Abstract
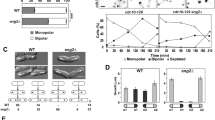
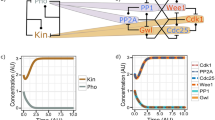
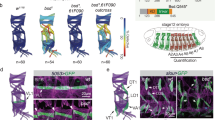
In many cells the timing of entry into mitosis is controlled by the balance between the activity of inhibitory Wee1-related kinases (Swe1p in budding yeast) and the opposing effect of Cdc25-related phosphatases (Mih1p in budding yeast) that act on the cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc2 (Cdc28p in budding yeast)1. Wee1 and Cdc25 are key elements in the G2 arrest mediated by diverse checkpoint controls2. In budding yeast, a `morphogenesis checkpoint' that involves Swe1p and Mih1p delays mitotic activation of Cdc28p3. Many environmental stresses (such as shifts in temperature or osmolarity) provoke transient depolarization of the actin cytoskeleton, during which bud construction is delayed while cells adapt to environmental conditions. During this delay, the morphogenesis checkpoint halts the cell cycle in G2 phase until actin can repolarize and complete bud construction, thus preventing the generation of binucleate cells4. A similar G2 delay can be triggered by mutations or drugs that specifically impair actin organization5, indicating that it is probably actin disorganization itself, rather than specific environmental stresses, that triggers the delay. The G2 delay involves stabilization of Swe1p in response to various actin perturbations6, although this alone is insufficient to produce a long G2 delay7.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morgan, D. O. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 261– 291 (1997).
Russell, P. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 399–402 (1998).
Lew, D. J. & Reed, S. I. J. Cell Biol. 129, 739–749 (1995).
Lew, D. J. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 10, 47–53 (2000).
McMillan, J. N., Sia, R. A. L. & Lew, D. J. J. Cell Biol. 142, 1487– 1499 (1998).
Sia, R. A. L., Bardes, E. S. G. & Lew, D. J. EMBO J. 17, 6678– 6688 (1998).
McMillan, J. N. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 6929– 6939 (1999).
Ferrell, J. E. Jr Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 33, 1– 60 (1996).
Marshall, C. J. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 4, 82–89 (1994).
Gustin, M. C., Albertyn, J., Alexander, M. & Davenport, K. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62, 1264– 1300 (1998).
McMillan, J. N., Sia, R. A. L., Bardes, E. S. G. & Lew, D. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 5981–5990 (1999).
Heinisch, J. J., Lorberg, A., Schmitz, H. P. & Jacoby, J. J. Mol. Microbiol. 32, 671–680 (1999).
Kamada, Y., Jung, U. S., Piotrowski, J. & Levin, D. E. Genes Dev. 9, 1559–1571 (1995).
Martin, H., Rodriguez-Pachon, J. M., Ruiz, C., Nombela, C. & Molina, M. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1511–1519 (2000).
Marini, N. J. et al. EMBO J. 15, 3040–3052 (1996).
Zarzov, P., Mazzoni, C. & Mann, C. EMBO J. 15, 83– 91 (1996).
Guthrie, C. & Fink, G. R. (eds) Guide to Yeast Genetics and Molecular Biology (Academic Press, San Diego, 1991).
Ausubel, F. M. et al. (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (John Wiley and Sons, New York, 1995).
Brewster, J. L., de Valoir, T., Dwyer, N. D., Winter, E. & Gustin, M. C. Science 259, 1760–1763 (1993).
Russell, P., Moreno, S. & Reed, S. I. Cell 57, 295– 303 (1989).
Ma, X-J., Lu, Q. & Grunstein, M. Genes Dev. 10, 1327– 1340 (1996).
Stuart, D. & Wittenberg, C. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 4788–4801 (1994).
Irie, K. et al. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3076– 3083 (1993).
Buehrer, B. M. & Errede, B. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17, 6517–6525 ( 1997).
Gehrung, S. & Snyder, M. J. Cell Biol. 111, 1451–1464 (1990).
Baudin, A., Ozier-Kalogeropoulos, O., Denouel, A., Lacroute, F. & Cullin, C. Nucleic Acids Res. 21 , 3329–3330 (1993).
Sikorski, R. S. & Hieter, P. Genetics 122, 19–27 (1989).
Wach, A. Yeast 12, 259–265 ( 1996).
Goldstein, A. L. & McCusker, J. H. Yeast 15, 1541–1553 (1999).
Gietz, R. D. & Sugino, A. Gene 74, 527 –534 (1988).
Stueland, C. S., Lew, D. J., Cismowski, M. J. & Reed, S. I. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 3744–3755 (1993).
Watanabe, Y., Takaesu, G., Hagiwara, M., Irie, K. & Matsumoto, K. Mol. Cell. Biol. 17 , 2615–2623 (1997).
Kamada, Y. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 9193– 9196 (1996).
Ozaki, K. et al. EMBO J. 15, 2196–2207 (1996).
Sheu, Y. J., Santos, B., Fortin, N., Costigan, C. & Snyder, M. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 4053– 4069 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Zyla for help with strain construction, S. Kornbluth for critical reading of the manuscript, and G. Ammerer, R. Ballester, B. Errede, J. Heitman, D. Levin, N. Marini, J. McCusker, J. McMillan, M. Snyder, L. Stolz, K. Irie, K. Matsumoto, D. Stuart and C. Wittenberg for strains, plasmids and oligonucleotides. We also thank J. McMillan, K. Swenson and members of the Lew laboratory for discussions. This work was supported by a grant from the US Public Health Service grant to D.J.L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harrison, J., Bardes, E., Ohya, Y. et al. A role for the Pkc1p/Mpk1p kinase cascade in the morphogenesis checkpoint . Nat Cell Biol 3, 417–420 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35070104
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35070104
This article is cited by
-
Methylglyoxal inhibits nuclear division through alterations in vacuolar morphology and accumulation of Atg18 on the vacuolar membrane in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Not just the wall: the other ways to turn the yeast CWI pathway on
International Microbiology (2020)
-
Ribosome quality control is a central protection mechanism for yeast exposed to deoxynivalenol and trichothecin
BMC Genomics (2016)
-
Control analysis of the eukaryotic cell cycle using gene copy-number series in yeast tetraploids
BMC Genomics (2013)
-
The yeast mitogen-activated protein kinase Slt2 is involved in the cellular response to genotoxic stress
Cell Division (2012)