Abstract
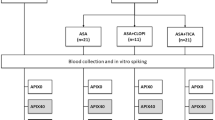
Aliskiren, an octanamide, is nonpeptide, low molecular weight, orally active renin inhibitor effectively preventing angiotensin and aldosterone release. This drug has been recently approved for the treatment of hypertension. Considering potential links between hypertension, platelets, the coagulation cascade and fibrinolysis we sought to evaluate the effect of aliskiren on human biomarkers of hemostasis. In vitro effects of whole blood preincubation with escalating concentrations of aliskiren (500, 1000 and 2000 ng ml−1) were assessed in 20 aspirin-naive volunteers with multiple risk factors for vascular disease. A total of 33 biomarkers were measured, of which 18 are related to platelet function, 12 to coagulation and 3 to fibrinolysis. Pretreatment of blood samples with aliskiren 500 ng ml−1 resulted in a significant increase of antithrombin-III (AT-III) activity (P=0.003). All other tested biomarkers were not significantly affected. Spiking whole blood with the higher aliskiren doses was associated with various trends in biomarker activity, where 1000 ng ml−1 concentration mostly decreased (7/33), and 2000 ng ml−1 mostly increased (6/33) some biomarkers. In the therapeutic concentration of 500 ng ml−1 aliskiren does not affect hemostatic biomarkers, except for a moderate but highly significant (P=0.003) increase of AT-III activity. Higher aliskiren doses were associated with more profound biomarker changes, but they are likely not to be clinically relevant since they show diverging (that is, both mild antiplatelet and platelet-activating) trends, and considering the 2- to 4-fold safety margin. It is suggested that antithrombotic properties of aliskiren be explored further in an ex vivo clinical setting.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Report. Reducing Risk, Promoting Healthy Life. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2002.
Freis ED . Treatment of essential hypertension with chlorothiazide. JAMA 1958; 166: 137–141.
Black JW, Stephenson JS . Pharmacology of a new adrenergic beta-receptor blocking compound. Lancet 1962; 2: 311–315.
Cushman DW, Cheung HS, Sabo EF, Rubin B, Ondetti MA . Development of specific inhibitors of angiotensin I converting enzyme (kininase II). Fed Proc 1979; 38: 2778–2782.
Whitebread S, Mele M, Kamber B, de Gasparo M . Preliminary biochemical characterization of two angiotensin II receptor subtypes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1989; 163: 284–291.
Blann AD, Nadar S, Lip GY . Pharmacological modulation of platelet function in hypertension. Hypertension 2003; 42: 1–7.
Medical Research Council Working Party. Stroke and coronary heart disease in mild hypertension: risk factors and the value of treatment. BMJ 1988; 296: 1565–1570.
Lip GYH, Blann AD . Does hypertension confer a prothrombotic state? Virchow's triad revisited. Circulation 2000; 101: 218–220.
Serebruany VL, Glassman AH, Malinin AI, Nemeroff CB, Musselman DL, van Zyl LT, et al., Sertraline AntiDepressant Heart Attack Randomized Trial Study Group. Platelet/endothelial biomarkers in depressed patients treated with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor sertraline after acute coronary events: the Sertraline AntiDepressant Heart Attack Randomized Trial (SADHART) Platelet Substudy. Circulation 2003; 108: 939–944.
Serebruany VL, Pokov AN, Malinin AI, O′Connor C, Bhatt DL, Tanguay JF et al. Valsartan inhibits platelet activity at different doses in mild to moderate hypertensives: Valsartan Inhibits Platelets (VIP) trial. Am Heart J 2006; 151: 92–99.
Gislason GH, Jacobsen S, Rasmussen JN, Rasmussen S, Buch P, Friberg J et al. Risk of death or reinfraction associated with the use of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and nonselective nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2006; 113: 2906–2913.
Gradman AH, Schmieder RE, Lins RL, Nussberger J, Chiang Y, Bedigian MP . Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent antihypertensive efficacy and placebo-like tolerability in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2005; 111: 1012–1018.
Ruggeri ZM . New insights into the mechanisms of platelet adhesion and aggregation. Semin Hematol 1994; 31: 229–239.
