Abstract
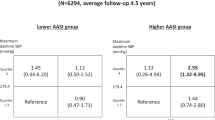
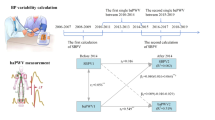
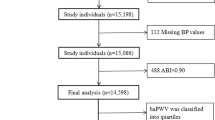
In a cross-sectional study, visit-to-visit blood pressure (BP) variability was shown to be associated with artery remodelling. Here, we investigated the impact of visit-to-visit BP variability and average BP on the carotid artery remodelling progression in high-risk elderly according to different classes of antihypertension medication use/non-use. BP measurements and carotid ultrasound were performed in the common carotid artery in 164 subjects (mean age 79.7 years at baseline, 74.7% females) with one or more cardiovascular risk factors. Based on 12 visits (1 × /month for 1 year), we calculated visit-to-visit BP variability expressed as the standard deviation (s.d.), coefficient of variation (CV), maximum BP, minimum BP and delta (maximum−minimum) BP. We measured mean intima-media thickness (IMT) as well as stiffness parameter β were measured at baseline and at the mean 4.2-year follow-up. In a multiple regression analysis, the maximum, minimum, s.d. and average of systolic BP (SBP) were significantly associated with a change in β-values between the baseline and follow-up after adjustment for age, smoking, lower high-density lipoprotein level, baseline β-value and follow-up period. There were no significant associations between the visit-to-visit BP variability measures and the change in mean IMT. Significant associations of maximum, minimum, s.d. and average SBP were found with increased β-values in the subjects without calcium channel blocker (CCB) use and in the subjects using renin–angiotensin system inhibitors (RASIs). Thus, exaggerated visit-to-visit SBP variability and a high average SBP level were significant predictors of progression in carotid arterial stiffness in high-risk elderly without CCBs use and in those using a RASI.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cuffe R, Howard SC, Algra A, Warlow CP, Rothwell PM . Medium-term variability of blood pressure and potential underdiagnosis of hypertension in patients with previous transient ischemic attack or minor stroke. Stroke 2006; 37: 2776–2783.
Rothwell PM, Howard SC, Dolan E, O’Brien E, Dobson JE, Dahlof B et al. Prognostic significance of visit-to-visit variability, maximum systolic blood pressure, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010; 375: 895–905.
Salonen JT, Salonen R . Ultrasonographically assessed carotid morphology and the risk of coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb 1991; 11: 1245–1249.
O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr . Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 1999; 340: 14–22.
Hirai T, Sasayama S, Kawasaki T, Yagi S . Stiffness of systemic arteries in patients with myocardial infarction. A noninvasive method to predict severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Circulation 1989; 80: 78–86.
Stork S, van den Beld AW, von Schacky C, Angermann CE, Lamberts SW, Grobbee DE et al. Carotid artery plaque burden, stiffness, and mortality risk in elderly men: a prospective, population-based cohort study. Circulation 2004; 110: 344–348.
Nagai M, Hoshide S, Ishikawa J, Shimada K, Kario K . Visit-to-visit blood pressure variations: new independent determinants for carotid artery measures in the elderly at high risk of cardiovascular disease. J Am Soc Hypertens 2011; 5: 184–192.
Okada H, Fukui M, Tanaka M, Inada S, Mineoka Y, Nakanishi N et al. Visit-to-visit variability in systolic blood pressure is correlated with diabetic nephropathy and atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2012; 220: 155–159.
Simbo D, Shea S, McClelland RL, Viera AJ, Mann D, Newman J et al. Associations of aortic distensibility and arterial elasticity with long-term visit-to-visit blood pressure variability: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Am J Hypertens 2013; 26: 896–902.
Webb AJ, Fischer U, Mehta Z, Rothwell PM . Effects of antihypertensive-drug class on interindividual variation in blood pressure and risk of stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010; 375: 906–915.
Nagai M, Hoshide S, Ishikawa J, Shimada K, Kario K . Visit-to-visit blood pressure variations: new independent determinants for cognitive function in the elderly at high risk of cardiovascular disease. J Hypertens 2012; 30: 1556–1563.
Kario K, Hoshide S, Shimizu M, Yano Y, Eguchi K, Ishikawa J et al. Effect of dosing time of angiotensin II receptor blockade titrated by self-measured blood pressure recordings on cardiorenal protection in hypertensives: the Japan Morning Surge-Target Organ Protection (J-TOP) study. J Hypertens 2010; 28: 1574–1583.
