Abstract
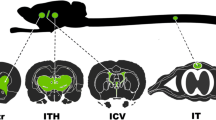
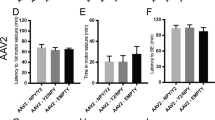
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) provides a promising platform for clinical treatment of neurological disorders owing to its established efficacy and lack of apparent pathogenicity. To use viral vectors in treating neurological disease, however, transduction must occur under neuropathological conditions. Previous studies in rodents have shown that AAV5 more efficiently transduces cells in the hippocampus and piriform cortex than AAV2. Using the kainic acid (KA) model of temporal lobe epilepsy and AAV2 and 5 carrying a hybrid chicken β-actin promoter driving green fluorescent protein (GFP), we found that limbic seizure activity caused substantial neuropathology and resulted in a significant reduction in subsequent AAV5 transduction. Nonetheless, this reduced transduction still was greater than AAV2 transduction in control rats. Although KA seizures compromise blood–brain barrier function, potentially increasing exposure of target tissue to circulating neutralizing antibodies, we observed no interaction between KA seizure-induced damage and immunization status on AAV transduction. Finally, while we confirmed the near total neuronal-specific transgene expression for both serotypes in control rats, AAV5–GFP expression was increasingly localized to astrocytes in seizure-damaged areas. Thus, the pathological milieu of the injured brain can reduce transduction efficacy and alter viral tropism- both relevant concerns when considering viral vector gene therapy for neurological disorders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noe F, Pool AH, Nissinen J, Gobbi M, Bland R, Rizzi M et al. Neuropeptide Y gene therapy decreases chronic spontaneous seizures in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2008; 131 (part 6): 1506–1515.
McCown TJ . Adeno-associated virus-mediated expression and constitutive secretion of galanin suppresses limbic seizure activity in vivo. Mol Ther 2006; 14: 63–68.
McCown TJ . Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated expression and constitutive secretion of galanin suppresses limbic seizure activity. Neurotherapeutics 2009; 6: 307–311.
Shimpo M, Ikeda U, Maeda Y, Takahashi M, Miyashita H, Mizukami H et al. AAV-mediated VEGF gene transfer into skeletal muscle stimulates angiogenesis and improves blood flow in a rat hindlimb ischemia model. Cardiovasc Res 2002; 53: 993–1001.
McPhee SW, Janson CG, Li C, Samulski RJ, Camp AS, Francis J et al. Immune responses to AAV in a phase I study for Canavan disease. J Gene Med 2006; 8: 577–588.
Kaplitt MG, Feigin A, Tang C, Fitzsimons HL, Mattis P, Lawlor PA et al. Safety and tolerability of gene therapy with an adeno-associated virus (AAV) borne GAD gene for Parkinson's disease: an open label, phase I trial. Lancet 2007; 369: 2097–2105.
Lawlor PA, Bland RJ, Das P, Price RW, Holloway V, Smithson L et al. Novel rat Alzheimer's disease models based on AAV-mediated gene transfer to selectively increase hippocampal Abeta levels. Mol Neurodegener 2007; 2: 11.
Ryan DA, Mastrangelo MA, Narrow WC, Sullivan MA, Federoff HJ, Bowers WJ . Abeta-directed single-chain antibody delivery via a serotype-1 AAV vector improves learning behavior and pathology in Alzheimer's disease mice. Mol Ther 2010; 18: 1471–1481.
Crespel A, Coubes P, Rousset MC, Brana C, Rougier A, Rondouin G et al. Inflammatory reactions in human medial temporal lobe epilepsy with hippocampal sclerosis. Brain Res 2002; 952: 159–169.
van Vliet EA, da Costa Araujo S, Redeker S, van Schaik R, Aronica E, Gorter JA . Blood-brain barrier leakage may lead to progression of temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2007; 130 (part 2): 521–534.
Wyss-Coray T, Mucke L . Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease--a double-edged sword. Neuron 2002; 35: 419–432.
