Prod. Rep. 29, 1074–1098 (2012).
Hertweck, C. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn Engl. 48, 4688–4716 (2009).
Gaudelli, N.M., Long, D.H. & Townsend, C.A. Nature 520, 383–387 (2015).
Gaudelli, N.M. & Townsend, C.A. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10, 251–258 (2014).
Bachmann, B.O. & Ravel, J. Methods Enzymol. 458, 181–217 (2009).
Marchler-Bauer, A. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D222–D226 (2015).
Li, R., Oliver, R.A. & Townsend, C.A. Cell Chem. Biol. 24, 24–34 (2017).
Kobylarz, M.J. et al. Chem. Biol. 21, 379–388 (2014).
O'Sullivan, J. & Abraham, E.P. Biochem. J. 186, 613–616 (1980).
Quadri, L.E. et al. Biochemistry 37, 1585–1595 (1998).
Belshaw, P.J., Walsh, C.T. & Stachelhaus, T. Science 284, 486–489 (1999).
Fersht, A. Structure and Mechanism in Protein Science: A Guide to Enzyme Catalysis and Protein Folding (Freeman, New York, 1999).
Gehret, J.J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 14445–14454 (2011).
Gu, L. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 16033–16035 (2009).
Walsh, C.T. et al. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 5, 525–534 (2001).
Hubert, C.B. & Barry, S.M. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 44, 738–744 (2016).
Haslinger, K., Peschke, M., Brieke, C., Maximowitsch, E. & Cryle, M.J. Nature 521, 105–109 (2015).
Peschke, M., Gonsior, M., Süssmuth, R.D. & Cryle, M.J. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 41, 46–53 (2016).
Pispas, S. J. Polym. Sci. A Polym. Chem. 44, 606–613 (2006).
Native-PAGE. in Biology Assays & Protocols Vol. 2017 (Sino Biological Inc., 2017).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NIH (AI014937 and AI121072). We thank J. Liu of the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill for providing DNA encoding PAPS synthesis proteins and I.P. Mortimer at the Johns Hopkins Mass Spectroscopy Facility for UPLC–HRMS data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.A.T. and R.A.O. designed and directed the study. R.A.O. carried out the syntheses and biochemical reactions. R.A.O. and R.F.L. cloned and expressed proteins. All authors analyzed the data and discussed the results. R.A.O., R.F.L., and C.A.T. prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figures 1–14 (PDF 9731 kb)
Supplementary Note
General synthetic methods (PDF 2744 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, R., Li, R. & Townsend, C. Monobactam formation in sulfazecin by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase thioesterase. Nat Chem Biol 14, 5–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2526
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2526
This article is cited by
-
Structure of a bound peptide phosphonate reveals the mechanism of nocardicin bifunctional thioesterase epimerase-hydrolase half-reactions
Nature Communications (2019)
-
Refining and expanding nonribosomal peptide synthetase function and mechanism
Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology (2019)