Serebruany VL, McKenzie ME, Meister AF, Fuzaylov SY, Gurbel PA, Atar D et al. Whole blood impedance aggregometry for the assessment of the platelet function in patients with congestive heart failure (EPCOT trial). Eur J Heart Fail 2002; 4: 461–466.
Smith JW, Steinhubl SR, Lincoff AM, Coleman JC, Lee TT, Hillman RS et al. Rapid platelet-function assay. An automated and quantitative cartridge-based method. Circulation 1999; 99: 620–625.
Mammen EF, Comp PC, Gosselin R, Greenberg C, Hoots WK, Kessler CM et al. PFA-100 system: a new method for assessment of platelet dysfunction. Semin Thromb Hemost 1998; 24: 195–202.
Serebruany VL, Gurbel PA . The relations of major platelet receptor expression during myocardial infarction. Monitoring efficacy of GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors by measuring P-selectin? Thromb Haemost 1999; 81: 314–316.
Saksela O, Rifkin DB . Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiologic functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol 1988; 4: 93–126.
Vaughan DE . Angiotensin and vascular fibrinolytic balance. Am J Hypertens 2002; 15 (1 Part 2): 3S–8S.
Lottermoser K, Hertfelder HJ, Vetter H, Dusing R . Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system and fibrinolysis. Med Klin (Munich) 2000; 95: 683–688.
Vaughan DE, Lazos SA, Tong K . Angiotensin II regulates the expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 995–1001.
Kerins DM, Hao Q, Vaughan DE . Angiotensin induction of PAI-1 expression in endothelial cells is mediated by the hexapeptide angiotensin IV. J Clin Invest 1995; 96: 2515–2520.
Powell JS, Clozel J-P, Muller RKM, Khun H, Hefti F, Hosang M et al. Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme prevent myointimal proliferation after vascular injury. Science 1989; 245: 186–188.
Taubman MB, Berk BC, Izumo S, Tsuda T, Alexander RW, Nadal-Ginard B . Angiotensin II induces c-fos mRNA in aortic smooth muscle: role of Ca2+ mobilization and protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem 1989; 264: 526–530.
Schindler R, Dinarello CA, Koch K-M . Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors suppress synthesis of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Cytokine 1995; 7: 526–533.
van den Eijnden-Schrauwen Y, Kooistra T, de Vries RE, Emeis JJ . Studies on the acute release of tissue-type plasminogen activator from human endothelial cells in vitro and in rats in vivo: evidence for a dynamic storage pool. Blood 1995; 85: 3510–3517.
Ohira N, Matsumoto T, Tamaki S, Takashima H, Tarutani Y, Yamane T et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme insertion/deletion polymorphism modulates coronary release of tissue plasminogen activator in response to bradykinin. Hypertens Res 2004; 27: 39–45.
Vaughan DE, Rouleau JL, Ridker PM, Arnold JM, Menapace FJ, Pfeffer MA . Effects of ramipril on plasma fibrinolytic balance in patients with acute anterior myocardial infarction. HEART Study Investigators. Circulation 1997; 96: 442–447.
Sakata K, Pawlak R, Urano T, Takada A . Effects of a long-term pharmacological interruption of the renin-angiotensin system on the fibrinolytic system in essential hypertension. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 2002; 32: 67–75.
Matsumoto T, Minai K, Horie H, Ohira N, Takashima H, Tarutani Y et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition but not angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonism augments coronary release of tissue plasminogen activator in hypertensive patients. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003; 41: 1373–1379.
Napoleone E, Di Santo A, Camera M, Tremoli E, Lorenzet R . Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors downregulate tissue factor synthesis in monocytes. Circ Res 2000; 86: 139–143.
Suzuki H, Shibata H, Murakami M, Sato A, Naito M, Ichihara A et al. Modulation of angiotensin II type 1 receptor mRNA expression in human blood cells: comparison of platelets and mononuclear leucocytes. Endocr J 1995; 42: 15–22.
Shibata H, Suzuki H, Murakami M, Sato A, Saruta T . Angiotensin II type 1 receptor messenger RNA levels in human blood cells of patients with primary and secondary hypertension: reference to renin profile. J Hypertens 1994; 12: 1275–1284.
Touyz RM, Schiffrin EL . Effects of angiotensin II and endothelin-1 on platelet aggregation and cytosolic pH and free Ca2+ concentrations in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1993; 22: 853–862.