Mitchell AM, Nicolson SC, Warischalk JK, Samulski RJ . AAV's Anatomy: roadmap for optimizing vectors for translational success. Curr Gene Ther 2010; 10: 319–340.
Burger C, Gorbatyuk OS, Velardo MJ, Peden CS, Williams P, Zolotukhin S et al. Recombinant AAV viral vectors pseudotyped with viral capsids from serotypes 1, 2, and 5 display differential efficiency and cell tropism after delivery to different regions of the central nervous system. Mol Ther 2004; 10: 302–317.
Boutin S, Monteilhet V, Veron P, Leborgne C, Benveniste O, Montus MF et al. Prevalence of serum IgG and neutralizing factors against adeno-associated virus (AAV) types 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, and 9 in the healthy population: implications for gene therapy using AAV vectors. Hum Gene Ther 2010; 21: 704–712.
Oprica M, Eriksson C, Schultzberg M . Inflammatory mechanisms associated with brain damage induced by kainic acid with special reference to the interleukin-1 system. J Cell Mol Med 2003; 7: 127–140.
Minami M, Kuraishi Y, Satoh M . Effects of kainic acid on messenger RNA levels of IL-1 beta, IL-6, TNF alpha and LIF in the rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1991; 176: 593–598.
Sperk G, Lassmann H, Baran H, Seitelberger F, Hornykiewicz O . Kainic acid-induced seizures: dose-relationship of behavioural, neurochemical and histopathological changes. Brain Res 1985; 338: 289–295.
Nadler JV . Minireview. Kainic acid as a tool for the study of temporal lobe epilepsy. Life Sci 1981; 29: 2031–2042.
Nitsch C, Klatzo I . Regional patterns of blood-brain barrier breakdown during epileptiform seizures induced by various convulsive agents. J Neurol Sci 1983; 59: 305–322.
Ruth RE . Increased cerebrovascular permeability to protein during systemic kainic acid seizures. Epilepsia 1984; 25: 259–268.
Klein RL, Dayton RD, Leidenheimer NJ, Jansen K, Golde TE, Zweig RM . Efficient neuronal gene transfer with AAV8 leads to neurotoxic levels of tau or green fluorescent proteins. Mol Ther 2006; 13: 517–527.
Haberman RP, Samulski RJ, McCown TJ . Attenuation of seizures and neuronal death by adeno-associated virus vector galanin expression and secretion. Nat Med 2003; 9: 1076–1080.
Richichi C, Lin EJ, Stefanin D, Colella D, Ravizza T, Grignaschi G et al. Anticonvulsant and antiepileptogenic effects mediated by adeno-associated virus vector neuropeptide Y expression in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 3051–3059.
Silver J, Miller JH . Regeneration beyond the glial scar. Nat Rev Neurosci 2004; 5: 146–156.
Hendriks WT, Eggers R, Verhaagen J, Boer GJ . Gene transfer to the spinal cord neural scar with lentiviral vectors: predominant transgene expression in astrocytes but not in meningeal cells. J Neurosci Res 2007; 85: 3041–3052.
Kreutzberg GW . Microglia: a sensor for pathological events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci 1996; 19: 312–318.
Bartlett JS, Samulski RJ, McCown TJ . Selective and rapid uptake of adeno-associated virus type 2 in brain. Hum Gene Ther 1998; 9: 1181–1186.
Kloss CU, Werner A, Klein MA, Shen J, Menuz K, Probst JC et al. Integrin family of cell adhesion molecules in the injured brain: regulation and cellular localization in the normal and regenerating mouse facial motor nucleus. J Comp Neurol 1999; 411: 162–178.
Fasen K, Elger CE, Lie AA . Distribution of alpha and beta integrin subunits in the adult rat hippocampus after pilocarpine-induced neuronal cell loss, axonal reorganization and reactive astrogliosis. Acta Neuropathol 2003; 106: 319–322.
Summerford C, Bartlett JS, Samulski RJ . AlphaVbeta5 integrin: a co-receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 infection. Nat Med 1999; 5: 78–82.