Yamasaki Y, Katakami N, Sakamoto K, Kaneto H, Matsuhisa M, Sato H et al. Combination of multiple genetic risk factors is synergistically associated with carotid atherosclerosis in Japanese subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006; 29: 2445–2451.
Yamasaki Y, Katakami N, Furukado S, Kitagawa K, Nagatsuka K, Kashiwagi A et al. Long-term effects of pioglitazone on carotid atherosclerosis in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes without a recent history of macrovascular morbidity. J Atheroscler Thromb 2010; 17: 1132–1140.
Emoto M, Nishizawa Y, Kawagishi T, Maekawa K, Hiura Y, Kanda H et al. Stiffness indexes beta of the common carotid and femoral arteries are associated with insulin resistance in NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 1178–1182.
Kawasaki T, Sasayama S, Yagi S, Asakawa T, Hirai T . Non-invasive assessment of the age related changes in stiffness of major branches of the human arteries. Cardiovasc Res 1987; 21: 678–687.
Lee E, Emoto M, Teramura M, Tsuchikura S, Ueno H, Shinohara K et al. The combination of IMT and stiffness parameter beta is highly associated with concurrent coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetes. J Atheroscler Thromb 2009; 16: 33–39.
Crouse JR, Goldbourt U, Evans G, Pinsky J, Sharrett AR, Sorlie P et al. Risk factors and segment specific carotid arterial enlargement in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) cohort. Stroke 1996; 27: 69–75.
Whisnant JP, Homer D, Ingall TJ, Baker HL, O'Fallon WM, Wiebers DO . Duration of cigarette smoking is the strongest predictor of severe extracranial carotid artery atherosclerosis. Stroke 1990; 21: 707–714.
Szirmai IG, Kamondi A, Magyar H, Juhasz C . Relation of laboratory and clinical variables to the grade of carotid atherosclerosis. Stroke 1993; 24: 1811–1816.
Sander D, Kukla C, Klingelhofer J, Winbeck K, Conrad B . Relationship between circadian blood pressure patterns and progression of early carotid atherosclerosis. A 3-year follow-up study. Circulation 2000; 102: 1536–1541.
Lorenz MW, Polak JF, Kavousi M, Mathiesen EB, Volzke H, Tuomainen TP et al. Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predict cardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT collaborative project): a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet 2012; 379: 2053–2062.
Mancia G, Facchetti R, Parati G, Zanchetti A . Visit-to-visit blood pressure variability, carotid atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events in the European Lacidipine Study on Atherosclerosis. Circulation 2012; 126: 569–578.
van Sloten TT, Schram MT, van den Hurk K, Dekker JM, Nijpels G, Henry RM et al. Local stiffness of carotid and femoral artery is associated with incident cardiovascular events and all cause mortality: the Hoorn study. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014; 63: 1739–1747.
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L et al. Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 2001; 37: 1236–1241.
van Popele NM, Grobbee DE, Bots ML, Asmar R, Topouchian J, Reneman RS et al. Association between arterial stiffness and atherosclerosis: the Rotterdam Study. Stroke 2001; 32: 454–460.
Franklin SS, Gustin W, Wong ND, Larson MG, Weber MA, Kannel WB et al. Hemodynamic patterns of age-related changes in blood pressure. The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1997; 96: 308–315.
Ni Y, Wang H, Hu D, Zhang W . The relationship between pulse wave velocity and pulse pressure in Chinese patients with essential hypertension. Hypertens Res 2003; 26: 871–874.
Pringle E, Phillips C, Thijs L, Davidson C, Staessen JA, de Leeuw PW et al. Systolic blood pressure variability as a risk factor for stroke and cardiovascular mortality in the elderly hypertensive population. J Hypertens 2003; 21: 2251–2257.
Ichihara A, Kaneshiro Y, Takemitsu T, Sakoda M . Effects of amlodipine and valsartan on vascular damage and ambulatory blood pressure in untreated hypertensive patients. J Hum Hypertens 2006; 20: 787–794.
Rothwell PM . Limitations of the usual blood-pressure hypothesis and importance of variability, instability, and episodic hypertension. Lancet 2010; 375: 938–948.
Muntner P, Shimbo D, Tonelli M, Reynolds K, Arnett DK, Oparil S . The relationship between visit-to-visit variability in systolic blood pressure and all-cause mortality in the general population: Findings from NHANES III, 1988 to 1994. Hypertension 2011; 57: 160–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, M., Dote, K., Kato, M. et al. Visit-to-visit blood pressure variability, average BP level and carotid arterial stiffness in the elderly: a prospective study. J Hum Hypertens 31, 292–298 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2016.77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2016.77