Ferri C, De Angelis C, Del Porto MA, Leonetti Luparini R, Giarrizzo C, Santucci A et al. Blood platelets and angiotensin II: angiotensin II release after platelet aggregation. J Hypertens Suppl 1988; 6: S69–S71.
Larsson PT, Schwieler JH, Wallen NH . Platelet activation during angiotensin II infusion in healthy volunteers. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 2000; 11: 61–69.
Guerra-Cuesta JI, Monton M, Rodriguez-Feo JA, Jiménez AM, González-Fernández F, Rico LA et al. Effect of losartan on human platelet activation. J Hypertens 1999; 17: 447–452.
Li P, Fukuhara M, Diz DI, Ferrario CM, Brosnihan KB . Novel angiotensin II AT(1) receptor antagonist irbesartan prevents thromboxane A(2)-induced vasoconstriction in canine coronary arteries and human platelet aggregation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2000; 292: 238–246.
Rahuel J, Rasetti V, Maibaum J, Rueger H, Goschke R, Cohen NC et al. Structure-based drug design: the discovery of novel non peptide orally active inhibitors of human renin. Chem Biol 2000; 7: 493–504.
Kushiro T, Itakura H, Abo Y, Gotou H, Terao S, Keefe DL . Aliskiren, a novel oral renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent efficacy and placebo-like tolerability in Japanese patients with hypertension. Hypertens Res 2006; 29: 997–1005.
Oh BH, Mitchell J, Herron JR, Chung J, Khan M, Keefe DL . Aliskiren, an oral renin inhibitor, provides dose-dependent efficacy and sustained 24-h blood pressure control in patients with hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007; 49: 1157–1163.
Vaidyanathan S, Jermany J, Yeh C, Bizot MN, Camisasca R . Aliskiren, a novel orally effective renin inhibitor, exhibits similar pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in Japanese and Caucasian subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006; 62: 690–698.
Azizi M, Ménard J, Bissery A, Guyenne TT, Bura-Rivière A, Vaidyanathan S et al. Pharmacologic demonstration of the synergistic effects of a combination of the renin inhibitor aliskiren and the AT1 receptor antagonist valsartan on the angiotensin II-renin feedback interruption. J Am Soc Nephrol 2004; 15: 3126–3133.
Shagdarsuren E, Wellner M, Braesen JH, Park JK, Fiebeler A, Henke N et al. Activation in angiotensin II-induced organ damage. Circ Res 2005; 97: 716–724.
Azizi M, Ménard J, Bissery A, Guyene TT, Bura-Rivière A . Hormonal and hemodynamic effects of aliskiren and valsartan and their combination in sodium-replete normotensive individuals. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2007; 2: 947–955.
Blann AD, Nadar S, Lip GY . Pharmacological modulation of platelet function in hypertension. Hypertension 2003; 42: 1–7.
Sokol SI, Portnay EL, Curtis JP, Nelson MA, Hebert PR, Setaro JF et al. Modulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system for the secondary prevention of stroke. Neurology 2004; 63: 208–213.
Dielis AW, Smid M, Spronk HM, Houben AJ, Hamulyák K, Kroon AA et al. Changes in fibrinolytic activity after angiotensin II receptor blockade in therapy-resistant hypertensive patients. J Thromb Haemost 2007; 5: 1509–1515.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the nurses and laboratory personnel for their technical excellence and outstanding effort in this study. The study was supported in part by a grant from Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ, USA. DA was supported by grants from the National Association of Norway for Public Health—the Norwegian Council for Heart and Vessels, the Eastern Regional Health Authority of Norway and the Aker University Hospital Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serebruany, V., Malinin, A., Barsness, G. et al. Effects of aliskiren, a renin inhibitor, on biomarkers of platelet activity, coagulation and fibrinolysis in subjects with multiple risk factors for vascular disease. J Hum Hypertens 22, 303–310 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2008.2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2008.2
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Potential Protective Role of Blood Pressure-Lowering Drugs on the Balance between Hemostasis and Fibrinolysis in Hypertensive Patients at Rest and During Exercise
American Journal of Cardiovascular Drugs (2019)
-
Effects of aliskiren on the fibrinolytic system in patients with coronary artery disease receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker
Heart and Vessels (2013)