Weller ML, Stone IM, Goss A, Rau T, Rova C, Poulsen DJ . Selective overexpression of excitatory amino acid transporter 2 (EAAT2) in astrocytes enhances neuroprotection from moderate but not severe hypoxia-ischemia. Neuroscience 2008; 155: 1204–1211.
Lawlor PA, Bland RJ, Mouravlev A, Young D, During MJ . Efficient gene delivery and selective transduction of glial cells in the mammalian brain by AAV serotypes isolated from nonhuman primates. Mol Ther 2009; 17: 1692–1702.
Mihaly A, Bozoky B . Immunohistochemical localization of extravasated serum albumin in the hippocampus of human subjects with partial and generalized epilepsies and epileptiform convulsions. Acta Neuropathol 1984; 65: 25–34.
Peden CS, Burger C, Muzyczka N, Mandel RJ . Circulating anti-wild-type adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) antibodies inhibit recombinant AAV2 (rAAV2)-mediated, but not rAAV5-mediated, gene transfer in the brain. J Virol 2004; 78: 6344–6359.
Sanftner LM, Suzuki BM, Doroudchi MM, Feng L, McClelland A, Forsayeth JR et al. Striatal delivery of rAAV-hAADC to rats with preexisting immunity to AAV. Mol Ther 2004; 9: 403–409.
Grieger JC, Choi VW, Samulski RJ . Production and characterization of adeno-associated viral vectors. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 1412–1428.
Xiao X, Li J, Samulski RJ . Production of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in the absence of helper adenovirus. J Virol 1998; 72: 2224–2232.
Johnson JS, Li C, DiPrimio N, Weinberg MS, McCown TJ, Samulski RJ . Mutagenesis of adeno-associated virus type 2 capsid protein VP1 uncovers new roles for basic amino acids in trafficking and cell-specific transduction. J Virol 2010; 84: 8888–8902.
Ferrari FK, Samulski T, Shenk T, Samulski RJ . Second-strand synthesis is a rate-limiting step for efficient transduction by recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. J Virol 1996; 70: 3227–3234.
Huang MM, Hearing P . Adenovirus early region 4 encodes two gene products with redundant effects in lytic infection. J Virol 1989; 63: 2605–2615.
Racine RJ . Modification of seizure activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 1972; 32: 281–294.
Moskalenko M, Chen L, van Roey M, Donahue BA, Snyder RO, McArthur JG et al. Epitope mapping of human anti-adeno-associated virus type 2 neutralizing antibodies: implications for gene therapy and virus structure. J Virol 2000; 74: 1761–1766.
Paxinos GWC . The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4 edn Academic Press: San Diego, 1998.
Zhao X, Ahram A, Berman RF, Muizelaar JP, Lyeth BG . Early loss of astrocytes after experimental traumatic brain injury. Glia 2003; 44: 140–152.
West MJ, Slomianka L, Gundersen HJ . Unbiased stereological estimation of the total number of neurons in thesubdivisions of the rat hippocampus using the optical fractionator. Anat Rec 1991; 231: 482–497.
Sterio DC . The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc 1984; 134 (part 2): 127–136.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Chengwen Li and Dr Matthew Hirsch of the UNC Chapel Hill Gene Therapy Center, and Michael Chua and Neal Kramarcy of the UNC Chapel Hill Michael Hooker Microscopy Core for technical advice, Swati Yadav for calculation of viral titers by qPCR, and Aadra Bhatt for manuscript review. This research was funded NINDS Grant NS35633 (TJM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weinberg, M., Blake, B., Samulski, R. et al. The influence of epileptic neuropathology and prior peripheral immunity on CNS transduction by rAAV2 and rAAV5. Gene Ther 18, 961–968 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.49
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gt.2011.49
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Destination Brain: the Past, Present, and Future of Therapeutic Gene Delivery
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2017)
-
Adenosine kinase, glutamine synthetase and EAAT2 as gene therapy targets for temporal lobe epilepsy
Gene Therapy (2014)