Abstract
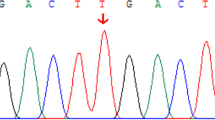
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP) typically presents in the late second or third trimester and carries an increased risk of fetal demise and neonatal morbidity and mortality. First trimester onset is rare and should alert the physician to explore a possible genetic basis for the disease. We present a 26-year-old Hispanic gravida 3, para 0202 with recurrent first-trimester onset ICP. Given her atypical history and presentation, a genetic cause was considered. She was found to have a novel heterozygous missense mutation in the ABCB4 canalicular membrane transport gene. First or early second trimester presentation of ICP should prompt investigation into genetic causes of the disease. Individualized family counseling and neonatal evaluation should be addressed if a disease-causing genetic mutation is diagnosed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geenes V . Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. World J Gastroenterol (Internet) 2009 (cited 26 Jan 2014) 15 (17): 2049. Available from http://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/15/2049.asp.
Geenes V, Chappell LC, Seed PT, Steer PJ, Dphil MK, Williamson C . Association of severe intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy with adverse pregnancy outcomes: a prospective population-based case-control study. Hepatology 2014; 59 (4): 1482–1491.
Anzivino C, Odoardi MR, Meschiari E, Baldelli E, Facchinetti F, Neri I et al. ABCB4 and ABCB11 mutations in intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in an Italian population. Dig Liver Dis (Internet) 2013 (cited 29 Oct 2013) 45 (3): 226–232. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23022423.
Nicolaou M, Andress EJ, Zolnerciks JK, Dixon PH, Williamson C, Linton KJ . Canalicular ABC transporters and liver disease. J Pathol (Internet) 2012; 226 (2): 300–315. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21984474.
Van der Woerd WL, van Mil SWC, Stapelbroek JM, Klomp LWJ, van de Graaf SFJ, Houwen RHJ . Familial cholestasis: progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol (Internet) 2010 (cited 5 Nov 2013) 24 (5): 541–553. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20955958.
Vallejo M, Briz O, Serrano MA, Monte MJ, Marin JJG . Potential role of trans-inhibition of the bile salt export pump by progesterone metabolites in the etiopathogenesis of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Hepatol. (Internet) 2006 (cited 29 Oct 2013) 44 (6): 1150–1157. Available from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16458994.
Kumar P, Henikoff S, Ng PC . Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat Protoc (Internet) 2009; 4: 1073–1081.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnston, R., Stephenson, M. & Nageotte, M. Novel heterozygous ABCB4 gene mutation causing recurrent first-trimester intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. J Perinatol 34, 711–712 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2014.86
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jp.2014.86
This article is cited by
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy after ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome with wild-type ABCB4 gene: a peculiar case and literature review
BMC Women's Health (2023)
-
Whole-exome sequencing identifies novel mutations in ABC transporter genes associated with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy disease: a case-control study
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth (2021)
-
Immunology of hepatic diseases during pregnancy
Seminars in Immunopathology (2016)